* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download chapter 2 section 3
Egyptian temple wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian medicine wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian race controversy wikipedia , lookup
Thebes, Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Chapelle Rouge wikipedia , lookup
Index of Egypt-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Amenhotep III wikipedia , lookup
Prehistoric Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Egypt (Roman province) wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian technology wikipedia , lookup
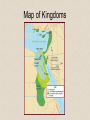
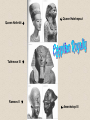
Chapter 2 Ancient Egypt Section 3 The Egyptian Empire Bell Ringer Map of Kingdoms The Middle Kingdom Pharaohs lost control of Egypt in about 2300 B.C. At that time, a new dynasty of pharaohs created a capital at Thebes. This began the Middle Kingdom, a time of stability, prosperity, and achievement. Egypt took control of other lands and forced conquered people to send tribute, or forced payments. The Middle Kingdom In this way, Egypt increased its riches. During the Middle Kingdom, the arts, literature, and architecture blossomed. The Middle Kingdom ended when the Hyksos attacked and conquered Egypt. The Hyksos ruled until around 1500 B.C., when the Egyptian Prince Ahmose led a revolt to drive the Hyksos out of Egypt. The Middle Kingdom This artwork with gold inlay from the Middle Kingdom period shows a funeral boat. Review Questions Why do you think arts, literature, and architecture flourished during the Middle Kingdom period? It was a period of political stability and economic prosperity. The New Kingdom During the New Kingdom period, Egypt grew richer and more powerful. Hatshepsut was the first woman to rule Egypt. Trade grew during Hatshepsut’s reign. Traders exchanged beads, tools, and weapons for ivory, wood, leopard skins, and incense. Trade made Egypt wealthier. The New Kingdom Thutmose III became pharaoh after Hatshepsut’s death. Thutmose conquered more lands, and Egypt grew richer from tributes. Slavery became common in Thutmose’s reign. Slaves had some rights. They could own land, marry, and eventually obtain freedom. New Kingdom Video Clip Queen Nefertiti Queen Hatshepsut Tuthmose III Ramses II Amenhotep III Hatshepsut Hatshepsut Video Clip Review Questions How was Hatshepsut unlike other pharaohs? She focused on trade instead of military conquests. The Legacies of Two Pharoahs Amenhotep IV came to power in 1370 B.C. Amenhotep felt priests were gaining too much power. He introduced a new religion with only one god. Priests who did not follow the new religion were removed from power. The Legacies of Two Pharoahs Most Egyptians refused to accept the new religion. Amenhotep became so devoted to his new religion that he neglected his other duties. He did not act when the Hittites attacked Egypt. As a result, Egypt’s empire greatly diminished. The Legacies of Two Pharoahs Tutankhamen, now called King Tut, was a boy ruler who took power after Akhenaton died. He ruled for only nine years before his death. In A.D. 1922, a British archaeologist found King Tut’s grave. King Tut’s Tomb with wife Ankhesenamun King Tut’s Sacred Eye Necklace King Tut’s Shoes King Tut’s Throne King Tut Video Clip Review Questions What happened as a result of the removal of the priests? The priests were experienced in ruling Egypt. When Amenhotep neglected his duties, the priests were no longer available to make important decisions. The End of the New Kingdom Ramses II was one of the most effective pharaohs of the New Kingdom. During Ramses’s rule, many temples were built throughout Egypt. Temples were used for services. Most Egyptians prayed at home because they believed the temples were houses for the gods and goddesses. Inner Sanctuary of great temple of Ramses II at Abu Simbel Ramses II Statue at Great Temple Abu Simbel Ramses II’s Mummy The End of the New Kingdom After Ramses rule, Egyptian rule began to decline. Egypt was attacked by neighboring groups and eventually controlled only the Nile delta. Beginning in the 900s B.C., Egypt was ruled by the Libyans, then the people of Kush, and finally the Assyrians. Review Questions In addition to religious purposes, what other purpose did the temples serve? The temples also served as banks. People stored valuable items in the temples, such as jewelry and oils. Review Questions What improvements did the Middle Kingdom rulers make? They added more waterways and dams for irrigation, increased the amount of land used for farming, built a canal between the Nile River and Red Sea, and improved art and architecture. Review Questions What purposes did temples serve in Egypt? Temple were houses for gods and goddesses, places for priests to perform rituals, banks, and warehouses. Review Questions Evaluate What was unusual about the reign of Hatshepsut? She was the first woman to rule Egypt in her own right. Review Questions Analyze How did Akhenaton upset the traditional order? He stopped worship of old gods in favor of one god. Ramses II