* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anatomy of oral cavity + pharynx
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
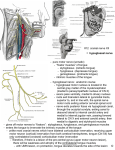
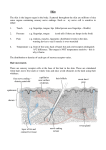
Anatomy of Oral Cavity, Pharynx & Oesophagus Dr. Vishal Sharma Oral Cavity Parts of Oral Cavity Floor of mouth Lymphatic drainage Intrinsic tongue muscles Extrinsic tongue muscles Coronal section of tongue Actions of tongue muscles Inferior Longitudinal: moves tip up & down Superior Longitudinal: moves tip up & down Transverse: narrows & lengthens tongue Vertical: flattens & depresses tongue Genioglossus: Prevents tongue from falling back Styloglossus: Pulls tongue up & back Palatoglossus: Pulls tongue back Hyoglossus: Depresses tongue Nerve Supply of Tongue Sensory Motor Taste Anterior 2/3 Posterior 1/3 Lingual Glossopharyngeal Hypoglossal *** Chorda tympani Glossopharyngeal *** except palatoglossus which is supplied by pharyngeal plexus Nerve Supply of Tongue Papillae in tongue Papillae in tongue Lingual taste buds sit on lateral borders of raised papillae. They are classified as: Fungiform: at tip & sides of tongue Circumvallate: just in front of terminal sulcus Foliate: at posterior lateral margins of tongue Filiform: centre of tongue, have no taste buds Papillae in tongue Tongue Map ? Sweet = Sucrose Salty = NaCl Sour = HCl Bitter = Quinine Umami = Glutamate Taste Bud Taste Pathway Pharynx Divisions Divisions Lower Limit of Nasopharynx Lower border of soft palate or Junction b/w hard & soft palate Oropharynx Tip of epiglottis or Body of hyoid bone or Base of vallecula Hypopharynx Lower border of cricoid or Lower border of C6 vertebra Anterior Relations Nasopharynx Nasopharyngeal isthmus Nasopharyngeal Isthmus Separates nasopharynx from oropharynx Bounded anteriorly by soft palate & posteriorly by mucosal ridge on nasopharyngeal wall called Passavant’s ridge (due to palatopharyngeus) Closure of this isthmus prevents nasal regurgitation & nasal intonation Parts of Oropharynx Parts of Oropharynx Oropharyngeal Isthmus Oropharyngeal Isthmus Separates oral cavity from oropharynx Boundaries are: Superior: Junction between hard & soft palate Inferior: Circumvallate papillae Lateral: Anterior tonsillar pillars (palatoglossus) Waldeyer’s Tonsillar Ring Waldeyer's tonsillar ring Vertically oriented, sub-epithelial lymphoid tissue ring located in pharynx, thought to function as a barrier to infection in first few years of life. Named after nineteenth century German anatomist Heinrich Wilhelm Gottfried von Waldeyer-Hartz. Parts of Hypopharynx Coronal section of Pharynx Layers of Pharyngeal Wall Mucosa: ciliated columnar in nasopharynx & stratified squamous elsewhere Pharyngo-basilar fascia Longitudinal muscles: stylo-pharyngeus + salpingo-pharyngeus + palato-pharyngeus Constrictor muscles: superior + middle + inferior Bucco-pharyngeal fascia Muscles Structures Passing Between Skull Base & Superior Constrictor (Sinus of Morgagni) Eustachian tube + Levator palatini + Tensor palatini + Ascending palatine artery Between Superior & Middle Constrictors Glossopharyngeal nerve & Stylopharyngeus muscle Between Middle & Inferior Constrictors Internal Laryngeal nerve & Superior Laryngeal artery Below Inferior Constrictor Recurrent Laryngeal nerve & Inferior Laryngeal artery Nerve Supply Nasopharynx: pterygo-palatine ganglion (V2) Oropharynx: glossopharyngeal & vagus nv Hypopharynx: Superior & recurrent laryngeal nv All muscles by pharyngeal nerve plexus (vagus nv carrying cranial part of accessory nv) except stylopharyngeus (glossopharyngeal nv) & cricopharyngeus (also by recurrent