* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
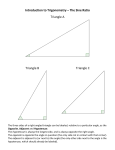
Download 2 - Angelfire
Abuse of notation wikipedia , lookup
Functional decomposition wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental theorem of calculus wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
SCHOOL CREED
•I have faith in myself
•I have faith in my teachers
•I will accept my duties and responsibilities
•I will respect others and seek their respect
•I have self respect
•I have self control
•I can learn if I study hard
•I will learn because I will study hard
•I love myself
•And loving myself
•I'll be myself
•And know myself`
•I am the one who is talking
•Balance
•Order
•Harmony
•Reciprocity
•Truth
•Justice
•Righteousness
•Look around you
•And behold us in our greatness
•Greatness is a Panther Possibility
•And you can make it yours!!!!!!!!!!!
Agenda for Mr. Hill’s class, room 705
Monday, June 1st, 2009
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Roll Check
Bell Ringer {Grade Monday’s, Return on Thursday}
Read Daily Bulletin {Period 2 only}
Reading 10 Minutes {Tuesday, Wednesday, Friday}
Code of Conduct
Help Desk update!
www.mrhillsclass.com
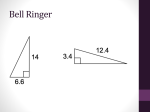
Today’s Bell Ringer
“Congratulations,
You are no longer maggots! You are now turds!”
You have graduated to Level 3, 4, 5 bell ringers!
1. In order to determine the measure of angle 6 in a regular
pentagon,
2. We use the formula; 180(n-2)/n
3. After substitution, we have; 180(5-2)/5
4. With simplification, we now have 180(3)/5 = 540/5 = 108o,
the measure of angle 6.
….and now, a word from our sponsor!
Hi Kids! My name is Minouche Jean.
Listen to everything that Mr. Hill says
and you are sure to be successful not
only in Mathematics, but also in life!
(Do Girl) ……. (Snitch) ………. (Goody Goody) ………………….
The Hill Cam
Death Penalty for
fighting in class!
Death Penalty for
Johnson!
What 9 weeks is this Turds!
Tough Love!
NEW RULE TURDS!
Tough Love!
-25 FOR NOT HAVING A
REFERENCE SHET WHEN
WE NEED A FORMULA!
If you can’t say it, ……
William Shakespeare
….. you can’t write it!
© FCAT Writes!
….and now, a word from our sponsor!
If you can perceive it,
you can ACHIEVE It!
Design by Ms. Kutrillion Wiley
….and now, a word from our sponsor!
Life got you down? Are you tired of
School? Tired of your stupid teachers?
Sick of your parents telling you what
to do? ….and don’t get me started on
the FCAT!!
Well, you don’t have to take it any more!
Quit school! Get a job making minimum
Wage! $1400.00 per month. Move out and
get an apartment for $600.00 per month
plus electric $175.00, cable $50.00, cell
phone $99.00, food $400.00 per month
clothes $150.00 per month, recreation
$200 per month. Oops! – ($274.00)!!
I know! I’ll get a second minimum wage job!! …………………………….
….and now, a word from our sponsor!
Life got you down? Are you tired of
School? Tired of your stupid teachers?
Sick of your parents telling you what
to do? ….and don’t get me started on
the FCAT!!
Well, you don’t have to take it any more!
Quit school! Get a job making minimum
Wage! $1400.00 per month. Move out and
get an apartment for $600.00 per month
plus electric $175.00, cable $50.00, cell
phone $99.00, food $400.00 per month
clothes $150.00 per month, recreation
$200 per month. Oops! – ($274.00)!!
I know! I’ll get a second minimum wage job!! …………………………….
….and now, a word from our sponsor!
Life got you down? Are you
tired of School? Tired of your
stupid teachers? Sick of your
parents telling you what to do?
….and don’t get me started on
the FCAT!!
Well, you don’t have to take it any more! Quit school! Get a job
making minimum Wage! $1400.00 per month. Move out and get an
apartment for $600.00 per month plus electric $175.00, cable $50.00,
cell phone $99.00, food $400.00 per month clothes $150.00 per
month, recreation $200 per month. Oops! – ($274.00)!!
I know! I’ll get a second minimum wage job!! …………………………….
….and now, a word from our sponsor!
ANNOUNCEMENT:
NOTEBOOK CHECKS BEGIN ON WEDNESDAY!
(1/23/09)
The most abused rules [-5 for each offense]
(-5)
(-5)
(-5)
(-5)
Differentiation Method
1.
1st Run – “Dog Eat Dog” KWL; What do you know now!
2.
2nd Run – Groups; Which questions are easy? Which are difficult?
Provide answers!
3.
3rd Run – Full Class: Assignment PowerPoint. This is a reading comprehension
activity. No Talking! Afterward: – QUESTIONS?
4.
4th Run – Student Presentations; 1 thru 10. The minute the presentations
cease or due to frequent interruptions, it’s time for the test!
….and now, a word from our sponsor!
Daily Participation is 25% of your grade!
Can you survive without 25% of your head?
….and now, a word from our sponsor!
ANNOUNCEMENT:
WE WILL NO LONGER HAVE TISSUE IN THIS
CLASS BECAUSE SOMEONE REMOVED IT FROM
MR HILL’S DESK AND DID NOT FEEL THE NEED
TO RETURN IT!
You work for me! I don’t work for you!
Bell Ringers
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the area of the above right triangle,
We use the formula A = bh/2.
Substituting the given values, we now have A = (4)(3)/2
After simplification, we have 12/2 or 6 inches2.
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the volume of the above right circular cone,
We use the formula V = pr2h/3.
Substituting the given values, we now have V = p(3)2 (6) /3.
After simplification, we have 54 p /3 = 18p inches2.
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the area of the above circle portion,
We use the formula pr2/2, since we see half of a circle.
Substituting the given values, we now have p(6)2/2
After simplification, we have 36p/2, or 18p inches2.
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the length of the above bar,
We must first align the end of the bar with zero on the ruler.
After doing so and by counting in 8th inch segments,
We observe a length of 2 1/8 inches.
180o – 44o = 136o
1. In order to find the measure of angle 8,
2. We must use the angle relationships formed with two
parallel lines and a transversal.
3. Since angles 1 and 3 are supplementary, angle 1 = 136o.
4. Since angles 1 and 8 are alternate exterior angles, angle
8 must also = 136o, since alternate exterior angles are
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the S. A. of the above rectangular solid,
We must use the formula, S.A. = 2(lw) + 2(hw) + 2(lh)
After substitution, we have S.A. = 2(12*6) + 2(2*6) + 2(12*2)
With Simplification, we have S.A. = 2(72) + 2(12) + 2(24) or
144 + 24 + 48 = 216 inches2.
