* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Object Oriented Programming
Go (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
Falcon (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
Design Patterns wikipedia , lookup
Abstraction (computer science) wikipedia , lookup
Name mangling wikipedia , lookup
Class (computer programming) wikipedia , lookup
C Sharp (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to Object
Oriented
Programming
Java
Resources
If you are new to programming in Java,
there is an online book which is serves
as a good introduction:
●Thinking in Java 3rd edition
This can be found at:
http://www.mindview.net/Books/TIJ/
Development Environment
You can use the command line and
notepad to edit and compile java
programs.
You can also use jedit
BlueJ is a tool which will help you format
code, compile and test your programs.
OOP Introduction
Introduced in the 60s as a proposed
solution to the sprawl of software
Allowed designers to describe the
system entities in plain language and
design functions and attributes for each
entity.
The interaction or interfaces between the
entities can also be designed easily.
An OO Approach
class Student{
/* attributes */
String name;
int age;
int courseNumber;
int fees;
boolean enrolled;
/* Methods */
public getName(){ ... }
public int getAge() {...}
public int getFees() { ...}
}
class StudentRecords{
/* attributes */
Student [] database;
Course [] allCourses;
/* Methods */
public void
enrollStudent(Student s)
{ ... }
public void disenrollStudent
(Student s) { ... }
public int getTotalStudents()
{ ... }
}
Advantages of OO Programming
The software is modular and reusable
i.e. we could reuse our code for Student in
an examRecords system
It is extendable, and maintainable
i.e. if we decided to store students
mobile phone numbers, it'd just be a
small change to the Student class.
OO Programming Vocabulary
● class
● object
● method/attribute
● inheritance
● encapsulation
● abstraction
● polymorphism
Class
A class is a definition of a well defined
entity, containing attributes and methods.
This is a real world entity
class Employees {
}
Object
An object is an instance of a class.
e.g. Employee e1 = new Employee();
e1 is now an object of type Employee.
Method
A method is simply a well defined
function within a class.
Example methods in Employee...
getSalary();
getDOB();
add();
remove();
Attribute
● An attribute is an instance variable
which represents some data within a class. For
example, all employees have a name and a
salary.
so...
● class Student{
String name;
float salary;
..etc.
}
Inheritance
● Inheritance allows you to define classes
which inherit the behaviour and attributes of
other classes.
● For example, you may have one Employee
class, but 3 different types of employees
(permanent staff, part time staff and managers).
Rather than write 3 entirely separate classes
you can inherit the standard employee
characteristics from a base class.
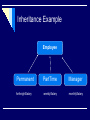
Inheritance Example
Employee
Permanent
forthnightSalary
PartTime
Manager
weeklySalary
monthlySalary
Advantages of this approach
Less code, therefore easier to maintain
Reusable Employee class
Encapsulation
● We've seen how to specify the
behaviour of an object, the idea of
encapsulation is to hide the details of
how something is achieved.
● e.g. If you are using a class that
someone else has written, you want to
be able to call a method (Save File for
example) without knowing what is
going on in the background.
Abstraction
● Abstraction a principle used to enable
inheritance.
● Using abstraction you develop general
classes that are appropriate to the
problem, and then for specific problems
inherit from these general classes.
● e.g. an Employee class models the typical
behaviours of employees, but for parttime staff
you'll need more specific methods.
Polymorphism
● Polymorphism is a type of encapsulation
that is aimed at decoupling software
systems.
● Polymorphism literally means “many
forms“, and its idea is to allow subclasses
to have their own specific
implementations of methods.
e.g. calculateSalary is a different process
for our three types of employee.