* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WWII Chapter 13 Notes
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
German occupation of Czechoslovakia wikipedia , lookup
Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Anglo-German Naval Agreement wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
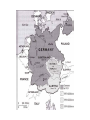
WWII Appeasement In what way did the Treaty of Versailles establish conditions that led to the outbreak of WWII? • A. It called for dissolving the League of Nations, thus removing an organization for resolving future conflicts • B. It gave Germany too much power by letting Germany keep the Alsace-Lorraine region of France • C. It weakened the Allied countries by making France, England and Russia reduce the size of their armies • D. It imposed harsh reparations payments on Germany, which led to economic and political instability Leaders in Power • Great Britain- Neville Chamberlain • France- Edouard Daladier • Soviet Union- Joseph Stalin – Communist • Italy- Benito Mussolini – Fascist • Germany- Adolph Hitler – Fascist Germany • National Socialist German Worker’s Party – Nazi Party – Fascism: extreme nationalism with racism – Wanted Germany to expand and NOT abide by the Treaty of Versailles • Adolph Hilter – – – – writes Mein Kampf (“My Struggle”) by 1932 the Nazi Party takes control of the Reichstag 1933 Hitler is appointed Chancellor 1934 Hitler becomes president • Der Fuhrer Italy • In 1919 Benito Mussolini founded the Fascist Party in Italy – exploited Italians fear of communism • Fascist militia- Blackshirts – threatened to march on Rome – cabinet resigns and king appoints Mussolini premier – quickly sets up a dictatorship – ll Duce- “The Leader” • In 1936 Hitler and Mussolini form the BerlinRome Axis Japan • Economic problems • Believed Japan was destined to dominate East Asia • In September 1931 Japan invaded Manchuria • Japanese prime minister was assassinated when he tried to stop the war • Led by Emperor Hirohito and General Hideki Tojo (Prime Minister 1941-1944) United States • President Franklin D. Roosevelt (FDR) • Democracy • Want to remain neutral at first Soviet Union • Vladimir Lenin led the Communist Party After the Russian Revolution • In 1922 Russian territories become the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) • Lenin died in 1924 and power struggle began between Leon Trotsky and Joseph Stalin – By 1926 Stalin is the new dictator • Began Five-Year Plans to industrialize • Family farms were turned into collectivesgovernment owned farms • Between 1932-1933 10 million peasants died • Stalin targeted political enemies, artists, intellectuals – used concentration camps (Gulags) in the Arctic – between 8-10 million people died by 1953 France • Edouard Daladier- Prime Minister at the beginning of the war • Replaced in 1940 by Paul Reynaud • Charles DeGualle led the “Free French” forces – Becomes leader after the war Great Britain • Neville Chamberlain is Prime Minister at the beginning of the war • Winston Churchill becomes Prime Minister in 1940 Exit Slip • Which nations did dictators govern in the years after WWI? Answer • Italy • USSR • Germany Which would be the most credible primary source about conditions in Nazi concentration camps during the Holocaust? • A. a novel set in a concentration camp • B. an account of camp life by a survivor of a concentration camp • C. a 1942 movie produced by the German government depicting concentration camp activities • D. a film about the camps directed by a person whose parents were in a concentration camp Starter • What type of government considered the nation more important than the individual? – – – – A. dictatorship B. monarchy C. fascism D. democracy Dr. Seuss Political Cartoon Appeasement • Accepting demands in order to avoid conflict Rhineland • Hitler invaded on March 9, 1936 • Treaty of Versailles had banned the German military from the region • German military was not prepared for a fight • France and Great Britain did nothing • 1936 Hitler and Mussolini formed an Berlin-Rome Axis Austria • March 1938 Hitler annexed Austria • Britain and France only protested Sudetenland • Was part of Germany • After WWII it became part of Czechoslovakia • Hitler decides he wants the territory back because of large German population • Sudeten-German Party is formed in 1935 First Meeting • In September of 1938 Neville Chamberlain met with Hitler • Hitler threatened to invade Czechoslovakia unless Britain supported Hitler’s plan to take over the Sudetenland • Chamberlain would not accept the plan Munich Conference • September 29, 1938 • Attended by Great Britain, France, Germany, and Italy • Chamberlain and Daladier agree to Hitler’s plan to prevent war • October 29, 1938 the German Army enters Czechoslovakia Appeasement • Policy of British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain • Thought by agreeing to the demands of Hitler and Mussolini he could avoid another war • Appeasement would end by 1939 when Hitler invades the rest of Czechoslovakia Poland • On March 31, 1939 Great Britain and France pledged to support Poland • Hitler signed a treaty with the Soviet Union • No longer had to worry about the Soviets • Invaded Poland on September 1, 1939 • Two days later Great Britain and France declared war on Germany Exit Slip • How did events