1. In order to find the radius of the above right circular cylinder,
2. We must use the formula V = pr2h and work backwards, since
we are given the volume at the beginning.
3. After substitution, we have 628 = pr2(8)
4. With simplification, we have, 628 = 25.12r2. Dividing both sides
by 25.12, we now have r2 = 25, r = 5 inches
1. In order to find the slope of the line formed by points A & B,
2. We must use the “rise over run” method.
3. Counting straight up from point “A” to the height of point “B”
then, over to point “B”,
4. Gives us 8 over 6 or a slope of 8/6.
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the surface area of the above sphere,
We use the formula 4pr2.
Substituting the given values, we now have 4p(1)2.
After simplification, we have 4p or 12.56 inches2.
1.
2.
3.
4.
To find the probability of the spinner landing on an even #,
We use the “is over of” method. (4 is what % of 8?)
Since we have 4 even numbers and 8 total numbers,
Placing 4 over 8 as a fraction gives us 4/8 = 1/2 = .5 = 50%.
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the area of the above trapezoid,
We use the formula, A = h/2(b1 + b2)
Since b1 is 40, b2 is 20 and the height is 20, A = 20/2(40 + 20)
After simplification, we have, A = 10(60) = 600 feet2.
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the surface area of the above square pyramid,
We use the formula, S.A. = 2LJ + L2
After substitution, we have, S.A. = 2(5)(5) + (5)2
With simplification, we have, S.A. = 50 + 25 = 75 cm.2.
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the volume of the above square pyramid,
We use the formula, V = lwh/3
After substitution, we have V = (5)(5)(5)/3
With simplification, we have, V = 125/3 = 41.67 cm.3.
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the circumference of the above circle,
We use the formula, C = 2pr
After substitution, we have C = (2)(p)(1)
With simplification, we have, C = 2p or 6.28 inches.
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the area of the above parallelogram,
We use the formula, A = bh
Since the base is 5 and the height, 3, we now have A = (5)(3).
With simplification, we have A = 15 square feet
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the volume of the above right circular cylinder,
We use the formula, V = pr2h
After substitution, we have V = p(3)2(8)
With simplification, we now have 72p or 226.08 cubic inches
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the volume of the above sphere,
We use the formula, V = 4pr3/3
After substitution, we have V = 4p(1)3/3
With simplification, we now have 4p/3 or 4.19 cubic inches
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the volume of the above rectangular solid,
We use the formula, V = lwh
After substitution, we have V = (9)(12)(1)
With simplification, we now have V = 108 cubic inches.
Any radical multiplied by itself
equals the radicand!
Radicand = 2
1. In order to find the area of the above right triangle,
2. We use the formula, A = bh/2
3. After substitution, we have A = ( 2 )( 2 )/2
4. With simplification, we now have A = 2/2 or 1 square inch.
1. In order to determine how 3-4-5 “Special Right Triangle”
uses the Pythagorean Theorem,
2. We use the formula a2 + b2 = c2
3. After substitution, we have (3)2 + (4) 2 = (5) 2
4. With simplification, we now have 9 + 16 = 25,
or 25 = 25
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the distance traveled by the bus,
We use the formula, D = (Rate)(Time)
After substitution, we have D = (50)(3)
With simplification, we now have D = 150 miles.
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the midpoint of the two points above,
We use the formula, Midpoint = (x2 + x1)/2, (y2 + y1)/ 2
After substitution, Midpoint = (3 + 3)/2, (6 + 4)/ 2
Simplification gives us Midpoint = (6)/2, (10)/ 2 [or] (3, 5)
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the slope and the y-intercept of the equation,
We use the formula, y = mx + b
Since m represents slope and b represents the y-intercept,
After reverse substitution, ……………………………
we have m = -5, the slope and b = 7, the y-intercept.
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the simple interest charged above,
We use the formula, I = prt
After substitution, we have I = ($1000.00)(.08)(1 yr.)
With simplification, we now have I = $80.00
Method #1
Method #2
1. In order to find the distance between the above two points,
2. We use the formula, D =
3. After substitution, we have D =
4. With simplification, we now have D =
=
=
=
Indicates
Subtraction!
1. In order to find the difference of the two medians,
2. We observe the median in Class A to be 74 while the
median in Class B is 60. (The chart increases by two!)
3. After implementation, we have 74 – 60 = 14 points.
1. In order to find the upper quartile in the series of points above;
0, 2, 4, 5, 7, 8, 10,
2. We must locate the lowest, or the first number in the upper quartile
by finding the midpoint between the median & the highest number.
3. Adding 5 (Median) and 10 (highest) and dividing by 2 gives us 7.5,
the 1st number of the upper quartile.
3. Therefore, the numbers of the given series that are located after 7.5
are 8 and 10, the upper quartile in the series of points above.
1. In order to find the mean and median of the points scored
2. We must 1st determine the numbers indicated on the stem & leaf plot.
3. First, using the key provided, we determine the numbers to be;
21, 30, 33, 41 and 42. (We must see a 10’s and 1’s column!)
4. Next we add them, then divide by 5 to find the mean, then we
simply use observation to find the median, the middle number.
21
30
33
41
42
167
5 = 33.4, the Mean
1. In order to find the mean of the dollar amount on the stem & leaf plot.
2. We must 1st determine the numbers indicated on the plot.
3. First, using the key provided, we determine the numbers to be;
$210.00, $300.00, $330.00, $410.00 and $420.00.
(We must see a 10’s and 1’s column!)
4. Next we add them, then divide by 5 to find the mean.
$210.00
$300.00
$330.00
$410.00
$420.00
$1670.00
5 = $33.40, the Mean
1. In order to find the length of arc AB,
2. We use the formula 2pr/10, since 36o represents 1/10 of a circle
and both sections above are equal by def. of vertical angles.
3. Substituting the given values, we now have (1/10)[2p(5)]
4. After simplification, we have 10p/10, or 3.14 inches.
1. In order to find the area of the above circle portion,
2. We use the formula pr2/10, since 36o represents 1/10 of a circle
and both sections above are equal by def. of vertical angles.
3. Substituting the given values, we now have (1/10)[p(5)2]
4. After simplification, we have 25p/10, or 7.85 inches2.
1. In order to find the area of required glass above,
2. We use the formulas A = pr2/2, for the half circle plus
A = 4(L)(W) for the 4 squares.
