* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download orb - jakeadams
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
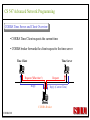
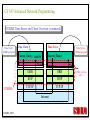
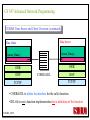
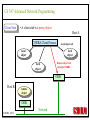
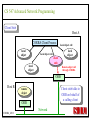
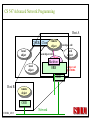
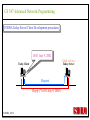
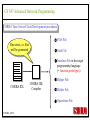
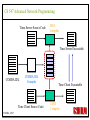
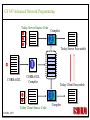
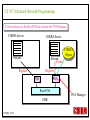
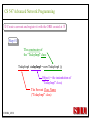
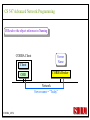
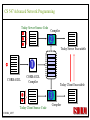
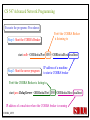
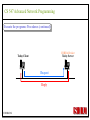
CS 547/CS490-003 Advanced Network Programming CORBA: Concept and Programming (2) Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Edwardsville Spring, 2010 Dr. Hiroshi Fujinoki E-mail: [email protected] CORBA_1/001 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Presentation Agenda 1. Overview for a simple CORBA application: CORBA Time Server and Client 2. CORBA Programming Concept 3. Coding IDL 4. Coding CORBA Time Server and Client 5. Executing the CORBA server and client CORBA_2/002 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming CORBA Time Server and Client Overview • CORBA Time Client requests the current time • CORBA broker forwards the client request to the time server Time Client Time Server Request Request (What time?) Reply Reply (Current Time) CORBA Broker CORBA/003 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming CORBA Time Server and Client Overview (continued) • CORBA Time Client requests the current time • CORBA broker forwards the client request to the time server CORBA Broker Time Server Time Client Request (What time?) Reply • Put the CORBA Broker at the server host CORBA/004 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming The CORBA ORB we are going to use • Java 2 SDK - the CORBA ORB developed by Sun Microsystems • Java 2 SDK Standard Edition v.1.4.0, rev. 01 (v.1.4.0_01) • Java IDL assumes JAVA for its programming language • Java 2 contains a free CORBA ORB • Java 2 SDK for Win32 environment is available - Posted in CS547/CS490-003 Home - A little bit big (about 32MB) - Sample server/client source will be posted CORBA_2/005 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Installing Java 2 SDK • Download java-2 SDK standard Edition for Win32 environment • Can be downloaded from the Sun web site for J2SE (http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.4/) J2SE J2SE CORBA Java IDL ORB CORBA_2/006 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming CORBA Time Server and Client Overview (continued) Time Client CORBA program CORBA Time Client Time Server Current_Time(); 11:01:58 Current_Time(); ORB ORB IIOP IIOP TCP/IP TCP/IP Internet CORBA_2/007 Time Server CORBA program CORBA Interface (IDL) CS 547 Advanced Network Programming CORBA Time Server and Client Overview (continued) Time Client What_time(); 11:01:58 Time Server 11:01:58 ORB ORB IIOP IIOP TCP/IP TCP/IP Internet CORBA_2/008 CORBA Interface (IDL) CS 547 Advanced Network Programming CORBA Time Server and Client Overview (continued) Time Client Time Server Current_Time(); Current_Time(); ORB ORB IIOP TCP/IP IIOP CORBA IDL TCP/IP • CORBA IDL to define the interface for the caller function • IDL file is not a function implementation but a definition of the function CORBA_2/009 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming CORBA Time Server and Client Overview (continued) Time Client “Stub” “Skeleton” Time Server Current_Time(); Current_Time(); ORB ORB IIOP TCP/IP CORBA IDL IIOP TCP/IP • After a CORBA IDL is compiled, the client stub and server skeleton are created • Client stub and server skeleton are the interface between your programming language and a CORBA ORB CORBA_2/010 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Client Stub 1. A client stub has exactly the same interface as the remote object a CORBA client is trying to call 2. The client stub communicates with the local ORB to talk to the actual remote object 3. The client stub also performs data marshaling/unmarshaling between a CORBA client and the local ORB Marshaling/unmarshaling = convert the format of data CORBA_2/011 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Client Stub • A client stub is a proxy object Host A CORBA Client Process Local object call local object local object local object Remote object call through CORBA ORB Host B remote object ORB Network CORBA_2/012 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Client Stub Host A CORBA Client Process local object Local object call local object Local object call client stub local object Remote object call through CORBA ORB Host B Client stub talks to ORB on behalf of a calling client remote object ORB Network CORBA_2/013 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Server Skeleton • A server skeleton is an ORB – remote method interface • A remote method is implemented in some high-level programming language (such as C++, Java, COBOL, FORTLAN, CGI…) • There