laryngeal) Arterial Supply Facial artery Lingual artery Ascending pharyngeal artery Ascending palatine artery Greater palatine artery Artery of pterygoid canal Superior laryngeal artery Venous Drainage Upper pharynx: Pharyngeal venous plexus situated on middle constrictor pterygoid venous plexus & internal jugular vein Lower pharynx: Inferior thyroid veins Lymphatic Drainage Nasopharynx: upper deep cervical + retropharyngeal + parapharyngeal + posterior triangle Oropharynx: upper deep cervical + retropharyngeal + parapharyngeal Hypopharynx: deep cervical + parapharyngeal + paratracheal + supraclavicular Killian’s Dehiscence Killian’s Dehiscence Triangular weak area between thyropharyngeus & cricopharyngeus part of inferior constrictor Mucosa herniates through it to form hypopharyngeal pouch (Zenker’s diverticulum) Perforation occurs here during forceful oesophagoscopy (gateway of tears) Oesophagus Introduction Also called gullet 23 to 25 cm long Extends from crico-pharyngeal sphincter (C6 vertebra) to cardiac orifice of stomach (T11 vertebra) Anterior Curvature Follows anteroposterior curve of vertebral column through neck, thorax (postr mediastinum) & upper abdomen Lateral curvatures Starts in midline → deviates to left at C7 → returns to midline at T5 → deviates to left again at T7 to reach gastric cardia Natural Constrictions Natural Constrictions Site Vertebral Level Distance from central incisor Cricopharynx C6 15 cm Aortic arch T4 25 cm Lt main bronchus T5 28 cm Oesophageal hiatus T 10 40 cm Importance of constrictions Common sites for lodgement of oesophageal foreign bodies Common sites for caustic stricture of oesophagus Blood Supply Part Arterial Venous Cervical Inferior thyroid Inferior thyroid Thoracic Descending thoracic aorta, Bronchial Left gastric, Inferior phrenic Azygos, Hemi-azygos Abdominal Left gastric, Abdominal azygos Oesophageal varices Left gastric vein is a site of portal-systemic anastomosis. Portal obstruction leads to varicose veins in lower oesophagus Nerve Supply Cervical: recurrent laryngeal nerve & cervical sympathetic trunk Thoracic: vagal trunks, oesophageal plexus & thoracic sympathetic trunk Abdominal: vagal trunks & thoracic sympathetic trunk Esophageal pain mimics cardiac angina due to common nerve supply Lymphatic Drainage deep cervical + posterior mediastinal + left gastric lymph nodes drain into coeliac lymph nodes thoracic duct Histology Histology Four coats from outside inwards: 1. Fibrous coat (adventitia) 2. Muscular coat (muscularis propria) 3. Submucous coat 4. Mucous coat Detailed Histology Mucous coat 1. Epithelium: non-keratinizing stratified sqamous 2. Lamina propria: loose areolar tissue with lymphoid aggregates 3. Muscularis mucosae: produces local movement of mucosa & helps in drainage of gland secretions Mucous coat Pink, smooth, protective oesophageal mucosa leads to red, mamillated, secretory gastric mucosa across Z (zigzag) line at 38-40 cm from incisors. Higher Z line seen in Barret’s esophagus. Z line in endoscopy Barret’s esophagus Submucous coat Loose supporting areolar tissue contains: Seromucous glands Blood vessels Lymphatic channels Parasympathetic ganglia forming Meissner's nerve plexus Muscularis propria External longitudinal muscle Internal circular muscle Parasympathetic ganglia forming Auerbach's nerve plexus lies b/w them Upper 1/3: striated muscle Middle 1/3: striated & smooth Lower 1/3: smooth muscle Fibrous coat (adventitia) Layer of loose, supportive fibrous tissue Conducts major vessels & nerves longitudinally A serosa formed by visceral peritoneum replaces adventitia of intra-abdominal segment of oesophagus Thank You