* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 13. submandibular-M.N.V2010-10
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
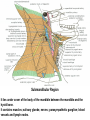
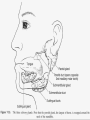
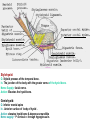
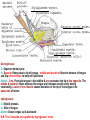
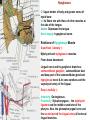
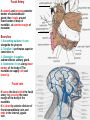
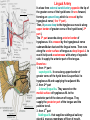
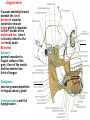
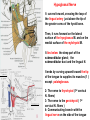
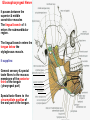
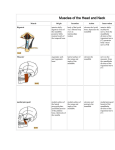
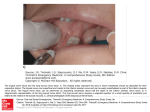
Submandibular Region It lies under cover of the body of the mandible between the mandible and the hyoid bone. It contains muscles; salivary glands; nerves; parasympathetic ganglion; blood vessels and lymph nodes. Digastric Muscle Origin and Insertion: The posterior belly arises from the medial surface of the mastoid process of the temporal bone. It passes downward and forward across the carotid sheath. It ends in the intermediate tendon. This tendon pierces the stylohyoid insertion and is held in position by a loop of deep fascia which binds the tendon down to the junction of the body and greater cornu of the hyoid bone. The anterior belly runs forward and medially and is attached to the lower border of the body of the mandible near the median plane in digastric fossa. Nerve supply: The posterior belly is supplied by the facial nerve & The anterior belly is supplied by the nerve to mylohyoid which is a branch of the inferior alveolar nerve of the mandibular nerve Action: Depresses the mandible or elevates the hyoid bone. Mylohyoid Muscle It is flat and triangular sheet of muscle. It arises from the whole length of the mylohyoid line of the mandible. Insertion: The fibers run downward and forward. The posterior fibers are inserted into the body of the hyoid bone. The anterior fibers are inserted into a fibrous raphe which extends from the symphysis menti to the body of the hyoid bone. Nerve Supply: Mylohyoid branch of the inferior alveolar nerve. Action: The 2 muscles support the tongue and floor of the mouth ( diaphragma oris ). When the mandible is fixed, they elevate the floor of the mouth and hyoid during the 1st stage of the swallowing. When the hyoid bone is fixed, it assists in the depression of the mandible and the opening of the mouth. Stylohyoid: O. Styloid process of the temporal bone. In. The junction of the body with the greater cornu of the hyoid bone. Nerve Supply: facial nerve. Action: Elevates the hyoid bone. Geniohyoid: O. inferior mental spine In . Anterior surface of body of hyoid . Action: elevates hyoid bone & depresses mandible Nerve supply: 1st cervical n. through hypoglossal n. Genioglossus: O. Superior mental spine In .Superior fibers pass to tip of tongue ; middle and posterior fibers to dorsum of tongue and few inferior fibers to body of hyoid bone Action: 2 ms. Protrude tongue in the midline & one protrudes the tip to the opposite. The middle & posterior fibers depress the tongue and increase mouth cavity during swallowing. Lesion of one muscle causes deviation of the tip of the tongue to he same side of lesion. styloglossus : O. Styloid process. In. Side of tongue. Action: Draws tongue up & backward N.B. The 2 muscles are supplied by hypoglossal nerve. Hyoglossus middle O. Upper border of body and greater cornu of hyoid bone In. Its fibers mix with those of other muscles at the side of the tongue. Action. Depresses the tongue. Nerve supply: hypoglossal nerve. styloglossus Relations of Hyoglossus Muscle Superficial ( laterally ): Mylohyoid and styloglossus muscles. From above downward: Lingual nerve and its ganglionic branches; submandibular ganglion ; submandibular duct and deep part of the submandibular gland and hypoglossal nerve & its vena comitans and the suprahyoid artery of the lingual. Deep ( medially ): Anteriorly: Genioglossus. Posteriorly: Stylopharyngeus ; the stylohyoid ligament and the middle constrictor of the pharynx. Also, the glossopharyngeal nerve and the second part of the lingual artery & its dorsal lingual branches. Facial Artery It ascends and grooves posterior border of submandibular gland, then hooks around lower border of body of mandible , at anterior margin of masseter. Branches 1- Ascending palatine: it runs alongside the pharynx 2- Tonsillar: it perforates superior constrictor m. 3- Glandular: it supplies submandibular salivary gland. 