* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download India & China
Pratyabhijna wikipedia , lookup
C. P. Ramaswami Iyer wikipedia , lookup
Neo-Vedanta wikipedia , lookup
California textbook controversy over Hindu history wikipedia , lookup
Women in Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Akhil Bharatiya Hindu Mahasabha wikipedia , lookup
Hinduism in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent wikipedia , lookup
Hinduism in Malaysia wikipedia , lookup
Anti-Hindu sentiment wikipedia , lookup
Tamil mythology wikipedia , lookup
Hindu–Islamic relations wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
History of Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Hindu deities wikipedia , lookup
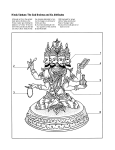
India has over a billion people(2nd largest country in terms of population) The capital is New Delhi There is no single founder of Hinduism Hindus believe in Brahman which is the belief that everything is a part of unchanging, all powerful spiritual force They also believe in Moksha which is ultimately, the goal of life. It is the union with Brahman Hindus also believe in reincarnation, the rebirth of the soul into another bodily form You can be reborn as another human, or an animal Moksha may take many lifetimes Karma is the belief that all the actions of a persons life affects his or her fate in the next life Dharma is the religious and moral duties of an individual These duties vary according to class, occupation, gender, or merit for the next life Ahimsa is the principle of nonviolence Jainism is a branch of Hinduism that takes Ahimsa to an extreme. They practice meditation and try to avoid killing anything. Some Jainists even carry around brooms so they won’t step on bugs in front of them. The Maurya Empire 321 B.C. – 185 B.C. The Maurya Empire was built by Chandragupta It started in the Ganges Valley and grew into the rest of India The capital was Pataliputra It was the largest and most prosperous city at the time This empire consisted of schools, libraries, palaces, and temples There was a huge wall surrounding the entire city This empire was 500 years after the Maurya empire The Gupta dynasty united much of India A.D. 320 – 550 was the golden age of India Most of the people were vegetarian Buddhists Trading & Farming flourished Wheat, Rice, Sugar Cain Artisans used materials such as cotton cloth, pottery, and metal ware Mathematicians of India created the “Arabic Numerals” we use today Concept of Zero Decimal system based on 10 Physicians used herbs and other remedies for various things To treat illness Setting bones Simple plastic surgery Buddhists built Stupas, large dome shaped shrines Buddhists and Hindu temples were covered in carvings of Gods & Goddesses The Guptas were eventually weakened by Civil war Weak rulers Foreign invaders The Huns overran the Gupta, & destroyed it’s cities & trade Again India split into many kingdoms Asoka is the emperor grandson of Chandragupta Asoka’s reign started from 268 B.C. He eventually converted to Buddhism He rejected violence & resolved to rule by moral example Asoka’s rule brought peace & prosperity He built roads, houses, & hospitals India was divided into the Deccan (south) and the Aryan (north) After Asoka died, India divided again & different princes regained rule The Deccan was divided into many kingdoms Each kingdom had their own capital with temples & workshops Many outside people wanted to trade with India Rome was their main trading partner Complex system of rules Governed every aspect of a person’s life Where people lived What they ate How they dressed How they earned a living To Hindus people from different castes were like different species of being Rules forbade marrying out of caste or eating with someone out of your caste If you were an “Untouchable", a member of the lowest caste, life was rough and restricted They include: Grave diggers Street cleaners Turning animal skin to leather Other castes feared even the shadow of an untouchable They had to live apart and wear a wooden clapper to warn of their approach Life was full of inequalities Most Indians lived in small villages Villages included homes in clusters made of earth or stone Beyond the home were farms which grew wheat, rice, cotton, & sugar cane Farming usually depended on the monsoons Too much or too little rain meant famine A village headman & council made decisions & dealt with outside authorities He was respected by people in the village Basic Indian families were joint families Joint Families were families in which the parents, children, grandchildren, and their offspring shared a common dwelling The family was patriarchal which mean that the father or eldest male headed the household He was thought to have wisdom and experience Usually he consulted the wife and other