* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A View of Life
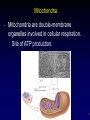
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Chapter 4 Organization and Regulation of Body Systems 1 Outline Today Finish Cell Respiration/Metabolism Chapter 3 and Start Chapter 4 (Tissue Types) Chapter 3 Metabolism Chapter 4 • Tissue Types – Epithelial – Connective – Muscular – Nervous 2 Mitochondria • Mitochondria are double-membrane organelles involved in cellular respiration. – Site of ATP production. 3 Cellular Metabolism • Cellular metabolism includes all the chemical reactions that occur in a cell. – Often organized into metabolic pathways. Most regulated by feedback inhibition. 4 Cellular Respiration • • Glucose breakdown requires three subpathways. – Glycolysis. – Citric Acid Cycle. – Electron Transport System. Altogether, the breakdown of one glucose molecule results in 36 ATP molecules. 5 Cellular Respiration 6 Fermentation • Fermentation is an anaerobic process that results in the buildup of lactate. – Lactate is toxic to cells and causes muscle cramps and fatigue. – Only produces two ATP per glucose molecule. 7 Types of Tissues • A tissue is composed of similarly specialized cells that perform a common function. – Categorized into four groups. Epithelial. Connective. Muscular. Nervous. 8 Epithelial Tissue • Epithelial tissue consists of tightly packed cells forming a continuous layer that serve in protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, and filtration. – Named according to shape of cell. Squamous - Flattened. Cuboidal - Cubed. Columnar - Column. 9 Epithelial Tissue 10 Junctions between Epithelial Cells • • • A tight junction forms an impermeable barrier as adjacent plasma membrane proteins join. A gap junction forms when two adjacent plasma membrane channels join. An adhesion junction forms when adjacent plasma membranes do not touch but are held together by intercellular filaments attached to cytoplasmic plaques. 11 Junctions Between Epithelial Cells 12 Connective Tissue • Connective tissue serves many functions including binding organs, providing support and protection, and producing red blood cells. – Three types of cells – Fibroblast, Macrophage and Mast cell – Separated by matrix of fibers. Collagen fibers. Reticular fibers. Elastic fibers. 13 Connective Tissue • • • Loose Fibrous and Dense Fibrous Tissues. – Loose fibrous connective tissue supports epithelium and many internal organs. – Dense fibrous connective tissue is made of tightly-packed collagen fibers and is found in tendons and ligaments. Adipose Tissue. – Fat storage. Reticular Connective Tissue. – Supporting meshwork of lymphatic system. 14 Connective Tissue • Cartilage. – Cells lie in lacunae separated by solid, flexible matrix. Hyaline cartilage. Elastic cartilage. Fibrocartilage. 15 Connective Tissue • Bone. – Most rigid connective tissue composed of matrix of inorganic salts. Compact bone. Spongy bone. Compact bone 16 Connective Tissue 17 Connective Tissue • Blood. – Matrix is made of plasma, not cells. Transports nutrients, oxygen, and wastes. Plasma. Formed Elements. Red blood cells. White blood cells. Platelets. 18 Blood 19 Muscular Tissue • Muscle (contractile) tissue composed of muscle fibers. – Contain actin filaments and myosin filaments. – Three types of muscle fibers. Skeletal muscle. Smooth muscle. Cardiac muscle. 20 21 Cardiac Tissue 22 Skeletal Tissue 23 Smooth tissue 24 Nervous Tissue • • • • • • Nervous tissue has three functions. Two Major cell types Neurons and Neuroglia Neurons are the functional cells – Sensory input. – Data integration. – Motor output. Neuron (nerve cell) composed of three parts. Dendrites. Cell body. Axon. Neuroglia service and support neurons. 25 Neuron and Neuroglia 26 Break Continue with Chapter 4 • • • • • Body Cavities Body Membranes Organ Systems Integumentary System Homeostasis 27 Body Cavities • • Ventral cavity divided into two parts. – Thoracic cavity. – Abdominal cavity. Dorsal cavity divided into two parts. – Cranial cavity. – Vertebral cavity. 28 Body Membranes • • • • Mucous membranes. – Line digestive, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems. Serous membranes. – Line thoracic and abdominal cavities. Synovial membranes. – Line freely movable joint cavities. Meninges. – Found in dorsal cavity protecting brain and spinal cord. 29 Organ Systems • Maintenance of the Body. – Digestive system. Receives and digests food. – Cardiovascular system. Transports nutrients and oxygen. – Lymphatic system. Collects and returns excess tissue fluid. 30 Organ Systems • Maintenance of the Body. – Respiratory system. Brings oxygen in and takes carbon dioxide out. – Urinary system. Rids body of nitrogenous wastes. 31 Organ Systems • Support and Movement. – Skeletal system. Protects body parts. – Muscular system. Moves body parts. 32 Organ Systems • Coordination and Regulation of Body Systems. – Nervous system. Conducts nerve impulses. – Endocrine system. Serves as messaging system maintaining homeostasis. 33 Organ Systems • Continuance of the Species. – Reproductive system. Provides ability to reproduce. 34 Integumentary System • The integumentary system is the collection of skin and its accessory organs. – Plays a significant role in maintaining homeostasis. Water Loss. Temperature. – Synthesizes certain chemicals. Vitamin D (helps with calcium absorption) 35 Integumentary System • Regions of Skin. – Epidermis. Stratified squamous epithelium. – Dermis. Collagen and elastic fibers. Lies beneath epidermis. Subcutaneous layer lies below the dermis and is composed of loose connective tissue and adipose tissue. 36 Accessory Organs of the Skin • • • Nails. Hair Follicles. – Oil Glands. Sweat Glands. 37 Human Skin Anatomy 38 Homeostasis • Homeostasis is the relative constancy of the body’s internal environment. – Fluctuation around a particular value. Maintained by negative feedback. Brings about reversal of the change. Activated by deviation from set point. Positive feedback brings about greater change in same direction. 39 The Integument and Homeostasis 40 Lecture Review • • • • • Be able to describe the four Major Tissue Types and give examples of where they are found in the body. – Epithelial – Connective – Muscular – Nervous List the Body Cavities and what organs are found in each. List the different types of Body Membranes List the eleven Organ Systems and give a general description and function of each. Describe the components of the Integumentary System 41