must be a translator program between an ORB and a remote object • The translator must know how to call the remote object (1) Type of programming language (2) Input parameters (parameter types) (3) Output parameters (parameter types) CORBA_2/014 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Host A remote CORBA Client Process object local object Local object call local object Local object call client Skeleton stub local object ORB ORB Host B remote object ORB Network CORBA_2/015 Remote object call through CORBA CS 547 Advanced Network Programming CORBA Today Server/Client Development procedures 18:01 July 9, 2002 CORBA Broker Today Server Today Client Request Reply (“18:01 July 9, 2002) CORBA_2/016 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming CORBA Today Server/Client Development procedures Example of Time Server/Client IDL: module TodayApp { interface Today { string which_day(); oneway void shutdown(); }; }; This IDL file is assumed to be saved as “Today.IDL” CORBA_2/017 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming IDL Syntax IDL is a language to define interface for Java and the following terms are defined: (1) Module: declares an object (2) Interface: defines a name of an object (3) Operation: declares a method in an object (4) Parameter: defines parameters in a method (5) Attribute: defines attributes in an object (6) Constant: declares constant(s) in an object (7) Exception: defines operations for exception (8) Type: data type definition CORBA_2/018 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming CORBA Time Server/Client Development procedures Example of Time Server/Client IDL: Module module TodayApp { interface Today { string which_day(); oneway void shutdown(); }; }; CORBA_2/019 Object Name Object Methods CS 547 Advanced Network Programming CORBA Time Server/Client Development procedures POA File If no error, six files will be generated Stub File Interface File in the target programming language (= function prototypes) Helper File CORBA IDL CORBA IDL Compiler Holder File Operations File CORBA_2/020 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Compiling IDL file by JAVA IDL compiler Make sure that the j2sdk/bin directory (or the directory of idlj, java, javac, and orbd) are in your path • You can make sure your current path setting by typing “PATH” at DOS command prompt • If the current path does not include a path to j2sdk/bin, you can include a path by modifying config.sys (a hidden Windows system file) Go to a command line prompt in Windows’ DOS box Change to the directory that contains your IDL file (*.idl file) Compile your IDL by: “idlj -fall Hello.idl” On success, the IDL output directory will be created with six files CORBA_2/021 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming POA (Portable Object Adapter) File • This file contains the abstract class for stream-based (connection-oriented) server skeleton • POA file provides basic CORBA functionality for a CORBA server (an object) • The server class (the server object) is implemented by extending this class • File name: “TodayPOA.java”, if the name of IDL is “Today.idl” This file is a skeleton (for CORBA server) CORBA_2/022 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Stub File • This is the client stub • The stub file provides basic CORBA functionality for a CORBA client • File name: “_TodayStub.java”, if the name of IDL is “Today.idl” CORBA_2/023 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Interface File Describe the last 3 output files from the IDL compiler CORBA_2/024 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Helper File • Contains the class that convert JAVA data types to/from CORBA data types • File name: “TodayHelper.java”, if the IDL file is “Today.idl” Holder File • Contains public functions and variables in the resulting JAVA program • Delegates to the methods in the Helper class for reading and writing • File name: “TodayHolder.java”, if the IDL file is “Today.idl” CORBA_2/025 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Operations File • Contains the methods in the client process • This file defines the signatures (the interface) of all methods • Shared by the stub and the skeleton • File name: “TodayOperations.java”, if the IDL is “Today.idl” CORBA_2/026 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Time Server Source Code JAVA Compiler Time Server Executable CORBA IDL CORBA IDL Compiler Time Client Source Code CORBA_2/027 Time Client Executable JAVA Compiler CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Today Server Source Code Compiler Today Server Executable CORBA IDL Compiler CORBA IDL Today Client Source Code CORBA_2/057 Today Client Executable Compiler CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Coding Time Server Program: Program Organization The CORBA server program consists of three sections: (1) Server Setup Section (2) Servant Section (3) Server Body Section Server Program CORBA_2/030 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Section 1: Server Setup Section // TodayServer.java import TodayApp.*; import org.omg.CosNaming.*; import org.omg.CosNaming.NamingContextPackage.*; import org.omg.CORBA.