3. Substituting the given values, we now have A = p(2)2/2
plus A = 4(2)(2)
4. After simplification, we have 2p plus 16 [or] 22.28 feet2.
1. In order to find the measure of angle UVW,
2. We use the formulas 180(n - 2)/n.
3. Since the figure represents a regular pentagon (5 sides)
with substitution, we now have 180(5 - 2)/5
4. After simplification, we have 540/5 = 108o, the measure
of all interior angles. Since UVW and UVR are
supplementary angles, subtracting 108o from 180o will
equal 72o, the measure of angle UVW.
1. In order to find the measure of angle BCD,
2. We use the theorem, opposite angles of parallelograms
are congruent.
3. Since the supplementary angle of angle A (interior) is 120o,
4. Subtracting 120o from 180o gives us 60o, the measure of angle
A (interior).
5. Since opposite angles of parallelograms are congruent,
angle C must also measure 60o.
(7.5 is the midpoint!)
1. In order to arrange the above set of numbers from smallest to greatest,
2. We must “Make the unfamiliar into the familiar” by converting to
radical form. Doing so, gives us ……….
3. Now that all numbers are in radical form, we are able to place them
in order, by the value of the radicands, since radical 63 is closer to
radical 64 than 7.5, the Midpoint. Therefore, we have ……
1. In order to find the area of the above special right triangle,
2. We use the formula, (b)(h)/2.
3. Since the 45-45-90 special right triangles are also isosceles,
substituting in the given values, we now have,
4. Since “any radical multiplied by itself equals the radicand”,
with simplification, we now have 2 or 1 square inch.
2
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the area of the above unit circle,
We use the formulas A = pr2,
Substituting the given values, we now have A = p(1)2.
After simplification, we have A = p [or] 3.14 units2.
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the circumference of the above unit circle,
We use the formulas C = 2pr,
Substituting the given values, we now have C = 2p(1).
After simplification, we have C = 2p [or] 6.28 units.
1. In order to find the area of the above circle portion,
2. We use the formula pr2 Since 72o represents 1/5 of a circle
4/5 of a circle represents the remaining portion.
3. Substituting the given values, we now have (4/5)[p(6)2]
4. After simplification, we have (4)36p/5, or 90.432 inches2.
1. In order to find the area of the above special right triangle,
2. We use the formula bh/2,
3. Since the above illustration is that of a 30-60-90
special right triangle, multiplying the short leg by
gives us,
or 6 square inches.
4. Substituting the given values gives us
or
=
1. In order to explain why a toss of seven is considered lucky,
2. We observe the various sums that naturally occur using
all combinations of the numbers 1 thru 6.
3. We observe, one; 2 & 12, two: 3 & 11, three: 4 & 10,
four: 5 & 9, five: 6 & 8 and six:7’s
4. Concluding that a toss of seven is not lucky, there are simply
more 7’s due to the properties of the numbers 1 thru 6.
45o
1. In order to find the height of the above figure,
2. We use the Pythagorean short cut for a 45-45-90 SRT.
3. Observing the left side of the figure only, we see a 45-45-90
special right triangle with a hypotenuse of
4. Using the reverse Pythagorean short-cut, dividing 6 radical 2
by radical 2 gives use 6, the length of each side.(height)
1. In order to find the distance between points “A” and “B”,
2. We connect both points with a line, inferring a right triangle.
3. When we observe the side measures, using the units on the grid,
we see a base of 6 units, a height of 8 units indicating a 6-8-10
special right triangle.
4. The hypotenuse of 10 units is the distance between “A” and “B”.
1. In order to find the shortest distance from home to 2nd base,
2. We draw a line of symmetry dividing the diamond into two
congruent 45-45-90 special right triangles.
3. Since all sides measure 90 feet, Using the Pythagorean
short-cut, we multiply either side by radical 2, giving us,
4.
or 127.28 feet
1. In order to find the area of the non-shaded region above,
2. We use the formula (L)(W) – pr2/2, since we see a shaded
½ circle within a square (2 ¼ circles).
3. Substituting the given values, we now have (15)(15) – p(10)2/2
4. After simplification, we have 225 - 50p = 225 – 157 = 68 units2.
1. In order to find the area of the shaded region above,
2. We use the formula [(L1)(W1) – (L2)(W2)]/4, since subtracting
the smaller square from the larger leaves 4 equal trapezoids.
3. Substituting the given values, we have [(10)(10) – (8)(8)]/4
4. After simplification, we have (100 – 64)/4 = 36/4 [or] 9 cm2.
1. In order to find the length of arc AB above,
2. We use the formula (2pr)/4, since the illustration is that of
a ¼ circle.
3. Substituting the given values, we now have [2p(7)]/4
*Count the spaces!
4. After simplification, we have 14p/4 = 43.96/4 [or] 10.99 units.
5
7
1
2
3
4
6
8
1. In order to find the area of the larger square above,
2. We use the formula (L)(W) and the method,
“count the equal parts”.
3. Observe; the smaller square has an area of 49 cm2, with 4 equal
triangles while the larger whole square contains 8 equal triangles.
4. Since 8 is twice 4, we multiply 49 by 2 giving us 98 cm2.
12 feet
6 feet
8 feet
1. In order to find the perimeter of the figure above,
2. We build a “ghost” triangle, forming a rectangle.
3. Using the top side to measure the bottom, we now have a right
triangle with a base of 8 feet, inferring a 6-8-10 SRT.
4. Using the left side to measure the unknown side, we now have
18 – 6 = 12 feet, giving us; 20 + 18 + 28 + 12 + 10 = 88 feet
1. In order to find the length of side AB,
2. We use the Pythagorean short-cut for a 3-4-5 SRT.
3. Counting the units in the frame, we observe a base of 3 units,
a height of 4 units and a hypotenuse of 5 units
4. Since side AB is also the hypotenuse, it also measures 5 units.
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the area of the above illustration,
We use the formula (L)(W) = 2pr2.
Substituting the given measures, we now have (8)(8) + p(4)2
After simplification, we have 64 + 16p or 64 + 50.24 = 114.24.
5 in.
45o
5 in.
45o
= 10 in.
45o
5 in.
1. In order to find the length of AB the above illustration,
2. We use the Pythagorean short-cut for a 45-45-90 SRT.
3. Since the hypotenuse of each 45-45-90 SRT also serves
as the sides of the inner square inferred by the illustration,
4. Using the Pythagorean short-cut for a 45-45-90 SRT once
again gives us side AB, the diagonal of the square and the
= 10 in.
hypotenuse of yet another 45-45-90 SRT.