after WWI lead to dictatorships? Answer • Many nations were dissatisfied with the Treaty of Versailles, and a worldwide financial depression made people desperate. Starter • Which factor encouraged an American policy of neutrality during the 1930s? – A. disillusionment with WWI and its results – B. decline in the military readiness of other nations – C. repeal of prohibition – D. economic prosperity of the time period Nazi-Soviet Pact • Aug 23, 1939: Nazi-Soviet Non-aggression Pact – -Hitler and Stalin agree that if Hitler invades Poland they will split it half • Germany takes the Western half • Soviet Union takes the Eastern half Blitzkrieg • Military tactic • “Lightning War” • Use tanks, artillery, and soldiers moving by truck and quickly taking Poland • Poland collapses in a month • War stalls for a period— “Phony War” Continued Attacks • April 9, 1940 Hitler attacks Denmark and Norway • May 10, 1940 Hitler attacks Belgium, Netherlands, and France • June 14, 1940 Germans reached Paris and France surrendered • In 3 months Hitler conquered most of Western Europe Vichy Government in France • Puppet government set up by Germany in the town of Vichy • Marshal Philippe Petain is the leader • Officially neutral in the war, but helped the Nazis • U.S. recognized the Vichy government • Charles de Gualle led the Free French forces from England and the colony of Algiers • Worked with Allies to free France Battle of Britain • 1,000 planes a day attacked Britain • Royal Air Force (RAF) kept them away • December 1940 Germany began bombing London and started 1,500 fires – “Never in the field of human conflict was so much owed by so many to so few”- Churchill • Attacks ended in 1941 • 20,000 had been killed and 73,000 injured Starter • What did Hitler call Germany’s quick air strikes? – – – – A. Blitzkrieg B. Kristallnacht C. Anchluss D. gestapo American Response- Isolationism Isolationism • A national policy of avoiding involvement in world affairs Neutrality Acts • Americans were disillusioned by WWI • Many thought the U.S. had enough of its own problems • From 1935-1939 Congress passes a series of Neutrality Acts – U.S. would withhold weapons and loans from all nations at war – All nonmilitary goods sold to them had to be transported by them • “Cash and Carry” Policy Neutrality Act of 1939 • Allowed France and Great Britain to buy weapons from the U.S. on a cash-and-carry basis • Later allowed them to be transported on U.S. merchant ships Involvement Grows • September 1940 FDR traded 50 destroyers to Britain for the ability to build permanent bases on British territory • Selective Service Act (1940)- required all males 21-36 to register for the draft Lend-Lease Act • March 1941 • Allowed the president to aid any country or nation whose defense was vital to America’s security • “Great arsenal of democracy” Atlantic Charter • Aug. 1941 • Churchill and Roosevelt • Agreement that committed both to a postwar world of democracy, nonaggression, free trade, economic advancement, and freedom of the seas • Roosevelt developed a “shoot-on-sight” policy toward German submarines • by the end of 1941 several U.S. destroyers had been fired upon – the Reuben James sank, killing 115 Exit Slip • Why did many American support isolationism? Answer • They felt that remaining apart from European conflicts would avoid another war. Starter • With which country did Germany sign a non-aggression pact? – – – – A. Czechoslovakia B. Austria C. Soviet Union D. All of the above War in Europe Why did Britain and France declare war on Germany in 1939? • A. The German army invaded Poland • B. Germany violated the Versailles Treaty • C. Hitler broke his agreement not to take over the Sudentenland • D. The Lend-Lease Act supplied Britain with ships and supplies Battle of Stalingrad • June 1942 Germans began advancing into the Soviet Union – Scorched earth policy as they retreated • September 1942 Germans began bombing the city – Lasted 2 months – Jan 31, 1943 Germans surrendered – Winter was too hard on Germany • Lost 330,000 troops • Turning point of the war in the east D-Day • • • • • June 6, 1944 Largest landing by sea 4,600 invasion craft and warships deployed 1,000 bombers went ahead 23,000 British and American soldiers were dropped in behind • 150,000 troops came on shore along 60 miles of Normandy coast • Omaha Beach- allies had 2,000 casualties • Within a week 500,000 men came ashore • By the end of July there were 2 million Allied troops in France Battle of the Bulge • Late August 1944 American troops liberated Paris • Britain and Canada freed Belgium • By September Allies attacked Holland and crossed the western border of Germany • Germans launched a counter-attack in Belgium and Luxembourg in Dec. 1944 – Battle of the Bulge • Largest battle in Western Europe in WWII • Involved 600,000 American GIs – 80,000 were killed, wounded or captured • Germans lost 100,000 • Germans knew the war was lost North Africa • October 1935 Italy invades Ethiopia • Beginning in August 1940 Great Britain, Italy, and Germany were fighting in North Africa • November 1942 Great Britain won at El Alamein in Egypt • British and U.S. troops land in Morocco and Algeria • May 1943 Germans are forced to surrender when allies reach Tunisia Casablanca Conference • Churchill and Roosevelt meet in January 1943 • Plan for the rest of