*; import org.omg.PortableServer.*; import org.omg.PortableServer.POA; import java.util.Properties; CORBA_2/031 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Section 2: Servant Section Implementation of “which_day” method class TodayImpl extends TodayPOA { private ORB orb; public void setORB(ORB orb_val) { orb = orb_val; } public String which_day() { return ("\n18:01 July 9, 2002"); } } CORBA_2/032 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Servant • An ORB creates an object (= activates a servant) based on a servant when a CORBA client makes a request to it • Servant is a CORBA server service registered to an ORB = implementation of your CORBA server object CORBA_2/028 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Object Adapter • When a CORBA server is started, CORBA object may not be created • OA creates (instantiates) and deletes local CORBA objects • Most popular OA is POA (Portable Object Adapter) • When a CORBA server is started, the operations are registered to its ORB CORBA_2/029 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Object Adapter What is OA (Object Adapter)? • OA (Object Adapter) is an ORB component • OA manages (creates and deletes) local CORBA objects CORBA Server Servant Create Register ORB CORBA_2/029 POA CORBA Object CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Section 3: Server Body Section Initialize the local ORB Get reference to RootPOA & activate the POAmanager Create an ORB servant and register it with the ORB setup at Get object reference from the servant created at Get the root naming context Bind the object reference in naming Wait for invocation from clients CORBA_2/033 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Initialize the local ORB Pointer to ORB properties (default = NULL) ORB orb = ORB.init (args, null); “args” in main () can be passed here • ORB.init initializes the local ORB and needs to be called at the beginning • The call to the ORB’s init () method passes in the server’s command line arguments, allowing you to set certain properties at runtime • Special ORB properties can be specified CORBA_2/034 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Get reference to the RootPOA & activate the POAManager POA rootpoa = POAHelper.narrow (orb.resolve_initial_references(“RootPOA”); Rootpoa.the POAManager().activate(); • The reference to the root POA is retrieved in the first line • The POA Manager is activated CORBA_2/035 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Get reference to the RootPOA & activate the POAManager CORBA Server CORBA Server Servant Servant Create Register Register POA1 POAn Root POA ORB CORBA_2/036 CORBA Object POA Manager CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Create a servant and register it with the ORB created at There are two steps to perform 1. TodayImpl todayImpl = new TodayImpl (); 2. today_impl.setORB(orb); CORBA_2/037 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Create a servant and register it with the ORB created at Step #1 The constructor of the “TodayImpl” class TodayImpl todayImpl = new TodayImpl (); Object (= the instantiation of “TodayImpl” class) The Servant Class Name (“TodayImpl” class) CORBA_2/038 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Create a servant and register it with the ORB created at Step #2 Register an object to ORB (POA) todayImpl.setORB (orb); setORB method registers this object to ORB (POA) Servant object name (not servant class name) CORBA_2/039 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Get object reference for the servant created at Host C CORBA Broker • IP address • Port # ORB CORBA client ORB = • Protocol = TCP Host A Object Reference Host B remote object ORB CORBA_2/040 TCP/IP Internet Object Reference = a set of information that physically identify a target CORBA remote object CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Get the root naming context CORBA Server CORBA Object Get object reference Servant Register POA1 Root POA ORB CORBA Broker CORBA_2/041 Network Create Created CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Get the root naming context • It is not a good idea to let a CORBA client to identify each CORBA server by the object reference • In CORBA, a CORBA client can call a CORBA server by its server name • We have to give a CORBA server a name to a CORBA Broker CORBA_2/042 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Get the root naming context CORBA Server Server Name CORBA Object Object Reference Servant Register POA1 Root POA ORB CORBA Broker CORBA_2/043 Network Create Get object reference CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Get the root naming context orb.omg.CORBA.Object objRef = Object name (instantiation) of naming Class name of naming context context orb.resolve_initial_references (“NameService”); “resolve_initial_references” advertises POAs in an ORB Constant “NameService” required CORBA_2/044 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Get the root naming context NamingContextExt ncRef = Object name (instantiation) of naming Class name of naming context context NamingContextHelper.narrow(objRef); “resolve_initial_references” advertises POAs in