* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 脑神经
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
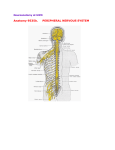
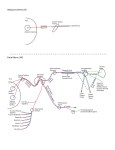
脑 神 经 The cranial nerves 黄绍明 广西医科大学解剖教研室 20030406 Nervous System Central nervous system Brain Spinal cord Peripheral Cranial nerves nervous Spinal nerves system Section 2 The Cranial Nerves There are twelve pairs of cranial nerves which are attached to the brain. The cranial nerves can be designated in two way and listed as follows: Section 2 The Cranial Nerves I Olfactory n. II Optic n. Ⅲ Oculomotor n. Ⅳ Trochlear n. Ⅴ Trigeminal n. Ⅵ Abducent n. Ⅶ Facial n. Ⅷ Vestibulocochlear n. Ⅸ Glossopharyngeal n. Ⅹ Vagus n. Ⅺ Accessory n. Ⅻ Hypoglossal n. The cranial nerve nuclei (review) Functional components of the cranial nerve nuclei: 1.General somatic motor nuclei 2. Special visceral motor nuclei 3. General visceral motor nuclei 4.General and special visceral sensory nuclei 5.General somatic sensory nuclei 6. Special somatic sensory nuclei Cranial nerves contain seven components: 1. General and special somatic afferent (sensory) fibers 2. General and special visceral afferent (sensory) fibers 3. General somatic efferent (motor) fibers 4. General and special visceral efferent (motor) fibers Classification of cranial nerves According to the components and functions , the cranial nerves are divided into three types: 1. sensory nerves:Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅷ (contain only sensory fibers) 2. motor nerves: Ⅲ, Ⅳ, Ⅵ, Ⅺ, Ⅻ (contain only motor fibers) 3. mixed nerves:Ⅴ, Ⅶ, Ⅸ, Ⅹ (contain both sensory and motor fibers) The Superficial origins of the cranial nerves on the brain Ⅰ Telencephalon (olfactory bulb) Ⅱ Diencephalon (lateral geniculate body) Ⅲ Midbrain (interpeduncular fossa ) Ⅳ Midbrain (beneath the inferior colliculus) Ⅴ Pons (the junction between basilar part of pons and the middle cerebellar peduncle) Ⅵ Ⅶ Pons (bulbopontine sulcus) Ⅷ IX Ⅹ Medulla oblongata (behind the olive) Ⅺ Ⅻ Medulla oblongata (between the pyramid and olive) I. Olfactory nerve Anterior ethmoidal n. Olfactory bulb Olfactory n. Olfactory tract Cribriform plate of ethmoid bone Nasoplatine n. Anterior ethmoidal n. Pterygopalatine ganglion Posterior nasal br. Nasal conchae Platine n. Olfactory n. II. Optic nerve Optic n. Optic chiasma Optic n. Optic chiasma Optic tract Ledial geniculate body Optic radiation III. Oculomotor nerve Oculomotor nuclus Accessory nuclus of oculomotor n. Accessory nuclus of oculomotor n. Supplies the levator palpebrae superioris, medial rectus, superior rectus, inferior rectus and inferior obliquus. The sphincter pupillae,ciliary muscle. Oculomotor n. Oculomotor nuclus Ciliary ganglion Ciliary ganglion The parasympathetic nerve fiber of the oculomotor nerve Accessory nuclus IV. Trochlear nerve Trochlear nucleus Trochlear n. Superior orbital fissure Superior obliquus Superior obliquus Trochlear n. Trigeminal ganglion V. Trigeminal nerve Motor nucleus of the trigeminal n. Potine nucleus of the trigeminal n. spinal nucleus of the trigeminal n. Trigeminal ganglion The motor fibers supplies the masticatory muscles, mylohyoid, anterior belly of digastric, tensor veli palatini and tensor tympani etc. The sensory fibers distributed to the skin of the face, the mucous membranes of the eye, tongue, oral cavity, nasal cavity and the paranasal sinuses as well as the teeth, the eyeball, the lacrimal gland and the meninges. ophthalmic n. Trigeminal Maxillary n. nerve Frontal n. Lacrimal n. Nasociliary n. Infraorbital n. Zygomatic n. Pterygopalatine n. Superior alveolar n. Auriculotemporal n. Buccal n. Mandibular n. Lingual n. Inferior alveolar n. The nerves of masticatory museles Ophthalmic n. Maxillary n. Mandibular n. VI. The abducent nerve Abducent nucleus Abducent n. Superior orbital fissure Lateral rectus Abducent n. VII. The facial nerve Facial nucleus Superior salivatory nucleus Nucleus of the solitary tract Pterygopalatine ganglion Submandibular ganglion Geniculete ganglion The muscles of expression The lacrimal gland The submandibular and sublingual glands and