* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download From World War I to World War II
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
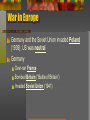
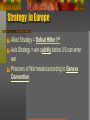
From World War I to World War II SOL: VUS.9b -12 U.S. involvement in World War I (VUS.9b) After the War Wilson wrote the Fourteen Points to eliminate causes of war, but France and Britain insisted on punishing Germany. The Treaty of Versailles resulted in the creation of new nations in Europe and also included a League of Nations, but the US Senate refused to approve it. The 1920s (VUS.10a) = Changes led to Conflict Popular Culture (radio, jazz, movies, and magazines) reflected the prosperity of the 1920s Conflict = traditional vs. modern values Scopes Trial: Religion v. Science Flappers: traditional v. modern roles for women Rise of KKK: open immigration v. nativism Prohibition: speakeasies v. respect for law Great Depression (VUS.b,c) Causes of Depression Overspeculation in the stock market Using borrowed money to buy stock Hawley Smoot Tariff and other high tariffs Failure of the Federal Reserve System Impact of Depression Unemployment (25%) and homelessness bank closings Labor unions became more violent Farm foreclosures and migration New Deal Made the government more active in economy Roosevelt: “We have nothing to fear, but fear itself.” Relief – help people directly (WPA). Recovery -- bring nation out of depression (AAA). Reform – fix unsound banking and investment practices (FDIC). Social Security Act offered safeguards for workers. World War II Allies (France, Great Britain & the Soviet Union) vs. Axis (Japan, Germany & Italy) War in Europe Germany and the Soviet Union invaded Poland (1939); US was neutral Germany Over-ran France Bombed Britain (“Battle of Britain”) Invaded Soviet Union (1941) US Involvement US helped Britain by Trading bases for destroyers Lend-Lease Act (“like a garden hose!”) War in Asia Japan invaded Manchuria and China (1930s) US imposed an embargo on the sale of oil and steel to Japan Japan bombed Pearl Harbor (12/7/1941) FDR said “a date which will live in infamy” US declared war on Japan Germany & Japan declared war on US Strategy in Europe Allied Strategy = Defeat Hitler 1st Axis Strategy = win quickly before US can enter war Prisoners of War treated according to Geneva Convention Turning Point Battles El Alamein – blocked Axis from Middle East oil Stalingrad – blocked Axis from Soviet oil Normandy – began liberation of Western Europe Strategy in Pacific Allied Strategy = island hopping; submarine warfare Axis Strategy = invade Philippines & Indonesia, head for Australia & Hawaii; hoped US would accept dominance Prisoners of War treated badly (Bataan Death March) Turning Point Battles: Midway – “Miracle”, destroyed Japanese navy Iwo Jima & Okinawa – close to Japan, high casualties Hiroshima & Nagasaki – use of atomic bomb Minority Involvement War in Europe Tuskegee Airmen (African American) Nisei Regiments (Japanese Americans) Mexican American soldiers not segregated War in Asia Navajo Code-talkers Holocaust Genocide: systematic and purposeful destruction of a racial, political, religious or cultural group Final Solution: Germany’s decision to exterminate all Jews; also affected Poles, Slavs, Gypsies, and undesirables Resulted in Nuremberg Trials – held Nazi leaders individually responsible for actions committed during war Increased demand for a Jewish homeland World War II at Home Government and industry worked together; businesses changed to wartime production Rationing, war bonds, income taxes and Selective Service (Draft) New Roles Women: served in non-combat roles in the military, worked in industry (Rosie the Riveter) New Roles African Americans: migrated to cities for jobs in war plants, Double-V Campaign New Roles Japanese Americans: sent to internment camps because of prejudice and fear of spies; Supreme Court upheld the internments Media and Communications Government censored war reporting Entertainment Industry (movies and plays) supported the war effort