* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download European TheaterA
Wehrmacht forces for the Ardennes Offensive wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Operation Torch wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Italian resistance movement wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Budapest wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Écouché in the Second World War wikipedia , lookup
Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
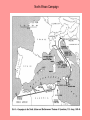
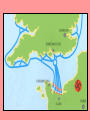
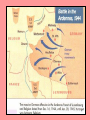
European Theater 6B, 6C, 9A I. Two Front War • Pacific Front • North African-European Front • FDR chose to focus on defeating Germany first II. Strategy • Stalin (USSR) needed a second front in Europe to take the pressure off his army. • FDR and Churchill chose to liberate North Africa first • Hitler’s success began to fade when the Soviets won the Battle of Stalingrad (Sept 1942- Feb 1943) A major turning point of the European Theater of WWII. Stalingrad North African Campaign III. North Africa Campaign • 1942, U.S. troops landed in North Africa • The inexperienced troops struggled when they fought veteran German troops, “Afrika Korps”, under General Erwin Rommel. • Eventually, US troops under Gen. George Patton combined with British troops to force a surrender on May 13, 1943. Sicily-Italy Campaign IV. Italy Campaign • After liberating Sicily( July 10, 1943- Aug 18, 1943), the Allied forces invaded Italy “Soft Underbelly” Mainland Italy was next. • Italian King/Generals placed Mussolini under arrest (July 25, 1943) and negotiated for surrender (Sept. 8, 1943) • Hitler angrily orders German troops into Northern Italy and puts Mussolini back into power (later, arrested and executed) • With bitter fighting & high casualties (over 300,000 Allied), the Allied Forces secure areas to use as airfields V. Strategic Bombing • RAF and Army AF significantly increased bombing of Germany • Destroy – Military installations – Industrial areas – Fuel and oil storage tanks – Railroad system – Morale of the German people VI. Invasion of Normandy (France) • Operation Overlord • Largest invasion in history • Combined forces of mostly U.S., Britain, and Canada • Problem: cross English Channel undetected, then rush the beaches & climb cliffs to secure the coast; paratroopers land behind enemy lines • June 6, 1944 “D-Day” • Quickly move eastward to liberate Paris Decoy bases • Inflatable jeeps, tanks • Wooden planes, structures • To fool the Germans into thinking the invasion would occur at Pas-de-Calais The Rubber Army! Rommel inspecting German defenses… Allied Commander of Operation Overlord, Gen. Dwight D. Eisenhower In Eisenhower’s pocket… “Our landings in the Cherbourge-Havre area have failed to gain a satisfactory foothold and I have withdrawn the troops. My decision to attack at this time and place was based upon the best information available. The troops, the air and the Navy did all that Bravery and devotion to duty could do. If any blame or fault attaches to the attempt it is mine alone.” American paratrooper loading into plane Order of the Day Soldiers, Sailors and Airmen of the Allied Expeditionary Force! You are about to embark upon the Great Crusade, toward which we have striven these many months. The eyes of the world are upon you. The hopes and prayers of liberty-loving people everywhere march with you. In company with our brave Allies and brothers-in-arms on other Fronts, you will bring about the destruction of the German war machine, the elimination of Nazi tyranny over the oppressed peoples of Europe, and security for ourselves in a free world. Your task will not be an easy one. Your enemy is well trained, well equipped and battle hardened. He will fight savagely. But this is the year 1944! Much has happened since the Nazi triumphs of 1940-41. The United Nations have inflicted upon the Germans great defeats, in open battle, man-to-man. Our air offensive has seriously reduced their strength in the air and their capacity to wage war on the ground. Our Home Fronts have given us an overwhelming superiority in weapons and munitions of war, and placed at our disposal great reserves of trained fighting men. The tide has turned! The free men of the world are marching together to Victory! I have full confidence in your courage and devotion to duty and skill in battle. We will accept nothing less than full Victory! Good luck! And let us beseech