the war • Decide to focus on Europe then the Pacific • Will only accept unconditional surrender of Germany, Italy, and Japan Italy • • • • • • • July 1943 American attack Sicily Take it in 38 days Mussolini is overthrown By September new government surrenders German troops in Italy continue to fight Battle of Anzio- Allies capture Rome April 1945 German troops in Italy surrender Berlin • By 1944 British and American forces began conducting air raids in Germany to prepare for invasion • Soviets fought into Berlin in April 1945 • April 25, 1945 Americans and Soviets meet on the Elbe River V-E Day • May 1 Hitler commits suicide • May 8, 1945 Germany surrenders • Yalta Conference: February 1945 Roosevelt, Stalin, and Churchill meet at Yalta in S.U. – Agree to split Germany into 4 zones & split Berlin – Stalin promised to allow elections in nations the Soviets had liberated from Germany – Also promised to enter war in the Pacific Yalta Conference Division of Germany War in the Pacific What did Hitler call Germany’s quick air strikes? • A. Blitzkrieg • B. Kristallnacht • C. Anschluss • D. Gestapo Japan • Japan wanted and needed raw materials and land for growing population • 1931 Japan attacked Manchuria (northern China) • 1937 Japan increased attacks against China • By 1940 Japan controlled most of eastern China • Began attacks on Southeast Asia and the Dutch East Indies • July 1940: Congress gave FDR the power to limit the sale of strategic materials – airplane fuel, scrap iron • September 1940 Japan joined the Axis powers American Response • 1938 -FDR begins building up the Navy in the Pacific • 1939 - moved the Pacific fleet to Pearl Harbor from San Diego Pearl Harbor • 1941 Japan took control of French colonies in Indochina – FDR froze Japanese assets in the U.S. and cut off trade • Oct. 1941 Gen. Hideki Tojo became Prime Minister • U.S. warned them against taking more territory and demanded they move out of conquered land and pact with axis Pearl Harbor • December 7, 1941Japan attacked with 180 planes • Lasted 2 hours • 2,400 Americans were killed • 1,800 wounded • 188 planes destroyed • 18 ships sunk • U.S. was finally forced to enter the war Germany Declares War • On December 11, Germany and Italy declare war on the U.S. Fall of the Philippines • A few hours after Pearl Harbor the Japanese attacked American airfields in the Philippines • U.S. is forced to retreat Starter • In a dictatorship, power is most likely acquired through – – – – A. a free election B. military force C. presidential appointment D. an inherited position Bataan Death March • May 6, 1942 Americans and Filipinos surrender on the Bataan Peninsula • 78,000 became prisoners of war • Japanese marched them for 6-12 days to the railroad to be taken to prison camps • 10,000 died on the way • America didn’t know until 3 years later when prisoners escaped Doolittle Raid on Tokyo • April 18, 1942 • B-25 bombers bombed Japan for the first time • B-25s could attack from farther away but could not land on the aircraft carriers • would have to land in China The Battle of the Coral Sea • March 1942: U.S. decoded messages about Japan’s plans to attack New Guinea • Carriers Yorktown and Lexington intercepted the Japanese and prevented the attack • Kept supply lines to Australia open Battle of Midway • June 4, 1942 • Japanese hoped to destroy the rest of the Pacific fleet by engaging in battle at Midway (island northwest of Hawaii) • American planes found them while they were loading bombs • Japan lost 4 carriers and 250 planes – Crippled the Japanese navy Island-Hopping in the Pacific • In order to defeat Japan the U.S. began “hopping” from one island to the next to get closer to Japan • Also, take the Soloman Islands, New Guinea, and the Philippines • Many died because soldiers were forced to wade ashore because the water was too shallow for ships Iwo Jima • Island 700 miles from Japan • November 1944 Americans began bombing Tokyo • Over 74 days Americans dropped 7,000 tons of bombs & 20,000 shells • February 19, 1945 Marines landed on beaches • Took a month to capture the island • 25,000 casualties Firebombing • U.S. began dropping bombs filled with napalm – designed to explode and start fires • Killed more than 80,000 people • by the end of June 1945 much of Japan’s largest cities had been destroyed Okinawa • April to June 1945 • 350 miles from Japan- much closer than Iwo Jima • Suffered 50,000 casualties – 12,000 died • Left Japan open for attack Starter • Japanese suicide pilots were known as _____ pilots. – – – – A. Shinto B. Samurai C. Kamikaze D. Amphtrac Manhattan Project • August 1939 Albert Einstein wrote a letter to FDR saying a bomb could be built and that the Germans might already be working on one • 1942- Italian scientist, Enrico Fermi discovered the reaction they would need • July 16, 1945 tested it in New Mexico • Robert Oppenheimer headed project Final Decision • FDR died in April 1945 and Harry Truman took over • August 6, 1945 the bomb was dropped on Hiroshima- Little Boy – 140,000 died in explosion and in the months after • 3 days later it was dropped on Nagasaki- Fat • Man • August 14, 1945 Japan accepted the U.S. terms for surrender – V-J Day Starter • What was the code name for the plan to build the atomic bomb? – – – – A. Manhattan Project B. Doolittle Raid C. Operation Overlord D. V-J Day