* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download FORENSIC ODONTOLOGY
Scaling and root planing wikipedia , lookup
Dentistry throughout the world wikipedia , lookup
Special needs dentistry wikipedia , lookup
Dental hygienist wikipedia , lookup
Dental degree wikipedia , lookup
Endodontic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Focal infection theory wikipedia , lookup
Remineralisation of teeth wikipedia , lookup
Periodontal disease wikipedia , lookup
Forensic dentistry wikipedia , lookup
Crown (dentistry) wikipedia , lookup
Impacted wisdom teeth wikipedia , lookup
Tooth whitening wikipedia , lookup
Dental emergency wikipedia , lookup
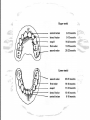
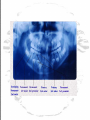
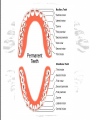
FORENSIC ODONTOLOGY What is a Forensic Odontologist? • A dentist, who consults in human identification cases, NOT FULL TIME • Works with cases of violent crime, child abuse, elder abuse, missing persons, and mass disaster scenarios • Dental evidence can aid victim identification, suspect identification, and assist with investigative casework Four Scenarios which Require Dental Examination • Intact body with little or no decomposition found with no identification – absence of personal effects or missing persons reports • Decomposing or skeletonized human remains • High energy accidents or terrorist acts – severe trauma, dismemberment and fragmentation • Homicide cases – possible bitemarks The Use of Teeth by Forensic Science • 20 deciduous teeth, 32 adult teeth • Transition period from 612 years • Asian and Native populations have shovel shaped incisors • Age of dental fillings • Orthodontic work – usually removal of four bicuspids Factors that can Change the Appearance of Teeth over a Lifetime • Severe wear caused by dietary habits • Dental work, medical devices, skull features, tooth changes • Faster and cheaper than DNA identification Language of Dental Identification • Two parts of a tooth: – The crown that shows in the mouth – The root that is embedded in the gums or jawbone • The front teeth have one root, the back teeth can have as many as four Human Tooth Morphology • Front teeth – Incisors – used for cutting and tearing food • Canines – eyeteeth, cuspids – longest rooted, used for tearing and shredding • Back teeth – Bicuspids – premolars • Molars – most chewing surfaces Analysis of Bitemark Evidence • Is the pattern a bitemark? Could it be human teeth? Does the area allow swabbing for DNA? Do the teeth marks present possess enough information to identify one person? • Typical locations of bitemarks – breasts, abdomen, thighs and genitals, if the bites are by an animal – extremities and face