1. In order to find the area of the above illustration,
2. We use the formula (L)(W) + pr2, since we see a square and
two half circles (1 whole circle)
3. With substitution, we now have, (8)(8) + p(4)2.
4. After simplification, we have 64 + 16p =
64 + 50.24 [or] 114.24 square inches
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the area of the above illustration,
We use the formula pr2/2, since we have only ½ circle.
Substituting the given measures, we now have p(4)2/2.
After simplification, we have 16p/2 = 8p or 25.12 cm2.
1.
In order to find the amount of baking soda required in a
32 ounce mixture.
2. We add the ratios to find a total of 16 parts.
3. Dividing the total 32 ounces by the 16 parts gives us
2 ounces per part.
4. Since baking soda is represented by 3 parts, multiplying
3 parts by 2 ounces gives us 6 ounces baking soda.
2
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the area of the shaded region above,
We use the formula pr2 – (L)(W).
Substituting the given measures, we now have p(1)2 – (
After simplification, we have, 3.14 – 2 = 1.14 units2.
)(
).
Reverse Pythagorean Short-cut
4 ft.
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the area of the shaded region above,
We use the formula A = (L)(W).
Substituting the given measures, we now have A = (
After simplification, we have 8 units2.
)(
).
pr2 = 3.14
r2 = 3.14
p
45
o
1
r2 = 3.14
3.14
2
r2 = 1
45o
r= 1
1. In order to find the area of the square in the circle above,
2. We use the formula A = pr2 and (L)(W).Working backwards,
we have…
3. Using the reverse Pythagorean short-cut, dividing 2 by
,
we now have 1.4142 in, the length of the sides of the square.
4. With substitution, we have A = (1.4142 )(1.4142 ) = 2 inches.
2 in.
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the area of the shaded region,
We use the formula A = (L)(W) – pr2.
With substitution, we have A = (2)(2) – p(1)2.
With simplification, we have A = 4 – 3.14 [or] .86 inches2.
1. In order to find the time required for this trip,
2. We use the formula d = (r)(t) [t = d/r] and we measure
the curved line with a flexible ruler!
3. Since the curved line measures 11.5 (inches) miles and the rate
of 60mph gives us = 1 mile per minute, we need 11.5 minutes.
12 miles
1.
2.
3.
4.
12 miles
12 miles
12 miles
In order to find the distance from point “A” to point “B”,
We must use the formula 2pr times 2, [or] 4pr. (2 circles)
With substitution, we have C = 4p(6).
With simplification, we now have C = 24p [or] 75.36 in2.
(Undefined)
Tan p/2 = Sin p/2
Cos p/2
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the length of side BC the above illustration,
We use the trigonometric ratio, Sin q = opposite/hypotenuse.
Substituting the given measures, we now have Sin 43o = x/2.
After simplification, we have .6820 = x/2, x = 1.36 inches.
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the length of side AC the above illustration,
We use the trigonometric ratio, Cosine q = adjacent/hypotenuse.
Substituting the given measures, we now have Cosine 43o = 3/x.
After simplification, we have .7314 = 3/x, x = 4.10 inches.
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the length of side AB the above illustration,
We use the trigonometric ratio, Tan q = opposite/adjacent.
Substituting the given measures, we now have Tan 43o = 4/x.
After simplification, we have .9325 = 4/x, x = 4.29 inches.
1. In order to find the length of the wire the above illustration,
2. We use the trigonometric ratio, Cosine q = adjacent/hypotenuse.
3. Substituting the given measures, we now have 40 ft. – 7 ft. = 33ft.,
the adjacent side. With q = 44o, we now have Cosine 44o = 33/x.
4. After simplification, we have .7193 = 33/x, x = 4.29 inches.
AC is a diagonal of
ABCD
Given
AB is parallel to DC
Definition of square
Angle 1
Def. of alternate interior angles
Angle 4
The square above has a length of
2 inches and a width of 2 inches
Given
Circle “C” has a diameter of 2 in.
and a radius of 1 inch.
Definition of diameter and radius
of a circle.
Area of a circle = pr2
Definition of area of a circle
Area of circle = p(1)2
Substitution
Area of circle = p
Multiplicative Identity Property
Line “A” is parallel to Line “B”
Given
Angle 2 measures 70o
Definition of supplementary Angles
Angle 7 measures 70o
Def. of alternate exterior angles
60O
30O
The above cone has a radius of
3 in. & a height of 2 radical 3.
Given
a2 +b2 = c2
Def. of Pythagorean Theorem.
(3)2 +(
f.
) 2 = c2
Substitution
9 + 27 = c2
Multiplication Property
36 = c2
Addition Property
6=c
f.
Definition of square root
f.
The probability of tossing a
6 or 8 is 5 out of 36
Properties of the numbers
1 thru 6
g.
The probability of tossing a
7 is 6 out of 36
Properties of the numbers
1 thru 6
The above die chart illustrates
the possibility of each die toss
The probability of tossing a
2 or 12 is 1 out of 36
The probability of tossing a
3 or 11 is 2 out of 36
The probability of tossing a
4 or 10 is 3 out of 36
The probability of tossing a
5 or 9 is 4 out of 36
Given
Properties of the numbers
1 thru 6
Properties of the numbers
1 thru 6
Properties of the numbers
1 thru 6
Properties of the numbers
1 thru 6
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
In order to find the measure of angle ABC,
We use the formula 180(n – 2)/n.
Substituting the given measures, 180(5 – 2)/5.
After simplification, we have 180(3)/5 = 540/5 = 108o.
Since angle ABC is supplementary to an interior angle
of the regular pentagon, subtracting 108o from 180o gives
us 72o, the measure of and ABC.
1. In order to find the cost (c) of manufacturing a specific
number (n) of units
2. We determine, by observation, that each unit on the horizontal
axis is a factor of it’s corresponding cost on the vertical axis
multiplied by 5 plus 1.
3. Therefore the formula is c = 5(n) + 1.
36o
6. Since a regular pentagon has
five equal sides, triangle ABC
is isosceles.
7. Since base angles of isosceles
triangles are congruent, angle BCA
must also measure 36o.
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the measure of angle ABC,
We use the formula 180(n – 2)/n.
Substituting the given measures, 180(5 – 2)/5.
After simplification, we have 180(3)/5 = 540/5 = 108o,
the measure of each interior angle.
5. Since Angle “A” is partially represented by a 72o angle,
the remaining portion above must equal 36o. (72o + 36o = 108o)
1. In order to find the measure of the angle represented at 5:00,
2. We must note, that the central angles of all circles total 360o
3. We must also note, that since there are 12 hours on the clock,
dividing 360 by 12 gives us 30o per hour.