the blessing of Almighty God upon this great and noble undertaking. SIGNED: Dwight D. Eisenhower German POWs French citizens placing flowers on D-Day graves… Bedford Boys • 6 June 1944, the Soldiers of Company A, 1st Battalion, 116th Infantry Regiment, 29th Division were in the first wave of allied troops to hit Omaha Beach in Normandy. • 34 of the Soldiers assigned to Company A were from the small rural town of Bedford, Virginia • By day's end, 19 of these brave men died storming the beach • another 3 died in the days that followed • Alex Kershaw's The Bedford Boys" is a written memorial to these boys from Bedford and the people they left behind. Eastward toward Germany Unexpected delays due to hedgerows… Liberating Paris (Aug 25, 1944) VII. Battle of the Bulge (Dec 16, 1944- Jan 8, 1945) • Hitler’s last desperate offensive • Allied troops caught by surprise • As German troops raced west, their lines bulged outward… • Gen. Patton lead his U.S. tank divisions and troops to the rescue • US won after 3 weeks of fighting Refugees evacuate the Belgian town of Bastogne while American troops hold the town against the power thrusts by the Germans. The pathfinder unit of the 101st Airborne Division, dropped by parachute, sets up radar equipment near Bastogne to guide planes with medical supplies and ammunition to the division, besieged by the Germans. December 23, 1944. Infantrymen, attached to the 4th Armored Division, fire at German troops, in the American advance to relieve the pressure on surrounded airborne troops in Bastogne. December 27, 1944. VIII. Race to Berlin • Soviet troops came from the east • US troops came from the west • Hitler committed suicide on April 30, 1945 as Berlin fell to the Soviets • Unconditional surrender by Germany on May 7, 1945 V-E Day! Roosevelt died a few weeks before V-E Day… IX. Harry Truman became president upon FDR’s death Manhattan Project Albert Einstein Albert Einstein wrote a letter to FDR warning him of the type of destruction splitting the atom could have Robert Oppenheimer, left, was the director of the Manhattan Project The project to develop the first nuclear weapon (atomic bomb) Research convinced FDR to begin a program to build an atomic bomb Decision to drop the bomb Person making the decision whether or not to use the atomic bomb is U.S. President Harry Truman Truman became president after death of FDR Harry S. Truman Truman decides to drop the bomb because Japanese soldiers were fighting to the death and because Japan would not surrender Truman talks over plan to drop atomic bomb with his Secretary of War Henry Stimson WWII Europe Map Assignment • Complete a map of WWII Europe showing the following (page 642): Cities: London, Paris, Rome, Stalingrad & Berlin Regions: Normandy and North Africa Draw direction arrows: Soviet military westward to Berlin Invasion of Normandy Liberation of North Africa Invasion of Italy Allied military eastward to Berlin Include major battles on your map I. Two Front War Turned into exactly what Hitler did NOT want. Since fighting a two front war in World War I had split Germany's forces, I t had weakened and undermined their offensive; thus, played a large role in Germany losing the First World War. Hitler was determined not to repeat the same mistakes. So, he planned ahead and made a pact with the Soviets - the Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact. II. Strategy But then Hilter broke the non-agression pact and invaded June 22, 1941 Soviets join the Allies FDR and Churchill chose to liberate N. Africa first Hitler’s success began to fade when soviets won battle of Stalingrad turning point Modern warfare – part of game you are sniper…based on battle of Stalingrad The capture of Stalingrad was important to Hitler for a few reasons --was center of manufacturing --center of communication for the south --city bore the name of his enemy Joseph Stalin --would be psychologically damaging Soviets refused to let Stalingrad fall b/c it bore leaders name -Germany had about 9/10 of the city but --winter hit --USSR launched counter attack --Hitler suffered stunning defeat early 1943 Turning point for war in Europe III. North Africa Campaign (left, Patton) Roosevelt decides to invade Morocco & Algeria for 2 reasons 1. Give army experience w/o requiring a lot of troops 2. Be able to help British troops fight Germans in Egypt Suez Canal -Egypt was important b/c of the Suez Canal -Britain’s empire (India, Hong Kong, Singapore, Malaya, Australia) used the canal to send