* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Astronomers - duerkopscience
Earth's rotation wikipedia , lookup
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
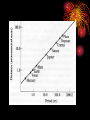
Astronomers All the “Dead White Guys” of Astronomy Aristotle (300 B.C) • Believed in geocentric universe – Earth is center • Proved Earth is round rather than flat due to eclipses and observing stars • Influenced people for 1000 years Ptolemy (140 A.D) • Believed also in geocentric universe • Developed geocentric model of the solar system explaining motions of planets using epicycles and deferents • Deferent: planet’s orbital path around Earth • Epicycle: planet’s smaller orbital path around the deferent • All orbits are circular Retrograde Motion: Apparent backwards motion of some planets in the sky Copernicus (1473-1543) • Heliocentric Theory: all planets orbit the sun, only the moon orbits Earth • Assumed Earth rotated which explained the seasons • Knew of 6 planets orbiting the sun • Made a new solar system model and placed them in order The closer a planet is to the sun, the faster it must be traveling…explained retrograde motion People did not believe him at first because the idea seemed so radical… believe it or not the universe does not revolve around you! Galileo (1564-1642) • Pioneered modern science – observation, experimentation, testing hypotheses • Studied motion, friction, acceleration…able to predict how far & fast bodies are moving in various lengths of time • Based on motion studies, adopted Copernicus’ heliocentric theory • 1st telescopic astronomer • invented telescope • Proved heliocentrism by observing the phase of Venus and 4 moons of Jupiter • Catholic church did not believe him and his books were forbidden Tycho Brahe (1546-1601) • Made observations of night sky for over 20 years on the island of Hveen (near Copenhagen) without use of telescope • Recorded positions of Sun, Moon, Earth for many years • Designed many astronomical instruments, calibrating and checking their accuracy often • Johannes Kepler assisted him and later used all of his data to work on his own theories Did not believe in heliocentrism, but did not completely agree with geocentrism either, so he combined the two ideas to form his model Kepler (1571-1630) • Used data to come up with the theory for planetary motion • Mathematician who made advances in calculus and geometry • Lived in poverty and died in poverty • Catholic church was trying to convert him and forced him to move around a lot Laws of Planetary Motion #1 Planets orbit the sun in elliptical orbits with the sun at one focus • Focus: point inside an ellipse • Ellipse: a curve for which the sum of the distances from any point on the ellipse to two points inside the ellipse is always the same. • Major Axis: widest diameter of the ellipse • Semimajor Axis: distance from the center of the ellipse to one end • Eccentricity: roundness of the ellipse Perihelion: closest point a planet gets to the sun Aphelion: farthest point a planet gets from the sun #2 A line from the sun to a planet will sweep out equal areas in equal times • Planets move faster when closer to the sun • Planets in circular orbits would always travel at the same speed 1st and 2nd laws allow us to calculate the speed of a planet at any point in the orbit #3 Distance3 = Period2 • Distance is the semimajor axis • Period is the time it takes for a planet to revolve around the sun once • Size of a planets orbit is related to its length of time needed to orbit the sun • 3rd Law proves a mathematical pattern for laws 1 and 2 Newton (1643-1727) • Found a conceptual framework to completely explain the observations/rules of Galileo, Brahe, and Kepler • Laws of Motion • Help to explain why the orbits are in elliptical paths and why they stay within those paths…GRAVITY Laws of Motion 1) Object a rest will stay at rest and an object in motion will stay in motion until it is acted upon by an outside force 2) Force = mass x acceleration 3) For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction