* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How do actors talk about their work?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
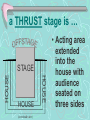
How do actors, directors, technicians & designers talk about their work? They speak the language of STAGECRAFT ©2006 EvaMedia, Inc. DRAMATIC MEDIA are … • Means of telling stories by way of stage, film, videotape, DVD, radio, television, or computer. to AUDITION is … • To try out for a role • Also called ‘reading’ for a part a CALL BACK is … • Getting a second audition for the same role • Similar to ‘making the cut’ in a sports tryout BLOCKING is … • The path an actor creates on stage • Usually determined by the director (with assistance from actor) • Often written down in a script using common theatrical symbols (X R means ‘cross down right’) a CUE is … • Something that precedes and prompts the next line or action • A signal to the actors to begin what happens next • Can be visual or aural ELECTRICS are … • Stage lights, including their mounts and wiring a BLACKOUT is … • All stage lights go off simultaneously and suddenly • More abrupt than ‘fade to black’ PROPS are … • Any objects, except costumes & scenery, used onstage • Can be hand props or set pieces DRESS REHEARSAL is … • Same as performance, but without an audience (usually) • A run-through of the whole show with tech, props & costumes in place DICTION is … • Selection & clear pronunciation of words • SPEAKING CLEARLY PROJECTION is … • How well the voice carries to the audience • SPEAKING LOUDLY ACOUSTICS means … • The quality of sound in a room, theatre, or performance space the HOUSE is … • Where the audience sits FRONT OF HOUSE is … • Box office & lobby of a theatre the STAGE is … • The acting area • Where the actors perform There are 3 kinds of STAGES: • Proscenium •Thrust •Arena PROSCENIUM is … • The most common type of stage • Walls that ‘frame’ the front of the acting area are called the ‘proscenium arch’ P R O S C E N I U M A R C H PROSCENIUM ARCH WINGS (offstage) STAGE (ACTING AREA) P R O S C E N I U M A R C H HOUSE APRON (front view) a THRUST stage is … HOUSE (overhead view) HOUSE HOUSE STAGE • Acting area extended into the house with audience seated on three sides an ARENA stage … • Has audience seated on all sides • Is sometimes called ‘theatre in the round’ (overhead view) BACKSTAGE is … • Hidden by scenery, walls or proscenium • Where cast & crew can work unseen by the audience • Dressing rooms here • Also called ‘wings,’ ‘offstage’ or ‘off’ DOWNSTAGE is … • Area of the stage closest to the audience (UPSTAGE is stage area farthest from audience) STAGE DIRECTIONS … apron (front-of-stage) DOWN LEFT DOWN CENTER DOWN RIGHT LEFT RIGHT CENTER CENTER CENTER UP LEFT UP CENTER UP RIGHT • Standard, universal • Prevents confusion • Saves rehearsal time • Indicates locations for actors, props, scenery. • From actor’s perspective when facing audience (overhead view) the COMPANY is … • Everyone associated with the production