supplies to Britain German forces in the area -known as Afrika Korps—commanded by General Erwin Rommel-brilliant leader aka Desert Fox (Hitlers) November 8 1942 -American invasion of North Africa began under the command of General Dwight D. Eisenhower -American troops struggled after they advanced into the mountains of western Tunisia -This is where they had to fight the German Army for the first time and they did not do well -Eisenhower fired the general who led the attack (at the battle of Kasserine Pass) & put Patton in command -With British support we pushed the Germans back. -May 13, 1943 last German forces in N Africa surrendered Churchill called Italy the “soft underbelly” of Europe & was convinced that the Italians would quit the war if the Allies invaded their homeland Guy on the right= Desert Fox – turns back on Hitler b/c realizes cant fight til the last bullet - - nat a crazy kill the jews guy but a military man. Died…no war crimes .IV. Italy Campaign At the Casablanca Conference FDR and Churchill decide to go for Italy After liberating Sicily forces head to the mainland Italian King… -attack on Sicily created a crisis within the Italian govt. -King of Italy Victor Emmanuel & a group of Italian generals decided that it was time to get rid of Mussolini -king invited the dictator to his palace…told him” My dear Duce, it’s no longer any good. Italy has gone to bits. The soldiers don’t want to fight anymore. At this moment, you are the most hated man in Italy” -king then placed Mussolini under arrest, and the new Italian gaovt. Began secretly negotiating w/ the allies for Italy’s surrender. -Hitler was not about to lose Italy to the allies so sends in tropps. -seized control of northern Italy, attacked Americans at Salerno and put Mussolini back in power. With bitter fighting… -Italian campaign was one of the bloodiest in the war -costing Allies more thank 300,000 casualties -but were able to secure some areas for airfields - - - Mussolini hung upside sown and wife – see bulliet in wifes head - - mussolini overthrown - - Hitler comes in & puts him back in power - - ppl had enough and take over - - - ppl see 6th army coming … hang him V. Strategic Bombing RAF= Royal Air Force -ok, think back…the attack on North Africa in November of 42 was the first large allied invasion of the war…. This showed that the Allies could mount large-scale invasions from the sea -FDR and Churchill met in Casablanca, Morocco in January of 43 known as Casablanca Conference Agreed to increase the bombing of Germany and when they decided to take on Italy (remember) Bombing did not really destroy Germany’s economy or undermine German morale but it DID cause a severe oil shortage & wrecked the railroad system Also destroyed so many aircraft factories that Germany’s air force could not replace its combat losses…so by the time troops landed in France allies had total control of the air, ensuring that their troops would not be bombed VI. Invasion of Normandy (France) Knowing that the Allies would eventually invade France, Hitler had fortified the coast. -these defenses were formidable (discouraged attack) -allies had one advantage –surprise -Germans did not know when or where the Allies would land. -Believed that Allies would land in Pas-de Calais (pa- de-ka-la) –the area of France closest to Britain DDAY ( date of deployment) 1st time have paratroopers come down behind enemy lings. Dummy parachutes and fake bases -Eisenhower’s planning staff referred to the day any operation began by the letter D…known as D day -a month later to July 20, 1944 –Valkerie • • • Map on Left is where Germans thought they would go Map on right is normandy Pa-de-ka-la Decoy bases To convince Germans they were right, Allies placed inflated rubber tanks, empty tents, and dummy landing craft along the coast across from Calais. -To German spy planes, decoys looked real -succeeded in fooling Germans -Patton had made himself available for the role by becoming a public relations liability during his brilliant campaign to invade Sicily in 1943. -Patton slapped soldier in hospital -The resulting firestorm in the press led to Patton’s being relieved of command. So instead of commanding troops on campaign in Italy, Patton was ordered to participate in a series of junkets around the Mediterranean, making speeches, inspecting facilities, and having his picture taken…and eventually put in charge of the decoy • ROMMEL inspeecting German defences - - - so during high-tide couldn’t see them; - keep bots from