4. Since 5:00 represents 5 hours, multiplying 5 by 30o gives us
150o, the angle measure represented at 5:00.
1. In order to find the length of side “AB”.
2. We would use the Pythagorean Short-cut for a 45-45-90 SRT,
[Angle Sum Theorem].
3. Since all 45-45-90 SRT’s are also isosceles, the height of the
above triangle also measures 6 inches.
4. Multiplying 6 in. by radical 2 gives us _____, the length of AB.
45o 45o
45o
45o
45o
45o
45o 45o
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the weight of the remaining portion …..
We would use the “Sum of the interior angles of a circle = 360o.
Since 360o – 315o = 45o, the slice measures 45o.
Since removing one 45oslice leaves seven 45oslices weighing
5 grams each, multiplying 5 x 7 gives us a remaining portion
of 35 grams.
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to determine the rate used in the chart above,
We use the formula d = (r)(t), and solve for r, giving us r = d/t
Substituting any given measure (360 miles), we have r = 360/6.
With simplification, we have r (rate) = 60 mph.
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to determine the data revealed in the chart above,
We must observe that the chart depicts an upward trend, score vs. % correct.
Also observing that a passing score of 300 will occur with only a 50%
success rate, we must conclude….
Relax! You only need to answer 50% of the questions on the F.C.A.T. correctly
in order to pass!
1. In order to determine the possible outcomes of a two coin toss,
2. We observe that there is only one possibility out of four for both
coins to land on heads. (HH)
3. Therefore, the mathematical expression for this is ¼.
1. In order to determine the possible outcomes of a two coin toss,
2. We observe that there is only one possibility out of eight for both
coins to land on heads. (HHH)
3. Therefore, the mathematical expression for this is 1/8.
108o
108o
108o
108o
108o
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the measure of angle ABC,
We use the formula 180(n – 2)/n.
Substituting the given measures, 180(5 – 2)/5.
After simplification, we have 180(3)/5 = 540/5 = 108o,
the measure of each interior angle.
5. Since angle ABC is vertical to an interior angle, it equals 108o.
5
6
1
3
7
2
4
8
1. In order to find the area of the shaded region,
2. We divide any 4ft. by 4ft. Square into 8 equal parts.
3. Since there are 4 equal triangles in the shaded region and 8 equal
triangles in the 4ft. by 4ft. section and 4 is ½ of 8,
4. Dividing 16 ft.2 by 2 gives us 8 ft2, the area of the shaded region.
4. Area of each right triangle = (4)(4)/2 = 8ft2.
5. Since there are 2 shaded right triangles, the
area of the shaded region = 2 x 8 = 16 ft2.
1. In order to find the area of the shaded region,
2. We divide the illustration into 8 equal parts.
3. Since each right triangle has a height of 4 and a base of 4,
using the formula for the area of a triangle, we have ……
4. 180(6)/8 = 1080/8 = 135o, the
measure of each interior angle.
5. Since angle ABC is supplementary
to an interior angle, subtracting 135o.
1. In order to find the measure of angle ABC,
2. We use the formula 180(n – 2)/n. [regular octagon].
3. Substituting the given measures, 180(8 – 2)/8.
1. In order to determine the possibility at least two coins landing on
heads,
2. We observe that there are four possibilities out of eight for two
or more coins to land on heads. (HHH), (HHT), (HTH), (THH)
3. Therefore, the mathematical expression for this is 4/8 [or] ½.
1. In order to determine the missing pattern in the sequence above,
2. We observe a 90o clock-wise rotation in the pattern above …
3. Therefore, the missing pattern is ……
72o
72o
72o
72o
36o 36o
4 ft.
1. In order to find the area of the above regular pentagon,
2. We use the formula (b)(h)/2 and Trigonometric ratios.
3. Since the illustration consists of 5 congruent triangles,
substituting the given values, we now have 5[(8)(5.5)/2]
4. With simplification, we now have 5[22] = 110 feet2.
5. With substitution, we now have .7265 = 4/x
6. With simplification, we now have .7265x = 4
7. After further simplification, we have x = 5.5,
the height of the triangle.
72o
72o
72o
72o
36o 36o
4 ft.
1.
2.
3.
4.
8. Substituting the determined value, we now
have A = (4)(5.5)/2, [or] 11 ft2.
9. Since the regular pentagon consists of 10
right triangles, 10(11) = 110 ft2, the total area.
In order to find the area of the above regular pentagon,
We use the formula (b)(h)/2 and Trigonometric ratios.
Since 360o/5 = 72o, the measure of each central angle = 72o.
Since the height of the outlined triangle is adjacent to a 36o
angle with an opposite side = to 4 ft, we use Tangent 36o = 4/x.
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
1. In order to find the area of the shaded region above,
2. We use the formula (L)(W) – 6pr2, since the
illustration is that of 6 circles within a rectangle.
3. After substitution, we now have, (36)(24) – 6p(6)2.
4. With simplification, we have 864 – 678.24 = 185.76 ft 2.
5. Since angle ABC is an exterior angle,
subtracting 120o from 180o gives us 60o,
the measure of angle ABC.
Shortcut; 360/6 = 60o.
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the measure of angle ABC,
We use the formula 180(n - 2)/n.
With substitution, we have 180(6 - 2)/6.
With simplification, we now have 180(4)/6 [or] 720/6 = 120o,
the measure of all interior angles of a regular hexagon.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1. In order to find the ratio of the shaded portion above to the
entire parallelogram,
2. We must observe that, “No matter how you slice it, a half
of a square is a half of a square”
3. Since we find 1 shaded half square out of 7 total halves, the
ratio of shaded portion to the total is 1 to 7.
1. In order to find the area of the above regular hexagon,
2. We use the formula (b)(h)/2 and Trigonometric ratios.
3. Since the illustration consists of 6 congruent triangles,
substituting the given values, we now have 6[(8)(
)/2]
4. With simplification, we now have 6[27.71] = 166.28 feet2.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
In order to find the area of the above illustration,
We must use a border to define a true image of the figure.
After observation, we see 4 quarter circles within a square
Subtracting the circle from the square gives us (L)(W) – pr2.
With substitution, we have (8)(8) – p(4)2.
With simplification, we have 64 – 50.24 = 13.76 ft2.
1. In order to find the incorrect choice,
2. We must observe that, “No matter how you slice it, a half
of a square is a half of a square.”
3. Since ½ + ½ = 1 whole, and A, B & C fit this format,
4. Choice “D” is incorrect since it depicts 3 halves, not 2.
12 mi.
12 mi.
12 mi.
12 mi.
1. In order to find the number of firefighters required to
man the diamond shaped area,
2. We must observe that, “No matter how you slice it, a half
of a square is a half of a square.”
3. Since each 72 square mile area contains 24 fire fighters,
multiplying 24 by 4 equals 96 miles2.
4. Multiplying 72 inches2 by 4
gives us 288 inches2, the area
of the unshaded region.
1. In order to find the area of the non-shaded region in the
above figure,
2. We must observe that, “No matter how you slice it, a half of
a square is a half of a square.”
3. Since the area of the rectangle in the legend is 72 inches2,
The area of each of the 4 congruent triangles in the unshaded
region is also 72 inches2.
4
6
2
2 2
3
2 2 3 = 12 days
1. In order to find the number of days that Fred will attend two
meetings, we must use Least Common Multiples (LCM).
2. Since the LCM of 4 and 6 is 12, every 12 days both groups
will overlap.
3. Therefore both groups will meet on the 12th and 24th day
out of 31 days.
NEED A VISUAL?
6
2
8
3 2
2
2
2 2 3 2 = 24
1. In order to find the number of minutes that will pass before
both lights will blink together, we must use Least Common
Multiples (LCM).
2. Since the LCM of 6 and 8 is 24, both lights will blink
together every 24 minutes.
NEED A VISUAL?
324
317
303
307
4
17
-7
14
3 = 4.667
1. In order to find the mean increase on the above bar graph,
2. We must read between the bars.
3. From 2003 to 2004 increase by (+ 4), 2004 to 2005 increases
by (+ 17), 2005 to 2006 decreases by (– 7).
4. Therefore the mean increase from 2003 to 2006 is 4.667
points.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
In order to find the conic cross-section which is not a result
of a conic cross-section,
We use Prior Knowledge & Observation.
Since an ellipse is formed when we cut a single cone at an angle,
An “X” is formed when we cut a double cone at an angle,
A parabola is formed when we cut a single cone at an angle,
The rectangle is the only image that is not the result of a conic
cross-section. It is used as the cutting tool!
Conic Cross-sections
1. In order to find the measure of angles in a triangle at a ratio of
1:2:6,
2. We add the ratios 1 + 2 + 6 to find 9 equal parts.
3. Since the angles of a triangles have a sum of 180o, dividing
180o by 9 gives us 20o per part.
4. Applying this formula to the ratio of 1:2:6 gives us
1(20o):2(20o):6(20o) [or] 20o + 40o + 120o, the measure of all
three angles of triangle ABC.
1. In order to find the perimeter of XYZA, we use the
Pythagorean Short-cut for a 30o-60o-90o SRT.
2. Since AZ measures 6 feet, doubling the short leg gives us
12 feet, the measure of WZ and XY.
3. Opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent, therefore
if WX = 18 feet, ZY also equals 18 feet.
4. Adding all sides give us 12 + 12 + 18 + 18 [or] 60 feet.
6 in.
1. In order to find the area of the shaded region above,
2. We use the formula A = (L)(W).
3. Since the length of the square edge is 6 inches and the width is
6 inches, the hypotenuse of the triangle formed must be
inches. (Also the width of the shaded region)
4. Substitution of the given values, we now have A = (9)(
)
=54
[or] 76.37 inches2.
1. In order to find the weight in cubic inches of the block of
cheese above,
2. We use the formula V = lwh.
3. Substituting the given values, we now have V = (6)(6)(6) = 216
cubic inches.
4. Since the block of cheese is made up of a ½ cube, dividing
216 by 2 gives 108 cubic inches. Since there is one ounce for
every 1.8 cubic inches, dividing 108 by 1.8 equals 60 oz.
3-4-5 Special Right Triangle!
1. In order to find the value of “x” in the illustration above,
2. We use the Pythagorean Theorem.
3. Substituting the given values, we now have;
(x+1)2 + (x+2)2 = (x+3)2 =
(x2 + 2x + 1) + (x2 + 4x + 4) = (x2 + 6x + 9)
4. After simplification, we have; 2x2 + 6x + 5 = x2 + 6x + 9,
then x2 = 4 [or] x = 2
(-x2) (-6x) (-5) (-x2) (-6x) (-5)
1. In order to find the angle measure represented at 7:00,
2. We divide the 360o in the clock by the 12 hours giving us
30o per hour.
3. Since 7:00 represents 7 hours, multiplying 30o by 7 gives
us 210o.
1. In order to find the angle measure represented at 10:00,
2. We divide the 360o in the clock by the 12 hours giving us
30o per hour.
3. Since 10:00 represents 10 hours, multiplying 30o by 10
gives us 300o.
1. In order to find the angle measure represented at 3:00,
2. We divide the 360o in the clock by the 12 hours giving us
30o per hour.
3. Since 3:00 represents 3 hours, multiplying 30o by 3 gives
us 90o.
1
1
2
1
1
2
1
2
1
1. In order to find the perimeter of the rectangle above,
2. We use the formula A = pr2.
3. Since 3.14 = pr2 indicates that each circle has a
radius of 1 and a diameter of 2,
4. Substitution using the given measures give us a rectangle
with a width of 6 units and a length of 2 units..
5. Therefore P = 2L + 2W [or] 2(2) + 2(6) = 4 + 12 = 16 units
…….…… 1
(1)2
Row 2 ………….
……… 4
(2)2
Row 3 …………..
……… 9
(3)2
Row 4 …….
2
……… 16 (4)
Row 1 ………………
1. In order to find the number of blocks required to construct
the base of the above pyramid, if we added an additional row,
2. We would use prior knowledge and observation, by noticing
a pattern in the number of blocks required for each row.
3. Since the number of blocks per row is the square of the row
number, the 5th row would require (5)2 [or] 25 blocks.
1. In order to find the area of the above regular octaagon,
2. We use the formula (b)(h)/2.
3. Since the illustration consists of 8 congruent triangles,
substituting the given values, we now have 8[(8)(9.66)/2]
4. After simplification, we now have 8(38.64) = 309.12 feet2.
+4
+2
+6?
+?
12
1
2
3
4
5
1. In order to determine the 4th number in the above sequence,
2. We must observe the numeric pattern either from number to
number, or box number to number within the box.
3. We multiply each box number by itself minus 1 [or] (n)(n-1).
4. After substitution, we have (4)(4-1) = (4)(3) = 12, the number
in the 4th box.
