* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bacterial Infection
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
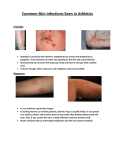
به نام خدا دکترعلیرضا واعظ شوشتری متخصص پوست Bacterial infections of Skin Normal flora of skin • Classification: 1. Resident flora: grow on skin & relatively stable in no. and composition at particular sites 2. Transient flora: lie on skin surface without attachment, unable to multiply & disappear within short time Normal Skin Flora • Major bacterial groups – Coryneforms - Staphylococci (Gram +ve cocci, aerobs) S. epidermidis, S. hominis, S.hemolyticus, S. saprophyticus • Minor bacterial groups – Acinetobacter (25%) – Micrococci • Fungal group – Pityriasporum Bacterial infection of the skin (Pyoderma) Classification of pyodermas 1. Primary Impetigo Ecthyma Folliculitis – Superficial – Deep * Furuncle * Carbuncle * Sycosis Barbae • • • • 2. Cellulitis/ Erysipelas Pyonychia SSSS TSS Secondary Secondary infection of preexisting dermatoses eg. Atopic dermatitis, Scabies Impetigo (contagious superficial infection) Non-bullous Bullous 1. Cause - Streptococcal (Group A) - Staph. aureus (Phage Groups II) 2. Pre-school and young school age 3. Very thin walled vesicle on an erythematus base 4. Transient 5. Yellowish-brain crusts (thick) Staph. aureus All ages Bullae of 1-2cm Persist for 2-3 day Thin, flat, brownish crust Contd… 6. Irregular peripheral extension without healing Central healing with peripheral extension 7. Regional adenitis 8. Constitutional symptoms present 9. Face (around the nose, mouth & limbs) 10. Palms & sole spared Rare Absent occur anywhere May involved Predisposing factors – Malnutrition – Diabetes – Immuno-compromise status Complications – – – – – Streptococcal infection PSGN (strep M-type 49) Scarlet fever Urticaria Erythema mutiforme Ecthyma • Streptococcal & staph • Common in children • Small bullae or pustules on erythematous base • Formation of adherent dry crusts • Beneath which ulcer present • Indurated base • Heals with scar and pigmentation • Buttocks, thighs and legs, commonly affected Folliculitis • Superficial folliculitis • Infection of hair follicles • Commonly caused by staph. aureus • Children • Scalp & limb • Rarely painful • Heals in a week Furuncle (Boil) • Acute • Staph. aureus • Small, follicular noduler -- Pustule--necrotic-discharge pus • Painful • Constitutional symptoms • Heals with scar • Age: Adult • Site: Neck, Wrist, Waist, Buttocks, Face Complication • Cavernous Sinus thrombosis, (upper lip & check) • Septicemia (malnutrition) Carbuncle • Extensive infection of a group of contagious follicles • Staph. aureus • Middle or old age • Predisposing factors – Diabetes – Malnutrition – Severe generalized dermatoses – During prolonged steroid therapy • Painful, hard lump • Suppuration begins after 5-7 days • Pus discharge from multiple follicular orificies • Necrosis of intervening skin • Large deep ulcer • Constitutional symptoms Sycosis barbae • Beard region • Pustules surrounded by erythema • Males • After puberty • After trauma • Upper lip and chin • Staph. aureus Cellulitis • Acute/sub-acute/chronic • Inflammation of loose connective tissue • Streptococcal (Group A) • Erythematous, edematous, swelling • Pain/tenderness • Constitutional upset Pyonychia • Acute • Erythematous swelling of proximal and lateral nail fold • Painful Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrom (Ritter’s Disease) • Exotoxin of staph (Phage Group II) • Acantholysis • Occult staph. upper respiratory tract infection or purulent conjunctivitis • Infants and children • Tender red skin Staphylococcal scalded skin synotrane (Ritter’s Disease) • Denuded skin • Heals 7 - 14 day • Don’t grow staph. from blister fluid • Complication 2% – Cellulitis – Pneumonia • Prognosis : good / 3% death Principles of therapy of pyoderma • Good personal hygiene • Management of predisposing factors – Local • Attend to traumas, Pressure, Sweating, Bites • Treat pre-existing dermatosis • Investigate carrier sites: Nose, Axilla, Perineum Systemic • Treatment of disease like DM • Nutritional deficiency • Immunodeficiency Principles of therapy of pyoderma • Local therapy – Cleaning with soap-water and weak KMN04 solution – Removal of crusts with KMN04 soluation – Application of antibacterial cream • Systemic therapy – Antibiotics Recurrent staphylococcal infection • Persistent nasal carriage • Abnormal neutrophitic chumotaxis • Deficient intracellular killing • Immunodeficient status • D.M. T/t of staph. carriage elimination • Nasal & perineal care • Rifampicin 600 mg/d 7-10 days • Clindamycin 150 mg/d 3 months • Topical mupirocin S.aureus produces skin infection I. Direct infection of skin and adjuscent tissues a. b. c. d. e. f. Impetigo Ecthyma Folliculitis Furunculosis Carbuncle Sycosis II.Cutaneous disease due to effect of bacterial toxin a. b. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome Toxic shock syndrome ß-hemolytic streptococcus produces skin infection I. Direct infection of skin or subcutaneous a. b. c. d. e. f. g. Impetigo (non bullous) Ecthyma Erysipelas Cellulitis Vulvovaginitis Blistering distal dactylitis Necrotizing fascitis II. Secondary infection Eczema infection III. Tissue damage from circulating toxin Scarlet fever IV. Skin lesion attributed to allergic hypersensitivity to streptococcal antigens E.Nodosum Vasculitis V. Skin disease provocated or influenced by streptococcal infection (mechanism uncertain) Guttate psoriasis Thank You For Your Attention Thank you