* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Operation Green (Ireland) wikipedia , lookup
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Écouché in the Second World War wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
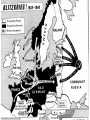
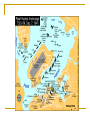
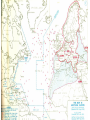
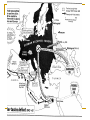
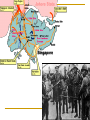
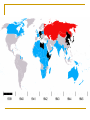
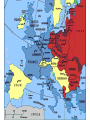
World War Two 1939-45 The Beginning of the War God at times has had a specific hand in warfare, giving directions, ensuring victory, causing others to recognize him - Joshua 10:8 The Greater Reich – Lil Hitler Anschluss Czechoslovakia The war began with the Nazi invasion of Poland on 1 September 1939. German forces unleashed a blitzkrieg across Poland. The German air force, Luftwaffe, was heavily relied upon. By late September, Poland had become a Nazi protectorate. In mid-September, the U.S.S.R. invaded the rest of Poland. The Soviets did not stop there and invaded the Baltic countries, as well as Finland. Both Britain and France declared war on Germany on 3 September 1939. After being betrayed over Czechoslovakia, France and Britain were ready to go to war. Phony War Starting on 3 September 1939, France and Britain began to bolster their armies and air forces. A lot of these troops were massed on the German border. Hitler considered all of this as diplomatic show over the winter. In this period, known as the Phoney War, agreements between nations could not be reached. The new year, 1940, found Britain and France formally at war with Germany, although no actual battles had been fought. In April 1940, Nazi forces overran Denmark and invaded Norway Blitzkrieg Add map The Course of the War France Fighting began in earnest on 10 May 1940 with the German invasion of France. British troops had been sent to the continent prior to this time. French troops were sent to the French frontier with Germany to strengthen the Maginot Line. German forces smashed through Belgium and Holland in a matter of days. The major German thrust came through the Ardennes at Sedan. The French had neglected this area in planning a defence strategy. In three days, the German Panzer divisions pushed 500 km into France. Northern attacks were at Dunkirk. Many French and British troops escaped to Britain. German troops entered Paris on the 14 June 1940. The Nazis permitted French officials to govern the interior. This Nazi-friendly government, known as Vichy France, controlled the southern end of France. Battle of Britain The actions of Germany in France left Britain and Germany as the only contenders for control of Europe. Nazi Germany would thus hasten plans to weaken the United Kingdom and take control of the British Isles. This plan was known as Operation Sea Lion. In this plan, the Luftwaffe would attack Britain. After the Luftwaffe weakened British defences, Germany would invade by land. These attacks were known as the Battle of Britain. The big attacks on London were known as the “Blitz” While Britain protected its southern cities, it also attached Germany by air. Destruction was extensive. By the summer of 1941, the “Blitz” had stopped as Hitler needed German bombers for an attack on the Soviet Union. "Arm yourselves, and be ye men of valour, and be in readiness for the conflict; for it is better for us to perish in battle than to look upon the outrage of our nation and our altar." Winston Churchill This was quoted by Churchill in his first broadcast as Prime Minister to the British people on the BBC, May 19, 1940, London. WWII DVDs “Battle of Britain” (scene 5 – to 45 min) Barborossa Operation Barbarossa, the German plan for Soviet invasion began 22 June 1941. This ended the NaziSoviet Non-Aggression Pact (Hitler had never intended to honour this agreement on a permanent basis). The attack was a surprise to the Russians. Millions of Russians were killed or captured. By the end of 1941, the Germans were within 30 km from Moscow. The Russian winter would be the only thing that would halt the Nazis. In the spring of 1942, the German pressed their way to Stalingrad. The Soviets were able to stall the Nazis at Stalingrad. This was a brutal urban fight. Soviets were able to surround the German army. Casualties were extensive. This ended any Nazi hopes of advances in the east. Tiger Tank (German) Ferdinand Tank (German) T-34 Tank (Russian) WWII – “Battle for Russia” (20 to 34 min) and “Enemy at the Gates” (scene 2 to Africa Africa was another theatre of war during the war. Allied troops fought Hitler’s troops in northern Africa that were under Rommel’s control. Eventually the allies were able to gain control of this theatre. USA Deeply isolationist population FDR wanted to help Britain Lend-Lease Act – USA gives warships to Britain for bases around the world Tried to get the Nazis to torpedo him on convoys Isolated Japanese from oil and steel they gave the USA friendship medals and pretended to negotiate SS 26-1 Pearl Harbour On the 7 December 1941 Japanese warplanes roared in over Pearl Harbor, the American navy’s main base in the Pacific Ocean. Both ship and soldier losses were great. On the 8 December 1941 the United States declared war on Japan. Since Germany was Japan’s ally, Hitler declared war on the USA. This brought the United States into the European and Asian theatres. Remember that the United States had been involved in the war through mechanisms such as the Lend-Lease Agreement. “Pearl Harbour” Battle of the Atlantic The success of the allies (Britain) depended on being able to get supplies and troops from other parts of the world. These resources needed to be delivered to Europe via the Atlantic Ocean. The Germans used U-boats to try to stop these convoys of ships making it to Europe. The allies needed to protect their ships, thus created maritime battles. The allies developed defences and convoy escorts to protect against German submarines This was effective. Of the 1162 German subs built, 1069 were sunk or surrendered. Italy In July 1943, Italians overthrew Mussolini, as a British-American advance seemed imminent. In September, a new Italian government made peace with the allies. By the spring of 1944, Hitler has rushed German troops into Italy to stop the allies in Italy. The allies would eventually push the Nazis out of Italy. Allied Advances There was common resistance to the Nazis throughout Europe by ordinary people. The year 1942 saw the turning of the tide, with the battles of Midway in the Pacific, El Alamein in Egypt, and Stalingrad in southern U.S.S.R. On 6 June 1944, D-Day, the long-awaited second front in Europe came with the allied invasion of Europe. Eight American, British and Canadian divisions landed by sea or parachuted down along a 100 km stretch of French coastline. Operation Overlord had been a success with 640, 000 allied troops landed in France within the first month. By December, the allies had pushed the Nazis back to their own border. “Saving Private Ryan” War’s End Surrender of Germany By late 1944, Hitler’s army was falling back everywhere. Russian soldiers had fought their way across Eastern Europe and into Germany. The British and Americans had pushed their way through France, the Low Countries and into Germany. In his bunker under Berlin, Hitler shot himself on 30 April 1945. German troops surrendered between the 7th and 9th of May. Pacific Theatre Japanese expansion. Pearl Harbour American success at the Battle of Midway. The Bomb - “Crusade in the Pacific” On 6 August 1945 an American bomber dropped an atomic bomb over the Japanese city of Hiroshima. It wiped out most of Hiroshima and killed almost 10,000 of its people. A few days later a second atomic bomb was dropped on the city of Nagasaki. Japan subsequently surrendered. Attrocities 50 to 60 million dead bombing of civilians Dresden Atomic bomb Rotterdam Holocaust Huge loss of infrastructure Suspension of human rights, world wide The War at Home Many Canadians had their lives touched by the war. Mobilized the population to contribute to “the war effort”. Women started to take jobs that men had. Exposure to propaganda. Dehumanization of enemies. Conferences Teheran a meeting between Stalin, Churchill and Roosevelt between 28 November and 5 December 1943. An agreement was reached on the creation of a second front in France to be launched in Jun 1944. Postwar Polish borders were also discussed. Yalta February 1945. The “Big Three” met and discussed the partition of Germany. The capital, Berlin, was to be divided into three zones and put under military occupation. German industries were to be dismantled and reparations levied. This was proposed by the Soviets and France and Britain supported the reconstruction of Europe. Potsdam End of July 1945. Disagreements broke out between Truman and Stalin on many issues. In a sense, the Cold War had begun. The map afterwards