* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download powerpt
Auditory processing disorder wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications relay service wikipedia , lookup
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Sound from ultrasound wikipedia , lookup
Olivocochlear system wikipedia , lookup
Lip reading wikipedia , lookup
Sound localization wikipedia , lookup
Hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Noise-induced hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
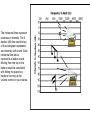
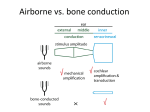
Understanding Students with Hearing Loss Chapter 14 Cochlear Implants What are the issues of controversy? Do you think Mariah, Ricquel, and Shylah should have an implant? Definition Deaf = hearing loss of 70 to 90 decibels or greater and cannot use hearing even with amplification Hard of hearing = hearing loss in the 20 to 70 dB range and benefits from amplification Prevalence (2003) 70,349 students ages 6-21 7,474 preschool ages 3-5 Hearing Process Audition = hearing process Vibration = interpreting patterns in the movement of air molecules Sound is described in pitch and frequency – Frequency measured in hertz (Hz) – Loudness measured in decibels (dB) Outer Ear Auricle, or pinna, and ear canal – Purpose to collect the sound waves – Funnel sound waves to the tympanic membrane (eardrum) – Vibrating air hits the eardrum which causes vibration Middle Ear Consists of 3 little bones known as the ossicular chain= malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), and stapes (stirrup) – Vibration of the eardrum causes the bones to vibrate and transmit sound through the middle ear – Eustachian tube also in middle ear equalizes air pressure when you yawn and swallow Inner Ear Cochlea – Snail-shaped bony structure - multiple rows of delicate hair cells connected to auditory nerve Vestibular mechanism – Semicircular canals that control balance Characteristics IQ range same as general population Mild to severe language delays Receptive speech impairments Communication Options Oral/aural communication – Amplification or cochlear implant – Emphasis on amplified sound to develop language Manual communication – Sign language – Finger spelling Total or simultaneous communication – Combines both sign and spoken communication Challenges Academic Achievement – Challenges with reading and writing Social and emotional development – Parent -child interactions – Peers and teachers - self concept – Social cues – Sense of isolation Causes Congenital - present at birth Acquired – Trauma – Disease – Exposure to excessive noise Hereditary 1 in 2,000 children Result of inherited autosomal recessive gene 70 documented inherited syndromes associated with deafness Prenatal Hypoxia Rubella Toxoplasmosis, herpes, syphilis, cytomegalovirus (CMV) Postnatal Bacterial meningitis Acute otitis media (ear infections) Postlingual Causes Blow to the skull causing trauma to the cochlea Excessive noise - firecrackers and air guns Exposure to loud noise over time - rock concerts and headphones – Noise levels of 100 to 110dB – Sustained 90dB levels damaging Hearing Tests Evoked otoacoustic emissions: EOAE Screening auditory brain stem response Audimetry - ABR Behavioral audiological evaluations older children An audiogram is a picture of your hearing. The results of your hearing test are recorded on an audiogram. The audiogram to the right demonstrates different sounds and where they would be represented on an audiogram. The yellow banana shaped figure represents all the sounds that make up the human voice when speaking at normal conversational levels. The horizontal lines represent loudness or intensity. The 0 decibel (dB) line near the top of the audiogram represents an extremely soft sound. Each horizontal line below represents a louder sound. Moving from the top to the bottom would be consistent with hitting the piano key harder or turning up the volume control on your stereo. The softest sound you are able to hear at each pitch is recorded on the audiogram. The softest sound you are able to hear is called your threshold. Thresholds of 0-25 dB are considered normal (for adults). The audiogram on the right demonstrates the different degrees of hearing loss. Types of Hearing Loss Conductive - air-conduction thresholds show loss but bone-conduction are normal Sensorineural - no blockage in middle or outer ear - loss is caused by sensitivity in cochlear or auditory nerve Mixed - both air-conduction/boneconduction and sensitivity IDEA Services Interpreting services Tutoring General classroom assistance Educational planning Sign language instruction Supplemental Aids Sound-field amplification system Loop systems Assistive technology – closed captioned – C-print: real-time translations of the spoken word http://www.dizziness-andbalance.com/testing/hearing_test.htm http://www.babyhearing.org/HearingAm plification/HearingLoss/audiogram.asp http://www.hdhearing.com/Learning/Pa rt2.htm