* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hearing Protection
Auditory system wikipedia , lookup
Olivocochlear system wikipedia , lookup
Hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
Sensorineural hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
White noise wikipedia , lookup
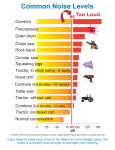
Hearing Protection Training PART 1 – THE PROBLEM © Copyright SHS 2006 Who is UniSafe? UniSafe® is a brand manufactured and distributed by Scott Health and Safety. The company behind the brand, Scott Health & Safety, has been manufacturing high quality personal protection equipment in Australia for over 65 years. UniSafe is striving to make the workplace safer for everyone with head, face, hearing and respiratory equipment that is effective and comfortable. When it comes to personal safety, achieving and exceeding Australian and New Zealand standards is our aim, and compromise is not an option. Training Requirements Objective To ensure AS/NZS 1269.3:2005 Hearing Protection Program for Hearing Conservation against noise exposure, are achieved. To protect your invaluable sense of hearing. Why is hearing protection important? It is a noisy planet, whether at work, home or leisure Some of those noises (unwanted sound) may damage your ears and prevent you from hearing important sounds Once damage irreversible has occurred it is How does hearing work? Hammer Anvil Pinna Stirrup Semicircular canals Auditory Nerves Outer Ear Canal Cochlea Eardrum Eustachian Tube Damage to the Cilia is Irreversible Fig A Scanning electron micrograph showing normal appearance of three rows outer hair cells and tectorial membrane (TM). Fig B Degenerating outer hair cells resulting from a 6- hour exposure to a 1-2 KHz octave band noise of 117 dB SPL. BEFORE AFTER (Lim, D.J & Melnick.W, 1971, Archives of Otolaryngology, 94, 294-305) Types of Injuries Hitting an object with a part of the body Falls/Trips/Slips Others Heat / Radiation Sound/Pressure Hit by moving object Source: New South Wales WorkCover 2001 Severity of Ear Injuries Less than 6 Months Permanent Disability 6 months and over Source: New South Wales WorkCover 2001 Effects of Noise Exposure What Exposure to Loud Noise Will Do Exposure to loud noise will inevitably cause hearing loss over time. Loud noise damages or destroys the nerves in the inner ear. Another effect can be “tinnitus” or permanent ringing in the ear. Effects of Noise Exposure Duration, Intensity and Frequency Our ears can recover from short exposure to loud noise, but over time nerve damage will occur. The longer and louder the noise, the greater chance permanent damage will occur. High exposure to various pitches can interfere with our ear’s ability to pick up sounds at certain frequencies i.e. “m”, “i”, “e” Effects of Noise Exposure Hearing Loss from Noise Exposure Hearing loss from noise exposure is usually not noticed because it is so gradual. Usually a person looses the ability to hear higher pitches first. Often the first noticeable effect is difficulty in hearing speech. Effects of Noise Exposure Tinnitus from Noise Exposure Exposure to high noise levels can also cause permanent ringing in the ear called “tinnitus”. Tinnitus sufferers usually complain of constant whistling, squealing, roaring or buzzing in one or both ears. Severe tinnitus may disrupt sleep, reduce concentration and cause irritability and depression. Effects of Noise Exposure What is too much Noise Exposure? Exposure to noise levels above Studies indicate Noise is: 115 decibels for even 5 - Anxiety, Lack of concentration, Reduced minutes is very risky. productivity (Noise & its effects, Suter, 1991) Impact or banging noise - Heart Disease (Federal above 140 decibels will cause environmental agency Germany, 2004) immediate damage to nerves - Elevated blood pressure (Univ. of Michigan, 2004) in the ear. Effects of Noise Exposure When is Noise too Loud? Noise is measured in units called “decibels” or “dB” If two people 3 feet apart must shout to be heard, the background noise is too loud (above 85 decibels). Noise above 140 decibels causes pain and immediate hearing loss. Duration Noise (dB) Permissible (Hrs) Exposure (Mins) 82 85 88 91 94 97 100 115 16 8 4 2 1 0 0 0 — — — — — 30 15 0 Duration Wear your hearing protector 100% of the time In Noisy areas removing hearing protection” just for a minute” is not recommended. Sometimes people will remove hearing protection for “just a minute” in a noisy area. If you wear a 30dB earmuff for 99% of the time its actual performance drops to 20dB Intensity Jet Aircraft Takeoff (25m away) Drilling Concrete Chainsaw Truck Rock Concert Lawn Mower Busy Road Telephone Power Mower Loud Radio Conversation Vacuum Cleaner Business Office Living Room Library Quiet Office Bedroom Leaves Rustling Frequency 15000 Hz 10,000 Hz 5000 Hz 1000 Hz 100 Hz 20-50 KHz Human Hearing Range Noise Levels Noisy areas and equipment at our Company Lets discuss your noisy equipment and noise sources and their noise levels here.