4- Submental: it runs along lower border of the body of The mandible to supply chin and lower lip. Facial vein It leaves the face behind the facial artery by crossing the lower margin of the body of the mandible. It is joined by anterior division of the retromandibular vein and ends in the internal jugular vein. Lingual Artery It arises from external carotid artery opposite the tip of the greater cornu of the hyoid bone It runs forward, forming an upward loop,which is crossed by the hypoglosal nerve ( the 1st part ). Then, it passes deep to the hyoglossus muscle along upper border of greater cornu of the hyoid bone( 2nd part ). The 3rd part ascends along anterior border of hyoglossus. It is crossed by the hypoglossal nerve submandibular duct and the lingual nerve. Then runs along the under surface of tongue as deep lingual A. to reach its tip and anastomoses with artery of opposite side. It supply the anterior part of the tongue. Branches : 1- from 1st part : suprahyoid A. It runs along upper border of greater cornu of the hyoid bone & superficial to hyoglossus M and supplying the adjacent Ms. 2- from 2nd part 2 dorsal lingual As. They ascend on the medial surface of hyoglossus M. to the posterior part of the dorsum of tongue. They supply the posterior part of the tongue and the palatine tonsil. 3- from 3rd part Sublingual A. that supplies sublingual salivary Lingual Veins The dorsal lingual veins drain the dorsum and sides of the tongue . They join to form the lingual vein, which accompany the lingual artery and lying in the interval between the hyoglosssus and genioglossus muscles. The lingual vein passes superficial to the internal and external carotid arteries. Near the greater cornu of the hyoid bone the lingual vein join the internal jugular vein. Lymph nodes They are situated on the superficial surface of the submandibular salivary gland. Lingual nerve It passes medially,forward beneath the lower border of superior constrictor muscle origin which is attached to the P. border of the mylohyoid line , here it is closely related to the last molar tooth. Branches Sensory: general sensation to lingual surface of the gum ; floor of the mouth and the anterior two third of tongue Ganglionic: secretory parasympathetic to lingual salivary gland Communicating with the hypoglossal n. Clinical Notes The lingual nerve passes forward into the submandibular region from the infratemporal fossa by running beneath the origin of the superior constrictor muscle which is attached to the posterior border of the mylohyoid line on the mandible. Here, it is closely related to the last molar tooth and is liable to be damaged in cases of extraction of an impacted third molar. Hypoglossal Nerve It curves forward, crossing the loop of the lingual artery just above the tip of the greater cornu of the hyoid bone. Then, it runs forward on the lateral surface of the hyoglossus M. and on the medial surface of the mylohyoid M. It lies below the deep part of the submandibular gland ; the submandibular duct and the lingual N. It ends by curving upward toward the tip of the tongue to supplies its muscles (1 ) except palatoglossus. 2- The nerve to thyrohyiod (1st cervical N. fibers) 3- The nerve to the geniohyoid ( 1st cervical N. fibers ) 4- Communicating branch with the lingual nerve on the side of the tongue Glossopharyngeal Nerve It passes between the superior & middle constrictor muscles The lingual branch of it enters the submandibular region. The lingual branch enters the tongue below the styloglossus muscle. It supplies: General sensory & special taste fibers to the mucous membrane of the posterior third of the tongue ( pharyngeal part) Special taste fibers to the circumvallate papillae of the oral part of the tongue.