* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 14-submandibular region I
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
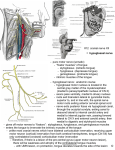
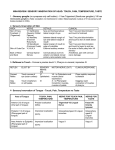
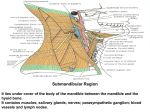
Dr. Ahmed Fathalla Ibrahim SUPRAHYOID MUSCLES DIGASTRIC MUSCLE: • Origin: by 2 bellies: 1. Anterior belly: from digastric fossa of mandible 2. Posterior belly: from mastoid notch • Insertion: both bellies unite in an intermediate tendon held by a fibrous loop into the hyoid bone • Nerve supply: 1. Anterior belly: nerve to myelohyoid 2. Posterior belly: facial nerve SUPRAHYOID MUSCLES STYLOHYOID MUSCLE: • Origin: styloid process • Insertion: hyoid bone • Nerve supply: facial nerve SUPRAHYOID MUSCLES MYELOHYOID MUSCLE: • Origin: myelohyoid line of mandible • Insertion: the muscles on both sides meet in a median raphe extending from symphysis menti to hyoid bone • Nerve supply: nerve to myelohyoid SUPRAHYOID MUSCLES GENIOHYOID MUSCLE: • Origin: inferior genial tubercle • Insertion: hyoid bone • Nerve supply: ventral ramus of C1 ACTIONS OF SUPRAHYOID MUSCLES 1. Fixation of hyoid bone (acting with infrahyoid muscles) during movement of tongue. 2. Depression of mandible to assist lateral pterygoid in opening of the mouth 3. Elevation of hyoid bone to elevate the floor of mouth & to improve tongue grip EXTRINSIC MUSCLES OF TONGUE STYLOGLOSSUS MUSCLE (MOST SUPERFICIAL): • Origin: styloid process • Insertion: whole length of side of tongue • Action: the muscles on both sides draw the tongue upwards & backwards EXTRINSIC MUSCLES OF TONGUE HYOGLOSSUS MUSCLE: • Origin: hyoid bone • Insertion: posterior half of side of tongue • Action: the muscles on both sides depress the tongue EXTRINSIC MUSCLES OF TONGUE GENIOGLOSSUS (DEEPEST MUSCLE): • Origin: superior genial tubercle • Insertion: whole length of side of tongue • Action: the muscles on both sides protrude the tongue EXTRINSIC MUSCLES OF TONGUE PALATOGLOSSUS: • Origin: soft palate • Insertion: back of side of tongue • Action: the muscles on both sides draw the tongue towards soft palate NERVE SUPPLY OF EXTRINSIC MUSCLES OF TONGUE • ALL MUSCLES ARE SUPPLIED BY HYPOGLOSSAL (12TH CRANIAL) NERVE EXCEPT: PALATOGLOSSUS (BY CRANIAL PART OF ACCESSORY NERVE) SUBMANDIBULAR REGION (Ramus of mandible is removed) S. P. Styloglossus Hyoglossus Myelohyoid Sublingual gland Stylohoid Submandibular Gland (Superficial part) Digastric Posterior belly Hyoid bone M A N D I B L E Digastric Anterior belly SUBMANDIBULAR REGION (Superficial part of submandibular gland is removed) S. P. Styloglossus Sublingual gland Hyoglossus Myeolohyoid M A N D I B L E Deep part of submandibular gland Digastric Posterior Belly Hyoid bone Digastric Anterior belly RELATIONS OF HYOGLOSSUS (Myelohyoid & digastric muscles are removed) Styloglossus Stylopharyngeus Lingual nerve Submandibular Deep part of submandibular ganglion gland Sublingual gland Submandibular duct Stylohyoid ligament Glossopharyngeal nerve Hyoglossus Genioglossus Hypoglossal nerve External carotid artery Lingual artery Geniohyoid SUBMANDIBULAR REGION 1 3 2 LINGUAL ARTERY • BEGINNING: from anterior aspect of external carotid artery, in the carotid triangle, opposite the tip of greater cornu of hyoid bone • COURSE: has a tortuous course, divided into 3 parts: • FIRST PART: forms a loop crossed by hypoglossal nerve • SECOND PART: runs along upper border of greater cornu of hyoid bone, deep to hyoglossus • THIRD PART: ascends along anterior border of hyoglossus & runs along the under surface of tongue to reach its tip & anastomoses with artery of opposite side BRANCHES OF LINGUAL ARTERY • FROM FIRST PART: Suprahyoid artery: runs along upper border of greater cornu of hyoid bone, superficial to hyoglossus, supplying adjacent muscles • FROM SECOND PART: Two dorsal lingual arteries: supply dorsum of tongue • FROM THIRD PART: Sublingual artery: supplies sublingual gland & mucous membrane of floor of mouth • N.B.: VEINS CORRESPONDING TO BRANCHES OF LINGUAL ARTERY UNITE TO FORM A SINGLE LINGUAL VEIN THAT DRAINS INTO INTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN SUBMANDIBULAR GANGLION • It is a small parasympathetic ganglion lying superficial to hyoglossus & is connected to lingual nerve by 2 roots (anterior & posterior) • Origin of fibers: superior salivary nucleus in pons • Preganglionic fibers: 1. Runs along chorda tympani branch of facial nerve 2. Chorda tympani transmits fibers to lingual nerve branch of mandibular nerve 3. Lingual nerve transmits fibers to ganglion through posterior root SUBMANDIBULAR GANGLION • Postganglionic fibers: 1. To submandibular gland: fibers are distributed directly to the gland 2. To sublingual gland: • Fibers pass along anterior root to lingual nerve again • Lingual nerve transmits fibers to sublingual gland RELATIONS OF HYOGLOSSUS SUPERFICIAL (LATERAL): • 2 MUSCLES: myelohyoid, styloglossus • 2 NERVES: lingual, hypoglossal • 2 GLANDS: superficial & deep parts of submandibular glands • 2 SUBMANDIBULAR: duct & ganglion RELATIONS OF HYOGLOSSUS DEEP (MEDIAL): • 1 MUSCLE: genioglossus • 1 NERVE: glossopharyngeal • 1 VESSEL: Lingual • 1 LIGAMENT: stylohyoid