* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 4 Integumentary System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
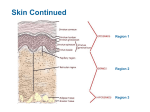
Chapter 4 Integumentary System Human Anatomy and Physiology Integumentary System Composed of – skin – Sweat glands – Oil glands – Hairs – Nails Functions Protection against – Damage – Ultraviolet radiation – Desiccation (drying out) Aids in temperature regulation Aids in excretion of urea and uric acid Synthesizes Vitamin D Structure of Skin Skin composed of two kinds of tissue that are firmly connected to each other – Epidermis – Dermis If these two layers separate, a blister forms. Deep to dermis is the subcutaneous tissue (hypodermis) – not actually considered a layer of skin – Made of adipose tissue – Anchors the skin to underlying organs Structure of Skin Epidermis Made of stratified squamous epithelium that can keratinize (become hard and tough) Avascular – no blood supply of its own Composed of five layers called strata – – – – – Stratum basale Stratum spinosum Stratum granulosum Stratum lucidum Stratum corneum Layers of Epidermis Stratum basale – Deepest cell layer – Only epidermal cells that receive adequate nourishment via diffusion of nutrients from the dermis – Constantly undergoing cell division Layers of Epidermis Cells move up to the next layer, Stratum Spinosum Then, Stratum Granulosum where they start to become flatter, increasingly full of keratin and finally the cells die Layers of Epidermis Stratum Lucidum – present where the skin is hairless and extra thick, palms of hands and soles of feet Layers of Epidermis Stratum Corneum – Outermost layer – 20-30 cell layers thick, ¾ of the epidermal thickness – Composed of dead cell remnants, completely filled with keratin Keratin waterproofs skin – Totally new epidermis every 25 to 45 days Melanin Pigment that ranges in color from yellow to brown to black Produced by melanocytes found in the stratum basale When skin exposed to sunlight, melanocytes produce more melanin and tanning occurs Melanin forms a protective umbrella over the cells’ nuclei which shields DNA from the damaging effects of the UV radiation Freckles and moles are seen where melanin is concentrated in one spot Dermis Made of dense connective tissue Two major regions: – Papillary layer – Reticular layer Dermis – Papillary Layer – Upper layer – Contain dermal papillae Uneven fingerlike projections which indent the epidermis Dermis – Papillary Layer Furnish nutrients to the epidermis Provide fingerprints Contain pain receptors: Meissner’s corpuscles Dermis Reticular layer – Deepest skin layer Dermis – Reticular Layer – Contains blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat and oil glands Rich nerve supply deep pressure receptors: Pacinian corpuscles Dermis – Reticular Layer Contains: –Collagen: responsible for toughness and attracts and binds water to help hydrate the skin –Elastic fibers: give skin elasticity • Decreases with age causing wrinkles Dermis and Body Temperature Blood vessels Sweat secretion Skin Color Three pigments: 1. Melanin amount and kind – yellow, black, or brown 2. Carotene Orange-yellow pigment found in carrots and other orange, deep yellow or leafy green vegetables 3. Amount of oxygen bound to hemoglobin Hemoglobin is the pigment in blood cells – gives the crimson color – rosy glow Appendages of the Skin Exocrine Glands – release secretions to the skin surface via ducts – Two groups: Oil glands (sebaceous glands) Sweat glands Hair and Hair Follicles Nails Sebaceous Glands Oil glands Found all over skin except palms and soles Produces sebum – Lubricant that keeps skin soft and moist – Contains chemicals that kill bacteria Sebaceous Gland Problems Whitehead: blocked by sebum Blackhead: If sebum dries it darkens Acne: active infection Increased secretion during adolescence cause skin problems Sweat Glands More than 2.5 million per person Two types: – Eccrine glands – Apocrine glands Eccrine Sweat Glands More numerous Found all over body Produce sweat that pours through pores Regulate body heat Sweat Sweat is a clear secretion that is made of – water – salts – vitamin C – traces of metabolic wastes like ammonia, urea, uric acid, and lactic acid (lactic acid attracts mosquitos) Acidic (pH 4 to 6 ) – Inhibits growth of bacteria Apocrine sweat glands Located mostly in axillary and genital areas Ducts empty into hair follicles Breakdown of secretion by skin bacteria produces musky odor. Hairs Millions all over body Serve protective function Hairs lost most of usefulness because we have other means of keeping warm unlike the early humans. Hair Anatomy Produced by hair follicle Flexible epithelial surface Root: part of hair enclosed in the follicle Shaft: part of hair projecting from the surface Why do my hairs stand on end? Arrector pili – Muscles that connect each side of the hair follicle to the dermal tissue – When these muscles contract, the hair is pulled upright, causing “goose bumps” Nails Visible part is called nail body Root is hidden by cuticle Nail bed changes color with blood flow change Tissue Repair Tissue injury stimulates inflammatory response. Wound healing (tissue repair) occurs two ways – Regeneration – Fibrosis Regeneration Replacement of destroyed tissue by the same kind of cells Fibrosis Repair by dense connective tissue by the formation of scar tissue Overview of Steps for Tissue Repair 1. 2. 3. 