* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - pic sciences
Fossil fuel phase-out wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Grid energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Renewable energy commercialization wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Intermittent energy source wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Renewable portfolio standard (United States) wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Renewable energy debate wikipedia , lookup
Energy applications of nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of electricity generation wikipedia , lookup
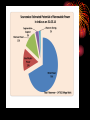
Energy Energy is the ability to do work. The word ‘work’ means transferring energy from one place to another. energy is neither destroyed nor created. It can only be changed. Thermal Electromagnetic Sound Types of Radiant Mechanical Energy Electrical Nuclear Chemical Any object in motion has mechanical energy. For example a ball flying through the air. Energy caused by the movement of electrons. Easily transported through power lines and converted into other forms of energy. • Comes from bonds between atoms in molecules • Chemical change = energy released • Examples: •Gasoline burning in a car •Food we eat Comes from reactions between atomic nuclei. Fission splits Fusion combines HUGE amounts of energy Includes energy from gamma rays, xrays, ultraviolet rays, visible light, infrared rays, microwave and radio bands. The Thermal energy is the internal kinetic energy and it considers the motion of every constitutive particle of the system (molecules, atoms, electrons, etc.). •Vibration of molecules in surrounding medium (usually air). Flows through empty space Examples: Sunlight Radio waves X-rays Among all energy forms, which one become prominent in Modern World ? Obviously we can say, Electrical energy. Because, Electricity has become very useful and has changed everyone's life since the day it was discovered. Of course, it couldn't be invented for it is a natural phenomenon. Individuals have become accustomed using the daily utilization of electricity for electricity illuminates houses, switch on our televisions, energy our laptops, cooks our food and then any other electrical products. Consider considering our everyday activity. Doesn't the majority of our actions involves electricity? Yes, it is... Every little single factor on the planet involves electricity. Now, are you able to imagine existence without electricity? According to 'Law of Conservation of Energy', Energy can neither be created nor destroyed. But can be changed from one form to another. So energy is inter-convertible. Non-renewable Renewable Non-renewable Energy (Conventional Sources of Energy) Those sources of energy which have been produced in nature over a very, very long time and cannot be quickly replaced when exhausted, are called non renewable sources of energy. COAL : Non- Renewable Energy Coal is the most abundant fossil fuel in the world. During the formation of coal, carbonaceous matter was first compressed into a spongy material called "peat," which is about 90% water. As the peat became more deeply buried, the increased pressure and temperature turned it into coal. COAL : Non- Renewable Energy COAL : Non- Renewable Energy Coal and Lignite Coal deposits are mainly confined to eastern and south central parts of the country. The states of Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, West Bengal, Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh and Maharashtra account for more than 99% of the total coal reserves in the country. The State of Jharkhand had the maximum share (26.81%) in the overall reserves of coal in the country as on 31st March 2014 followed by the State of Odisha(24.94%)(Table 1.1). As on 31.03.14 the estimated reserves of coal was 301.05 billion tons, an addition of 2.11 billion over the last year (Table 1.1). There has been an increase of 0.7% in the estimated coal reserves during the year 2013-14 with Odisha accounting for the maximum increase of 1.85% COAL : Non- Renewable Energy COAL : Non- Renewable Energy OIL Crude oil or liquid petroleum, is a fossil fuel that is refined into many different energy products (e.g., gasoline, diesel fuel, jet fuel, heating oil). Oil forms underground in rock such as shale, which is rich in organic materials. Petroleum and Natural gas ♦♦♦ The estimated reserves of crude oil in India as on 31.03.2014 stood at 762.74 million tons (MT) (Table 1.2). ❖ Geographical distribution of Crude oil indicates that the maximum reserves are in the Western Offshore (42.91%) followed by Assam (22.69%), whereas the maximum reserves of Natural Gas are in the Eastern Offshore (37.24%) followed by Western offshore (30.17%). (Table 1.2). Natural gas Natural gas production is often a byproduct of oil recovery, as the two commonly share underground reservoirs. Natural gas is a mixture of gases, the most common being methane (CH4). It also contains some ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8), and butane (C4H10). Natural gas is usually not contaminated with sulfur and is therefore the cleanest burning fossil