family members before they make a decision Brahma is the first God represented in the Hindu triad, or Hindu trinity He is the creator of the universe All living beings are said to have evolved from him The four Vedas (texts) are said to have originated from his head The four castes are also believed to have originated from Brahma Although Brahma is considered equal to Vishnu and Shiva, he is currently not widely worshipped There are several reasons for this One is that he is the creator, so his work is done Vishnu is the second God of the Hindu triad Vishnu is regarded as a major god in Hinduism and Indian mythology He is thought as the preserver of the universe He represents mercy and goodness Vishnu is a very popular deity and is widely worshipped He has over 1,000 names The third deity of the Hindu trinity Shiva is known as the Destroyer However, even though He represents destruction, He is viewed as a positive force He is viewed as the Destroyer of Evil Shiva literally means “auspicious, welfare” He has 1,008 names Shiva is believed to have many forms According to the Shiva Purana, Shiva is said to have 5 heads corresponding to his 5 tasks His tasks are Creation Establishment Destruction Oblivion Grace At an early age they had children & family duties Children worked with other relatives A young girl would learn that as a wife she would be expected to serve and obey her husband and his family Parents are responsible to arrange a good marriage The parents also finance costly wedding festivities In northern India, a brides family commonly provides a dowry or payment to the bridegroom After marriage, the daughter leaves her home and joins her husbands family A Hindu holy book where the god Krishna teaches the importance of Selfishness Performing religious duties Devotion to God It consists of 700 verses arranged in 18 chapters Tradition takes it back to 3000 BCE Spoken by Lord Krishna Contains the song of the Lord Gautama Buddha was born in 566 BC Grew up in a palace as a rich person Became aware of human suffering and left his lifestyle Wandered for years looking for the answers to life's secrets Became sick so he sat down to meditate until he understood the mystery of life 48 days went by until he finally figured out what is the cause and cure of suffering and sorrow When he rose he was no longer Gautama He was Buddha He spent the rest of his life teaching what he had learned Key part of Buddhism All life is full of suffering, pain , and sorrow The cause of suffering is desire for things that are really illusions The only cure for suffering is to overcome desire The way to overcome desire is to follow the Eight Fold Path Right views Right aspirations Right speech Right conduct Right livelihood Right mindfulness Right contemplations Eventually Buddhism split up into Theravada – complex - for monks and nuns Mahayana – simple and easy – for the ordinary person Confucianism Daoism Legalism Created By Confucius Laozi “Old Master” Hanfeizi When 500 BC 300 BC 221 BC Teaching Emphasized orderly personal and public conduct Strict Laws & Harsh Punishment Living in harmony with nature Great philosopher of 500 BC who was an advisor to Chinese rulers Believed rulers should set a good example Never wrote down his ideas so after he died his students did The book is called “The Analects” Stressed 5 key relationships Father to Son Elder brother to Younger brother Husband to Wife Ruler to Subject Friend to Friend Older people were superior to younger people Men were superior to women Mothers of Sons should be respected He taught Filial Piety which is the respect for your parents “While a father or mother is alive, a son should not travel far” “Do not do to others what you do not wish yourself” “People are naturally good” “The best ruler is a virtuous man who led by example” After Confucius died, his ideas spread Confucianism NEVER became a religion Legalism was created by Hanfeizi He taught that “The nature of man is evil” “His good is acquired”. Greed was the motive for most actions and causes of most conflicts His philosophy consists of Strict Laws and Harsh punishment Because of the emphasis on Law, Hanfeizi teachings were known as Legalism Daoism differed from Confucianism and Legalism Sought to live in harmony with nature Laozi was the founder “Old Master” He is credited with writing The Way Of Virtue Daoism evolved into a popular religion with Gods, and Goddesses Taoist priests experimented with Alchemy trying to transform ordinary metal into gold Taoists are thought to have invented gunpowder which they first used in firecrackers to scare away ghosts By AD 100 missionaries and merchants spread Buddhism from India to China Buddhism became popular Offered personal salvation unlike Daoism or Confucianism The three beliefs mixed By 400 AD Buddhism spread throughout China