* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Foundations of Government
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Operation Torch wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
Sh'erit ha-Pletah wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
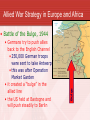
Daily Start 3 • Name 1 detail about the WWII service of each of the following groups: • Women • African-Americans • Japanese-Americans • Mexican-Americans Consider researching a bit of your family history. Do you have any relatives who served in one of these capacities? Part Three The War in Europe and North Africa EQ 4: How did the Allies turn the tide against the Axis in Europe? Hitler first Strategy • FDR agrees that Germany is a larger threat to the world • Britain and the USSR must not fall • the US may need more allies in the Pacific Alliance between Britain, U.S., and Soviet Union • Germany invaded the USSR in May, 1941 • Operation Barbarossa, 1941 • hopes to conquer Russia before winter stalled in the Balkans • Stalingrad became the linchpin • 3 million Germans and Russians killed Allied War Strategy in Europe and Africa • Operation Torch (North Africa), 1942 • the USSR demanded a second front • under Patton, the US invaded North Africa at Morocco • 275,000 Germans surrender • the US used North Africa to get to the island of Sicily and then to Italy • “soft underbelly of Europe” • the USSR complained it was taking too long Allied War Strategy in Europe and Africa • Strategic Bombing • the allies bombed Italy and Germany to destroy their industry • British bombed at night despite higher civilian casualties • U.S. continued daytime raids from England and Italy • 1.5 million tons of bombs were dropped on Germany • it’s debatable how effective the bombing was • they were psychologically traumatic Bombing of Dresden Allied War Strategy in Europe and Africa • Operation Overlord (DDay), June 6, 1944 • D-day was the largest amphibious assault in history • planned by Gen. Eisenhower • Ike was the Allied commander in Europe • numerous fake plans were leaked • 150,000 troops landed on five beaches • just under 7000 ships were involved • France and Belgium were liberated by September D-Day, June 6, 1944 Allied War Strategy in Europe and Africa • Germans try to push allies back to the English Channel • 250,000 German troops were sent to take Antwerp • this was after Operation Market Garden • it created a “bulge” in the allied line • the US held at Bastogne and will push steadily to Berlin Bulge • Battle of the Bulge, 1944 Allied War Strategy in Europe and Africa • V-E Day (May 8, 1945) • the US and Britain pushed into Germany from the West while the USSR came from the East • while Europeans cheered, Americans feared the war in Japan Essential Question 4: • How did the Allies turn the tide against the Axis in Europe? Part Three The War in Europe and North Africa EQ 5: How did the Holocaust develop and what were its results? How did Americans react to the Holocaust? The Holocaust • Kristallnacht, 1938 • at first Jews were segregated and forced to wear a Star of David • Hitler tried to get them to leave Germany • he watched the way the South treated blacks in the US • in one night, 7,500 Jewish shops and 400 synagogues burned • almost 100 Jews killed and 20,000 sent to concentration camps • this is the beginning of the holocaust The Holocaust • The Final Solution • the Nazis imprisoned slavs, gypsies, and other ethnic groups • the elderly, the insane, homosexuals, and the mentally retarded were executed • a combined program of eugenics and euthanasia • millions of Jews were segregated into Ghettos before being taken to concentration camps • Aushwitz and Dachau • 78% of Jews in Europe were killed • They were killed in showers using a pesticide called Zyklon-B and then burnt in ovens to hide the evidence • even when the war looked hopeless, Hitler pushed for the work to continue The Holocaust • America’s Response to the Holocaust • the US held to its immigration quotas • the Holocaust got little attention in the news • military resources were not used to destroy rail lines to the camps • after the war, we helped create Israel EQ 5: • How did the Holocaust develop and what were its results? How did Americans react to the Holocaust?