fuel. Natural gas Natural gas The estimated reserves of natural gas in India as on 31.03.2014 stood at 1427.15 billion cubic meters (BCM) (Table 1.2). Nuclear power In most electric power plants, water is heated and converted into steam, which drives a turbine-generator to produce electricity. Fossil-fueled power plants produce heat by burning coal, oil, or natural gas. In a nuclear power plant, the fission of uranium atoms in the reactor provides the heat to produce steam for generating electricity. • So, the reserves of Non Renewable sources are very limited. • They may extinct very soon. • At this time, we may face 'energy crisis'. So that we have to search for the alternative sources on war-foot. • Alternate sources are renewable : 1. Hydel energy 2. Wind energy 3. Solar energy 4. Biomass energy 5. Geothermal energy Renewable Energy Those sources of energy which are being produced continuously in nature and will never be exhausted, are called renewable sources of energy. 1.3 Renewable energy sources There is high potential for generation of renewable energy from various sources- wind, solar, biomass, small hydro and cogeneration bagasse. The total potential for renewable power generation in the country as on 31.03.14 is estimated at 147615 MW (Table 1.3). This includes wind power potential of 102772 MW (69.6%), SHP (small-hydro power) potential of 19749 MW (13.38%), Biomass power potential of 17,538 MW (11.88%) and 5000 MW (3.39%) from bagasse-based cogeneration in sugar mills. Biomass Biomass is a renewable energy resource derived from the carbonaceous waste of various human and natural activities. It is derived from numerous sources, including the by-products from the timber industry, agricultural crops, raw material from the forest, major parts of household waste and wood. Hydel Energy The energy in the flowing water can be used to produce electricity. Waves result from the interaction of the wind with the surface of the sea and represent a transfer of energy from the wind to the sea. Energy can be extracted from tides by creating a reservoir or basin behind a barrage and then passing tidal waters through turbines in the barrage to generate electricity. Hydel Energy Wind Energy Wind energy is the kinetic energy associated with the movement of atmospheric air. It has been used for hundreds of years for sailing, grinding grain, and for irrigation. Wind energy systems convert this kinetic energy to more useful forms of power. Wind energy systems for irrigation and milling have been in use since ancient times and since the beginning of the 20th century it is being used to generate electric power. Windmills for water pumping have been installed in many countries particularly in the rural areas. Geothermal Energy We live between two great sources of energy, the hot rocks beneath the surface of the earth and the sun in the sky. Our ancestors knew the value of geothermal energy; they bathed and cooked in hot springs. Today we have recognized that this resource has potential for much broader application. Geothermal Energy Solar energy Renewable sources Energy Solar energy is the most readily available source of energy. It does not belong to anybody and is, therefore, free. It is also the most important of the nonconventional sources of energy because it is non-polluting and, therefore, helps in lessening the greenhouse effect. Solar energy Renewable sources Energy Renewable sources Energy Tidal Energy Tidal power, also called tidal energy, is a form of hydropower that converts the energy of tides into useful forms of power, mainly electricity. Although not yet widely used, tidal power has potential for future electricity generation. Tides are more predictable than wind energy and solar power. Among sources of renewable energy, tidal power has traditionally suffered from relatively high cost and limited availability of sites with sufficiently high tidal ranges or flow velocities, thus constricting its total availability. Tidal energy Renewable sources Energy Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) Renewable sources Energy Ocean thermal energy conversion (OTEC) Ocean thermal energy conversion (OTEC) uses the temperature difference between cooler deep and warmer shallow or surface ocean waters to run a heat engine and produce useful work, usually in the form of electricity. OTEC is a base load electricity generation system, i.e. 24hrs/day all year long. However, since the temperature differential is small, the efficiency is low, decreasing the economic feasibility of ocean thermal energy for electricity generation. POWER GENERATION DIFFERENT FORMS OF ENERGIES CAN BE CONVERTED INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY Now this Electrical Energy can be utilized by an Electrical Appliances for its work over a time So Electrical energy can be called as ' Electric Power' (or) simply ' Power '. Electrical power is the rate at which electrical energy is converted to another form, such as motion, heat, or an electromagnetic field. The common symbol for power is the uppercase letter P. The standard unit is the watt,symbolized by W. In utility circuits, the kilowatt (kW) is often specified instead;1 kW = 1000 W.