an ORB Constant “NameService” required CORBA_2/045 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Bind the object reference in naming Server Name Bind CORBA Server CORBA Object Object Reference Servant Register POA1 Root POA CORBA Broker ORB Network Advertise the servant object by “Server Name” CORBA_2/046 Create Get object reference CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Bind the object reference in naming String name = “Today”; The server name to be advertised to a CORBA broker NameComponentPath path [ ] = ncRef.to_name (name); ncRef.rebind (path, href); CORBA_2/047 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Wait for invocation from a client orb.run (); After this, “Today” CORBA object (= Today CORBA Server) is up and running, waiting for a CORBA client CORBA_2/048 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Coding Time Client Program: Program Organization The CORBA client program consists of two sections: (1) Client Setup Section (2) Client Body Section Client Program CORBA_2/049 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Section 1: Client Setup Section import TodayApp.*; import org.omg.CosNaming.*; import org.omg.CosNaming.NamingContextPackage.*; import org.omg.CORBA.*; CORBA_2/050 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Section 2: Client Body Section Create and instantiate the local ORB Get the root naming context Resolve the object reference in Naming Invoke a remote CORBA object CORBA_2/051 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Initialize the local ORB = same as the one in the server side Pointer to ORB properties (default = NULL) ORB orb = ORB.init (args, null); “args” in main ( ) can be passed here CORBA_2/052 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Get the root naming context = This is the fifth step () in the server orb.omg.CORBA.Object objRef = Object name (instantiation) of naming Class name of naming context context orb.resolve_initial_references (“NameService”); “resolve_initial_references” advertises POAs in an ORB Constant “NameService” required CORBA_2/053 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Resolve the object reference in Naming CORBA Client Client ORB Server Name CORBA Broker Network Server name = “Today” CORBA_2/054 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Resolve the object reference in Naming static Today todayImpl; Object name (the one specified by “interface” keyword in IDL) String name = “Today”; todayImpl = TodayHelper.narrow (ncRef.resolve_str(name)); Call a CORBA Broker to find this object CORBA_2/055 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Invoke a remote CORBA object Class name of your CORBA object System.out.println (todayImpl.whcih_day()); You can call a remote CORBA object as if it were an ordinary local JAVA object (remote) CORBA method A method defined in Java library CORBA_2/056 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Today Server Source Code Compiler Today Server Executable CORBA IDL Compiler CORBA IDL Today Client Source Code CORBA_2/057 Today Client Executable Compiler CS 547 Advanced Network Programming CORBA Today Server/Client Development procedures (1) Create a project directory (such as “Time”) (2) Create the IDL file and save it in the directory created at (1) (3) Compile the IDL file (: “idlj –fall Today.idl” in the directory (4) If no error, a subdirectory, “TodayApp” will be created and the six output files from IDL compiler will be placed in the subdirectory (5) Create a server source code file in “Time” directory (TodayServer.java) (6) Compile the server program (: “javac TodayServer.java TodayApp/*.java”) (7) Create a client source code file in “Time” directory (TodayClient.java) (8) Compile the client program (: “javac TodayClient.java TodayApp/*.java”) CORBA_2/058 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Execute the programs: Procedures Port# the CORBA Broker is listening to Step1: Start the CORBA Broker start ordb –ORBInitialPort 1050 –ORBInitialHost localhost Step2: Start the server program IP address of a machine to start a CORBA broker Port# the CORBA Broker is listing to start java TodayServer –ORBInitialPort 1050 –ORBInitialHost localhost IP address of a machine where the CORBA broker is running CORBA_2/059 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Execute the programs: Procedures Step3: Start the client program Port# the CORBA Broker is listing to java TodayClient –ORBInitialPort 1050 –ORBInitialHost <IP of the broker> IP address of a machine where the CORBA broker is running CORBA_2/060 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Execute the programs: Procedures (continued) CORBA Broker Today Server Today Client Request Reply CORBA/061 CS 547 Advanced Network Programming Execute the programs: Procedures (continued) Expected output: 18:01 July 9, 2002 Today Client CORBA/062 CORBA Broker Today Server CS 547 Advanced Network Programming CORBA Today Server and Client Overview (continued) Time Client CORBA program Time Client Time Server Current_Time(); 11:01:58 Current_Time(); ORB ORB IIOP IIOP TCP/IP TCP/IP Internet Data transfer “pass by value” CORBA/063 Time Server CORBA program