* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth - Cinnaminson
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
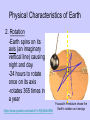
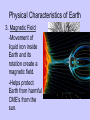
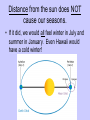
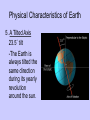
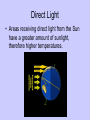
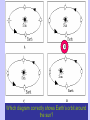
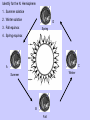
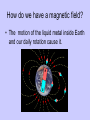
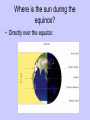
Earth Physical Characteristics of Earth 1. Spherical shape -satellite photos -curved shadow on moon during a lunar eclipse. -approaching ships “rise” over the horizon Physical Characteristics of Earth 2. Rotation -Earth spins on its axis (an imaginary vertical line) causing night and day. -24 hours to rotate once on its axis -rotates 365 times in a year https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R3jr0DaV8N8 Foucault’s Pendulum shows the Earth’s rotation as it swings Physical Characteristics of Earth 3. Magnetic Field -Movement of liquid iron inside Earth and its rotation create a magnetic field. -Helps protect Earth from harmful CME’s from the sun. Physical Characteristics of Earth 4. Revolution -Earth’s yearly orbit around the sun. (365 ¼ days) -Path is elliptical in shape. Farthest away from sun in July Closest to sun in January What causes the seasons? ? ? ? What do you know about the Seasons? • Summer – NJ-warm, longer days, June-August – Hawaii-80’s, 12 hours of light – Alaska- up to 24 hours of light – Australia-Dec-Feb • Winter – NJ-cold, longer nights, Dec-Feb – Hawaii- 70’s, 12 hrs of light – Alaska-up to 24 hours of darkness – Australia-June-Sept. Distance from the sun does NOT cause our seasons. • If it did, we would all feel winter in July and summer in January. Even Hawaii would have a cold winter! Physical Characteristics of Earth 5. A Tilted Axis 23.5˚ tilt -The Earth is always tilted the same direction during its yearly revolution around the sun. • Sunlight strikes the hemisphere tilted towards the sun more directly than the hemisphere tilted away. • Summer occurs in the hemisphere tilted towards the sun. (direct light) Sun Direct Light • Areas receiving direct light from the Sun have a greater amount of sunlight, therefore higher temperatures. Northern Hemisphere-Winter What season is it? Southern Hemisphere-Summer Sun So what causes the seasons? • The Earth’s tilt causes the seasons! http://lhsgems.org/Presentations/SSS%203-8%20NSTA%202009%20final.ppt#362,35,Another Model for Distance Solstice • The day when the sun reaches its greatest distance north or south of the equator. • Northern Hemisphere- (opposite of S. Hemi) – Summer solstice: June 21 or 22 (longest period of daylight of the year) – Winter solstice: December 21 or 22 (shortest period of daylight of the year) The sun’s path across the sky is higher in the summer and lower in the winter http://www.newscientist.com/blogs/shortsharpscience/2011/10/about-time-beer-can-freezes-ti-1.html Equinox • When the sun is directly above the Earth’s equator. Daylight hours are nearly equal all over Earth. – Neither the N. or S. Hemisphere is tilted towards the sun. – Spring equinox-March 20 or 21 – Fall equinox-September 22 or 23 Seasons demos • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DD_8J m5pTLk • http://esminfo.prenhall.com/science/geoani mations/animations/01_EarthSun_E2.html http://spiff.rit.edu/classes/phys301/lectures/gas_planets/Seasons_Nav.swf Northern Hemisphere Solstice and Equinox positions Seasons are opposite for the Southern Hemisphere Review Quiz Which diagram correctly shows Earth’s orbit around the sun? Identify for the N. Hemisphere: 1. Summer solstice 2. Winter solstice D 3. Fall equinox Spring 4. Spring equinox C A Winter Summer B Fall How do we know the Earth is a sphere? -satellite photos -curved shadow on moon during a lunar eclipse. -approaching ships “rise” over the horizon What is an axis? • The imaginary vertical line around which the Earth spins. What does “A” represent? What does “B” represent? A-Revolution B-Rotation B A How long does one complete rotation take on Earth? • 24 hours How long does one complete revolution of Earth take? • 365 days (1 year) Why is a magnetic field important? • It protects Earth from CME’s from the Sun How do we have a magnetic field? • The motion of the liquid metal inside Earth and our daily rotation cause it. What causes the seasons? • TILT! TILT! TILT! What season is it in the Southern Hemisphere? • Summer-southern hemisphere is tilted towards the sun = direct light = summer! Sun What type of light makes hotter temperatures? • Direct! Where is the sun during the equinox? • Directly over the equator. What’s the difference between northern and southern hemispheres’ seasons? • They are opposite! Christmas (December) in Australia is warm! Easter is celebrated in the fall (March or April) • http://www.teachnology.com/worksheets/science/earth/4/