* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dizziness Scenario A
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
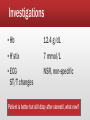
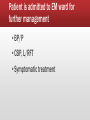
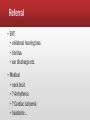
HKCEM College Tutorial Dizziness (Scenario A) Author Dr. TW Wong revised by Dr. Lam Pui Kin, Rex Oct., 2013 Scenario A--F/65, DM, HT ▪ Onset Today, gradual ▪ Provoke Hx of URI recently ▪ Quality Spinning sensation + ▪ Relief Better with eyes closed, worse with neck movement ▪ Severity Cannot get up ▪ Time for a few hours already ▪ Associated symptoms: Nausea + vomiting; no tinnitus/hearing loss ▪ Exam: essentially normal What are the common DDx of vertigo? ▪ CNS problem ▪ Cerebellar stroke ▪ Brain stem stroke ▪ TIA (vertebro-basilar insufficiency) ▪ CP angle tumor ▪ Demyelination disease ▪ Vestibular migraine ▪ Peripheral ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ Labyrinthitis Vestibular neuronitis BPPV Meniere’s disease Ramsay Hunt syndrome Concussion (labyrinthine) Acoustic neuroma Drugs can cause both types of vertigo Central Peripheral ▪ Vertigo less intense ▪ More intense ▪ Constant symptom ▪ Paroxysmal acute relapse ▪ Imbalance: severe ▪ Imbalance: milder ▪ Hearing loss and tinnitus less common ▪ Hearing loss and tinnitus more common ▪ CNS / Cerebellar sign +ve ▪ No cerebellar sign These are NOT INVARIABLE!!! Otogenic vertigo: DDx matrix What do you do now? ▪ Symptomatic treatment ▪ investigations... Vestibular sedatives ▪ Prochlorperazine (Stemetil) ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ Anti-emetic, phenothiazine group CNS acting Not for children Caution in young adults (dyskinesia) ▪ Dimenhydrinate (Gravol) ▪ First generation antihistamine ▪ Anti-motion sickness (unknown mechanism) Not For Brief Episodes ▪ Betahistine(Merislon)– antivertigo/selective vasodilator ▪ Diazepam (Valium)—BZD Beware: not useful if not vestibular ds. Investigations ▪ Hb 12.4 g/dL ▪ H’stix 7 mmol/L ▪ ECG ST/T changes NSR, non-specific Patient is better but still dizzy after stemetil, what now? Patient is admitted to EM ward for further management ▪ BP/P ▪ CBP, L/RFT ▪ Symptomatic treatment Any special test for vestibular disease? ▪ Dix-Hallpike test (For BPPV only) ▪ Head Thrust Test (to test on the vestibulo-ocular reflex) Dix-Hallpike test (Nylen-Barany) Dix Hallpike test (Nylen-Barany) Dix-Hallpike: Traditional and Sideway Position Traditional position Sideway position Barraclough, Kevin; Bronstein, Adolfo. Vertigo. BMJ. 339:b3493, September 26, 2009 Hallpike test +ve What manoeuvre can be done? ▪ Canalith-repositioning techniques ▪ The Epley manoeuvre ▪ The Semont manoeuvre The Epley manoeuvre Ann Emerg Med. April 2001;37:392-8. The Semont manoeuvre Ann Emerg Med. April 2001;37:392-8. Progress ▪ Patient’s condition gradually improves ▪ Gait is normal ▪ No neurological deficit ▪ Discharge with Stemetil Who should be referred? Referral ▪ ENT ▪ unilateral hearing loss ▪ tinnitus ▪ ear discharge etc. ▪ Medical ▪ neck bruit ▪ ? Arrhythmia ▪ ? Cardiac ischemia ▪ headache... The end BACK TO DIZZINESS (INTRODUCTION)