coming up the beach..pic is during low tide In Eisenhower’s pocket… This is what he had in his pocket should they not susceed Order of the Day This is what was read to our boys on the way over • • nearly 7,000 ships carrying more than 100,000 soldiers set sail for the coast of Normandy on June 6, 1944 -at same time 23,000 paratroopers were dropped inland, east and west of the beaches • With his cameras held high to keep them from getting waterlogged, Capa was pulled aboard the LCI and was soon out of harm's way. He had used three rolls of film and exposed 106 frames. After reaching England, he sped by train to London and delivered his precious film for developing. Bedford Boys he boys of Bedford were largely farmers who joined the National Guard during the Depression to earn an extra dollar a week to help feed their families. -stationed in England for a year before seeing combat for the first time on Omaha Beach -the boys land on Omaha beach. Kershaw talks about the overall battle enough to explain the extent of the carnage - for example, weather prohibited air and sea support that could have taken out German machine gun nests and made craters on the beach for Allied soldiers to take cover in; the decision to invade anyway probably killed many Allied soldiers. The boys die quickly, often within minutes of landing, and Kershaw describes the gore in detail without being gratuitous. Eastward toward Germany • mounds of earth to keep cattle in and to mark boundaries. Typically there was only one entry into the small field enclosed by the hedgerows, which were irregular in length as well as height and set at odd angles. On the sunken roads the brush often met overhead, giving the GIs a feeling of being trapped in a leafy tunnel. Wherever they looked the view was blocked by walls of vegetation. • Undertaking an offensive in the hedgerows was risky, costly, time-consuming, fraught with frustration. It was like fighting in a maze. Platoons found themselves completely lost a few minutes after launching an attack. VII. Battle of the Bulge (Dec 16, 1944- Jan 8, 1945) As Allies closed in on Germany, Hitler decided to stage one last desperate offensive. -goal was to cut off allied supplies coming through the port of Antwerp, Belgium -Dec. 16, 1944 Called Battle of the Bulge b/c: as German troops raced west, their lines bulged outward -Part of the German plan called for the capture of the town of Bastogne, where several important roads converged -American reinforcements raced to the town, arriving just ahead of the Germans -Germans surrounded the town & demanded that the Americans surrender….American commander sent back a one-word response “NUTS” -Eisenhower ordered General Patton to rescue them -in the middle of a snowstorm Patton’s troops slammed into the German lines. -As weather cleared, Allied aircraft began hitting German fuel depots. -X-mas eve out of fuel and weak from losses Germans forced to halt -2days laters Patton’s troops broke through to Bastogne -Fighting did cont. for 3 weeks, U.S. won the Battle of the Bulge -January 8, Germans began to w/draw • • • As Allies closed in on Germany, Hitler decided to stage one last desperate offensive. -goal was to cut off allied supplies coming throught the port of Antwerp, Belgium -Dec. 16, 1944 VIII. Race to Berlin As Soviets crossed Germany’s eastern border, American forces attacked Germany’s western border -by the end of February 1945, American troops had fought their way to the Rhine River, Germanys last major line of defense in the west. March 7, American soldiers captured the heights above the the town of Remagen. -Gazing down at the town, platoon leader Emmet. J. Burrows was amazed that the Ludendorf Bridge across the Rhine was still intact -Germans had not blownit up -amercan troops raced across the bridge driving back German defenders -American troops raced east close to Berlin -April 16, Soviet troops smashed through the German defenses on the Oder River -In his bunker, Hitler knew the end was near and on the 30 th of April, he put a pistol in his mouth and pulled the trigger -His secretary, Martin Bormann, carried Hitler’s body outside, doused it in gasoline, and set it on fire Hiter named Grand Admiral Karl Doenitz his successor -Doenitz tried to surrender to the Americans and British while continuing to fight the Soviets, but Eisenhower insisted on unconditional surrender -on May 7, 1945, Germany surrendered unconditionally. -the next day-May 8, 1945-was proclaimed V-E Day for Victory in Europe