small glands in the mucous membrane of the nose and palate. The taste buds on the anterior two-thirds of the tongue The branches of the facial nerve Braches within the facial canal ① Chorda tympani n. ② Greater petrosal n. ① Temporal branches Facial n. Braches outside the facial canal ② Zygomatic branches ③ Buccal branches ④ Marginal mandibular branch ⑤ Cervical branch VIII. Vestibulocochlear nerve Facial nerve Cochlear ganglion Cochlear n. Vestibular ganglion Vestibular n. Vestibular nucleus Cochlear nucleus IX. Glossopharyngeal nerve Supply or distribution: Origination: Nucleus ambiguus Inferior salivatory nucleus Otic ganglion Inferior ganglion Nucleus of the solitary tract Spinal nucleus of the trigeminal n. Superior ganglion The stylopharyngeus, The parotid gland The mucous membrane of the phartnx, the tonsils, the middle ear, the posterior 1/3 of the tongue, the carotid glomus and carotid sinus. The skin of the posterior surface of the auricle The man branches of the glossophayngeal nerve Superior ganglion ① Tympanic n. ② Carotid sinus branch ③ Lingual branches ④ Pharyngeal branches It srises from the inferior ganglion and enter the tympanic cavity to form the tympanic plexus which distributed to the mucous membrane of the middle ear. Inferior ganglion Parotid gland Otic ganglion Lesser petrosal n. Otic ganglion Parotid gland Inferior salivatory nucleus Tympanic n. Auriculotemporal n. The parasympathetic preganglionic fibers arises from the Inferior salivatory nucleus passe through the tympanic cavity and joins the otic ganglion. The postganglionic fibers supply the parotid gland. The man branches of the glossophayngeal nerve Superior ganglion ① Tympanic n. ② Carotid sinus branch ③ Lingual branches ④ Pharyngeal branches It distributed to the carotid glomus sensory and the They contain the taste and general They supply the mucous membrane of carotid sinus. They respond to the changes visceral fibers,with andsensory distributed to the the the pharynx branches, of eithermembrane increased carbon dioxide tension mucous of the posterior 1/3 of stylopharyngeus with motor branch. or thedecreased tongue. oxygen tension in the blood, and to the changes of the arterial pressure reflexly. Inferior ganglion Parotid gland Otic ganglion Lingual branches carotid sinus branch Supply or distribution: Origination: Nucleus ambiguus Dorsal nucleus of vagus n. Nucleus of the solitary tract Spinal nucleus of the trigeminal n. X. Vagus nerve Intramural or paramural parasympathetic ganglia Inferior ganglion Superior ganglion The striped muscle of the larynx and the pharynx The smooth muscles, cardiac muscles and glands of the viscera in the thoracic and abdominal. The visceral of the neck, thorax and abdomen. The skin of the auricle and external acoustic meatus and cerebral dura mater. The man branches of the vagus nerve Branches in the neck: superior laryngeal n. cervical cardiac branches pharyngeal branch Branches in the thorax: recurrent laryngeal n. broncheal branches esophageal branches anterior gastric branches Branches hepatic branches in the posterior gastric branches abdomen: Celiac branches Pharyngeal branch Superior laryngeal n. Cervical cardiac branches Recurrent laryngeal n. Broncheal branches Esophageal branches Hepatic branches Celiac branches Anterior gastric branches XI. Accessory nerve Nucleus ambiguus Accessory nucleus Cranial root Vagus nerve Spinal root Cranial root join the vagus nerve to the muscles of the soft palate and intrinsic muscles of the larynx. Spinal root supplies the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius. Accessory n. Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Hypoglossal n. Accessory n. XII. Hypoglossal nerve Hypoglossal nucleus Hypoglossal nucleus Supplies all the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue Hypoglossal n. The nerves supply the tongue 1. Trigeminal n. (mucous membrane of the ant. 2/3 of the tongue) 2. Facial n. (the taste buds of the anterior 2/3 of the tongue) 3. Glossopharyngeal n. (the taste buds and the mucous membrane of the posterior 1/3 of the tongue) 4. Hypoglossal n. (lingual muscles)