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the distance from Point “A” to Point “B”,
We use the formula C= 2pr.
Substitution, using the given values, we now have C= 2p(6)
With simplification, we now have C = 12p [or] 37.68 inches.
1.
2.
3.
4.
In order to find the distance from Point “A” to Point “B”,
We use the formula C= 2pr.
Substitution, using the given values, we now have C= 2p(6)
With simplification, we now have C = 12p [or] 37.68 inches.
4. Substitution, using the slant height,
we now have S. A. = p(3)(6) + p(3)2.
5. With simplification, we now have
S. A. = 18p + 9p = 27p [or] 84.78 in2.
6 inches
1. In order to find the surface area of the above right circular cone,
2. We use the formula S.A. = pr + pr2.
3. Since the illustration is that of a 30-60-90 Special Right
Triangle, application of the Pythagorean “Short-cut” gives
us a hypotenuse (slant height) of twice the short leg, or 6.
6-8-10 S.R.T.
10 ft.
6 ft.
8 ft.
14 ft.
1. In order to find the perimeter of the trapezoid above,
2. We use the Pythagorean Short-cut for a 6-8-10 SRT.
3. Since the base of the right triangle is 6 ft. with a height
of 8 ft., this infers a 6-8-10 special right triangle.
4. Since the unknown length of the hypotenuse of the SRT
is 12 feet, we now have Perimeter = 10 + 14 + 8 + 20 = 52 ft.
8 ft.
14 ft.
6 ft.
20 ft.
1. In order to find the area of the trapezoid above,
2. We use the Pythagorean Short-cut for a 6-8-10 SRT,
and the formula A = h(b1 + b2)/2
3. Substitution, using the formula, we now have A = 8(20 + 14)/2.
4. After simplification, we now have, A = 8(34)/2 [or] 136 ft2.
1. In order to determine the slope of BC, if the slope of AC = 3/5,
2. We must apply the rule, the product of the slopes of
perpendicular lines is equal to –1.
3. Since AB is perpendicular to AC, and AC has a slope of 3/5,
4. With substitution, we now have (x)(3/5) = –1, 3x = – 5.
Therefore x = – 5/3.
Describe a method, using Pascal’s Triangle, for determining
1. theInsum
order
sum
of+1,844,+10,
35, not
56, 84, 120,
of 1to+ determine
4 + 10 + 20the
+ 35
+ 56
120,20,
while
2. Using
We observe
thatorthis
number
sequence occurs in the 4th diagonal
a calculator
adding
manually.
from the right.
3. Since the sum of each diagonal appears to the lower right of the
final number, our sum is 330.
1. In order to determine the length of side AC,
2. We use the “reverse Pythagorean” short-cut for a 45-45-90 SRT.
3. Since AB represents the radius of a “unit” circle, it also measures
“1 unit”.
4. Using the reverse short cut, we divide the hypotenuse by radical
2 giving us,
=
or .7071.
12
25
36
2 2 3
5 5
2 2 3 3
2 x 2 x 3 x 5 x 5 x 3 = 900
1. In order to determine the Least Common Multiple of the
numbers above,
2. We may use a factor tree.
3. Matching all common factors with a counterpart, we have
4. Multiplying all common factors with the remaining unmatched
factors, we have, (2)(2)(3)(5)(5)(3) = 900.
1. In order to determine the length of side AB,
2. We use the Pythagorean” short-cut for a 45-45-90 SRT.
(All 45-45-90 Special Right Triangles are isosceles)
3. Since each equal side measures 1 unit, multiplying 1 by
gives us 1
, the measure of side AB.
1. In order to determine the measure of angle STU,
2. We must use the “Angle Sum Theorem”.
3. Since the sum of the angles of a triangle measure 180 degrees,
2x + 3x + 5x = 180o, 10x = 180 and x = 18o.
4. If x = 18, then 3x, the measure of angle RTS equals 54o. Since
angle RTS is supplementary to angle STU, subtracting 54 from
180o gives us 126o, the measure of angle STU.
1. In order to determine the coordinates for point “D”, if BC is
the median,
2. We must measure point D to be equidistant from point C, the
midpoint as is point A.
3. Since point A is located 7 units to the left of the median at
point (-7, 0), point D must be located 7 units to the right at
point (7, 0).
D
1. In order to determine the coordinates for point D, if BC is the
median of triangle ACD,
2. Using negative slope, (down 4, over 3) we calculate the
coordinate located at point “D” to be (14, 1).
1. In order to determine the number of square yards enclosed
in the curvilinear structure,
2. We use the estimation method.
3. 1st, we count the number of complete squares in the enclosure
(23), then estimate the number of complete squares that may be
formed by combining the incomplete squares. (approximately 8)
4. Therefore 23 + 8 = 31 complete squares.
4 in.
1. In order to find the volume of the above rectangular solid,
2. We use the formula V = (L)(W)(H).
3. Substitution, using the above dimensions, we now have
V = (8)(4)(8) = 256 cubic inches.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
In order to solve for x in the above expression,
We must use the distributive property.
Doing so, we now have
Squaring both sides we see,
After simplification, we have x2 + 5x = 36 [or] x2 + 5x –36 = 0
Factoring gives us (x + 9)(x – 4) = 0. Therefore x = – 9, 4
1. In order to determine the area of the circular conic cross section
above,
2. We use ratio and proportion.
3. Comparing the entire cone to the smaller cone inside, we have:
4. After cross-multiplication, we now have;
20
o
20o
1. In order to determine the measure of ECD,
2. We must use the “Angle Sum Theorem”.
3. Since triangle EBD contains a 90o and a 50o angle,
angle “E” must measure 40o. [Angle Sum Theorem]
4. When we now observe triangle ECD, we find angle E
measures 20o with angle D measuring 50o, a total of 70o,
therefore angle ECD must measure 110o. [Angle Sum Theorem]
C
10
4
8
5
2
B
3
D
6
1. In order to find the distance between points B and C,
2. We use the Pythagorean short-cut for a 3-4-5 S.R.T.
3. Since side BD is 6 and side CD is 8, side BC must be 10
5
4
1. In order to find the radius of the slice in the sphere above,
2. We use the definition of “radius of a sphere.”
3. Since the radius is defined as any segment originating at
the center of a sphere and extending to the outer surface,
we may extend a more convenient radii here…
4. Therefore, the value of “x” is 3. [3-4-5 Special Right Triangle]
1. In order to find the length of segment BC,
2. We use the Pythagorean short-cut for a 30o-60o-90o S.R.T.
3. Since the hypotenuse (AB), is twice the short leg, and the
hypotenuse measures 1 unit, [ definition of “radius”]
4. Dividing segment AB [1 unit] by 2 gives us ½, the measure of
segment BC.