4. blood escapes from dermal blood vessels, and blood clot soon forms blood clot and dried tissue fluid form a scab protecting the area blood vessels send out branches and fibroblasts migrate into the area fibroblasts produce new connective fibers, scab sloughs off Steps of tissue healing Capillaries allow fluid rich in clotting proteins and other substances to seep into injured area from the bloodstream. Leaked clotting proteins construct a clot, which stops loss of blood, holds wound together. This prevents bacteria from spreading to surrounding tissues. Clot exposed to air, dries and hardens, forming scab Steps of Tissue Healing Granulation tissue forms – Delicate pink tissue composed largely of capillaries that grow into damaged area from undamaged blood vessels. – Contain phagocytes that dispose of blood clot and fibroblast (connective tissue cells) that make collagen fibers (scar tissue) to permanently bridge the gap. Steps of Tissue Healing Surface epithelium begins to regenerate and makes its way across the granulation tissue just beneath the scab, which then detaches. Final result : fully regenerated surface epithelium that covers the scar. Scar can be visible or invisible. Keloid Scars result of an overly aggressive healing process extend beyond the original injury may affect mobility Possible treatments include surgical removal, or injections with steroids Contracture scars If your skin has been burned, you may have a contracture scar, which causes tightening of skin that can impair your ability to move; additionally, this type of scar may go deeper to affect muscles and nerves. Hypertrophic scars Raised and red scars that are similar to keloids, but do not breach the boundaries of the injury site. Possible treatments can include injections of steroids to reduce inflammation. Acne Scars If you've had severe acne, you probably have the scars to prove it. FYI…… Epithelial Tissue regenerate easily. Connective tissue including bone regenerate easily as well. Skeletal Muscle regenerates poorly, if at all. Cardiac Muscle and Nervous tissue are replaced only by scar tissue. Imbalances of the Skin Infections and Allergies – – – – – – Athlete’s Foot Boils and Carbuncles Cold Sores Contact dermatistis Impetigo Psoriasis Burns – 1st degree – 2nd degree – 3rd degree Skin Cancer – Basal cell carinoma – Squamous cell carcinoma – Malignant melanoma ABCD RULE Other Disorders – Erythema – Pallor – Jaundice – Decubitus ulcer – bruises Infections and Allergies Athlete’s Foot: – itchy fungal infection of the toes Infections and Allergies Boils and Carbuncles: – inflammation of hair follicles and sebaceous glands Infections and Allergies Cold Sores: – fever blisters; small fluid filled blisters that itch an sting, caused by herpes simples infection Infections and Allergies Contact dermatitis: – itching, redness, and swelling of the skin, progressing to blistering – Caused by exposure of the skin to chemicals like poison ivy that provoke allergic responses Infections and Allergies Impetigo – Pink, water-filled raised lesions that develop a yellow crust and eventually rupture – Causes by a highly contagious staphylococcus infection Infections and Allergies Psoriasis – Chronic condition characterized by reddened epidermal lesions covered with dry, silvery scales Burns Tissue damage and cell death caused by intense heat, electricity, UV radiation (sunburn), or certain chemicals (acids) When the skin is burned, two life threatening problem result: 1. Dehydration 2. Infection 1st threat: Dehydration The body loses fluids containing proteins and electrolytes This can lead to a shutdown of the kidneys and circulatory shock 2nd threat: Infection Leading cause of death Burned skin is sterile for about 24 hours, but after that pathogens easily invade and multiply rapidly Rule of Nines Divides the body area into 11 areas, each accounting for 9 percent of the total body surface, plus 1% surrounding the genitals BURNS Burns 1st degree – Only the epidermis is damaged – Becomes red and swollen – Not usually serious and generally heal in two to three days without any special attention – sunburn Burns 2nd degree – Involve injury to the epidermis and the upper region of the dermis – Skin is red and painful and blisters appear – Re-growth of the epithelium can occur – No permanent scars result if care is taken to prevent infection 3rd degree – Destroy the entire – – – – thickness of the skin Appears gray-white or blackened Nerve endings are destroyed so the burn is not painful Regeneration is not possible Skin grafting must be done to cover the underlying exposed tissues Burns Burns Considered critical if any of the following conditions exists: – 1. Over 25 % of the body has 2nd degree burns – 2. Over 10% of the body has 3rd degree burns – 3. Any third-degree burn of the face, hands, or feet Skin Cancer Most skin tumors are benign and do not spread Some are malignant (cancerous) and tend to invade other parts of the body Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer in the body Basal Cell Carcinoma Least malignant and most common Full cure rate in 99% of patients Squamous Cell Carcinoma Believed to be suninduced If it is caught early and removed surgically, good chance of complete cure Malignant Melanoma Cancer of the melanocytes Accounts for 5% of skin cancers Often deadly – 50% survival rate Usually appears as a spreading brown to black patch that metastasizes rapidly to surrounding lymph and blood vessels ABCD Rule Asymmetry: the two sides of the pigmented spot of mole do not match Border Irregularity: The borders of the lesion are not smooth but exhibit indentations Color: the pigmented spot contains areas of different colors Diameter: the spot is larger than 6 mm in diameter (size of pencil eraser) An abnormal yellow skin tone usually indicates a liver disorder in which excess bile pigments are absorbed into the blood, circulated throughout the body, and deposited in body tissues. Jaundice Decubitus ulcer Restriction of blood supply to the skin results in cell death, and if severe or prolonged, ulcers. Occur in bedridden patients who are not turned regularly Bruises Reveal sites where blood has escaped from the circulation and has clotted in the tissue spaces Hematoma: clotted blood mass An unusual tendency to bruising may signify a deficiency of vitamin C in the diet or hemophilia