4. After substitution, we now have
A=(
)(
) = 2 square units.
A = (L)(W)
1. In order to find the area of the above square with a unit circle,
2. We use the Pythagorean short-cut for a 45o-45o-90o S.R.T.
and the formula A = (L)(W).
3. Since the hypotenuse measures radical 2 times the measure of
either isosceles leg, multiplying 1 by radical 2 gives us radical
2, the measure of each side of the square.
A =pr2
10 in.
5. After substitution, we now have
A = p(10)2 [or] 100 p square inches,
the area of “Great Circle” “C”.
10 in.
1. In order to find the area of “Great Circle” “C”,
2. We use the formula A =pr2 and the Pythagorean short-cut for a
6-8-10 special right triangle.
3. Since the radius of the circle containing point “B” and segment
BC form a 6-8-10 S.R.T., the hypotenuse measures 10 inches.
4. By definition of radius, the radius of “Great Circle” “C”also
measures 10 inches.
1. In order to determine the length of side BC,
2. We use the Pythagorean short-cut for a 30o-60o-90o special
right triangle.
3. Since the hypotenuse (AB) of triangle ABC measures 1 unit,
(definition of radius) Side AC must measure ½ unit. Applying
the short-cut once more, we multiply ½ by radical 3 giving us
, the measure of side BC.
1. In order to determine the length of side AB,
2. We use the Reverse Pythagorean short-cut for a 45o-45o-90o
special right triangle.
3. Since the hypotenuse (AC) of triangle ABC measures 1 unit,
(definition of radius) side AB must measure
units.
4. After rationalization, we now have
(
)=
1. In order to determine the length of side AB,
2. We use the Reverse Pythagorean short-cut for a 45o-45o-90o
special right triangle.
3. Since the hypotenuse (AC) of triangle ABC measures 1 unit,
dividing 1by radical 2 gives us the length of both AB and BC.
4. Therefore;
*(
)=
(
)
( , )
45o
1. In order to determine the coordinates of point “A”,
2. We use the reverse Pythagorean short-cut for a 45o-45o-90o
special right triangle.
3. Since the hypotenuse measures 1 unit, dividing 1 by radical 2
gives us
=
=
, the x and y coordinate.
1. In order to determine the coordinates of point “A”,
2. We use the properties of the “unit circle”.
3. Since each radii of the unit circle measures one unit from
center “B”, and represents an “x” and “y” axis, point “A” is
located at coordinate (0, 1).
1. In order to determine the coordinates of point “A”,
2. We use reverse short-cut for a 45o-45o-90o S.R.T.
3. Since each radii of the unit circle measures one unit from
center “A”, and triangle ABC is a 45o-45o-90o S.R.T.,
dividing 1 by radical 2 gives us
*
=
, the
length of AC and BC.
4. Therefore the coordinates for point “B” are (
,
)
4. Finally, using the same short-cut
once again, and multiplying
½ by radical 3 gives us; ,
the length of AC. Therefore the
coordinates for point “B” are
(
, ½).
1. In order to determine the coordinates of point “B”,
2. We use reverse short-cut for a 30o-60o-90o S.R.T.
3. Since each radii of the unit circle measures one unit from
center “A”, and triangle ABC is a 30o-60o-90o S.R.T.,
dividing 1 by 2 gives us ½, the length of side BC.
4. Again, using the Pythagorean
short-cut for a 30o-60o-90o S.R.T.,
we multiply side AC by radical 3
giving us; the length of side BC.
5. Therefore, the coordinates for point
“B” are (½,
)
1. In order to determine the coordinates of point “B”,
2. We use reverse short-cut for a 30o-60o-90o S.R.T.
3. Since each radii of the unit circle measures one unit from
center “A”, and triangle ABC is a 30o-60o-90o S.R.T.,
dividing 1 by 2 gives us ½, the length of side AC.
54
2
M = 2916
M = 54
1. In order to determine the geometric mean of 18 and 162,
2. We use the formula; 18 = M
M 162
3. After cross-multiplication, we have;
4. Finding the square root of both sides, we have;
5. With simplification, we now have;
1. In order to determine the length of side AC, if AB is the
geometric mean of AD and AC,
2. We use the formula; X = M
M Y
3. After substitution, we have 25 = 125
125 Y
4. After cross-multiplication, we have; 25y = 15625 [or] y = 625.
D
1. In order to determine the length of side AC,
2. We use the Pythagorean short-cut for a 30o-60o-90o S.R.T.
3. Since triangle ABD is a 30o-60o-90o S.R.T., side AB =
(The long leg, AB is radical 3 times the short leg, BD)
4. Since triangle ABC is a 30o-60o-90o S.R.T., side AC =
(The hypotenuse, AC is double the short leg, AB)
1. In order to determine the length of side AB,
2. We use the Pythagorean short-cut for a 30o-60o-90o S.R.T.
3. Since triangle ABD is a 30o-60o-90o S.R.T., side AB =
(The long leg, AB s radical 3 times the short leg, BD)
1. In order to determine the length of side AD,
2. We use the Pythagorean short-cut for a 30o-60o-90o S.R.T.
3. Since triangle ABD is a 30o-60o-90o S.R.T., side AD = 12
(The hypotenuse AD is twice the short leg, BD)
5. Subtracting 6 from 18
gives us 12 in., the length of CD.
+ 12 in.
= 18 in.
1. In order to determine the length of side CD,
2. We use the Pythagorean short-cut for a 30o-60o-90o S.R.T.
3. Since triangle ABD is a 30o-60o-90o S.R.T., side AB =
(The long leg, AB is radical 3 times the short leg, BD)
4. Since triangle ABC is a 30o-60o-90o S.R.T., side BC = 18 in.
(The long leg, AB is radical 3 times the short leg, BD)
1. In order to determine the measure of angle 6 in a regular
pentagon,
2. We use the formula; 180(n-2)/n
3. After substitution, we have; 180(5-2)/5
4. With simplification, we now have 180(3)/5 = 540/5 = 108o,
the measure of angle 6.
#119
2.
5. After cross multiplication, we have;
6. Dividing both sides by .8660, we
now have, c = 2.
1. In order to determine the length of AB,
2. We use the “Law of Sines”.
3. Since angle “B” is given, substituting the given values,
we now have,
4. After simplification, we have;
STOP
Students - Please report to
Mr. Hill’s class in room 705
STOP