* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WWII Road to Berlin
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
German evacuation from Central and Eastern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Écouché in the Second World War wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
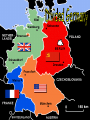
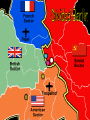
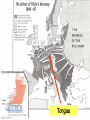
WWII Road to Berlin Mrs. Post-American Cultures II Allies Call for “Unconditional Surrender” (Jan. 1943, Casablanca) • This allows the Axis leaders to use a huge propaganda campaign in which they convince their citizens they will be slaves of the Allies if they lose. • Axis soldiers and citizens put more effort into the war • Roosevelt appoints General Dwight D. Eisenhower Supreme Allied Commander in Dec. 1943 • Allies know they need to strike Hitler (who had more than 3 years to prepare defenses) • By 1944, more than 3.5 million Allies preparing in England “In War time, truth is so precious that she should always be surrounded by a bodyguard of lies.” • Allies attempt to disguise their invasions in a variety of ways: – Spies – Double spies feeding false information • Operations of false-invasion – Zeppelin – Balkans (Churchill was believed to have actually prepared for this) – Fortitude North – Norway – Fortitude South – Pas de Calais • Goal: Convince Germans that invasion will take place at Pas de Calais. • How do you do this? – Logical place for Allies to invade (Closest to England) – Transmit false radio movements of troops/transports – Exchange German prisoners (Gen. Hans Kramer) with false information – General George S. Patton “Blood & Guts” placed in charge of First U.S. Army Group (Ghost Army – FUSAG) – Fly airplanes over English Channel towards Pas de Calais dropping aluminum to confuse radar German aerial view Inflatable tank Dummy landing craft • • • • • • 9 battleships 23 Cruisers 104 destroyers • 71 U-boats 150,000 troops set to cross the • English Channel in the invasion of • Hitler’s fortress of • Europe Nearly 10,000 Allied Casualties by end of first day (Between 4,000 and 9,000 Germans) Failed to drive Germans; Beachheads linked within 5 days July 25th – Allies break through beach August 25 – Paris freed Sept. 16 – U.S. troops reach German border http://www.history.navy.mil/ac/d-day/88199fh.jpg “Mulberries”: Portable harbors brought from England Allies land in Normandy Omaha Beach Rommel’s beach obstacles Statistics on D-Day • Greatest land, air, and sea invasion in military history – 50,000 motorcycles, tanks, bulldozers over 60 miles of English Channel – 5, 333 ships and 11,000 airplanes – 175,000 Allied soldiers fought – Total died – 1st day – 5,000; 2,000 died on Omaha beach Operation Market Garden – September 1944 Market Garden – breaking into Germany • Montgomery convinced Eisenhower to allow a ‘direct push’ operation into Germany. • The plan was to use 30,000 parachute troops to seize vital bridges across the Rhine in Holland. • An armoured thrust would then advance across these bridges in to Germany avoiding the German border defences (The Siegfried Line) and encircle the Ruhr from behind. • With the Ruhr factories taken, the German wareffort would collapse and a drive on Berlin could take place. Battle of the Bulge December 1944 – the ‘Battle of the Bulge’ • Hitler made one last offensive in the west in late December 1944. • The aim was to split the advancing British and American armies and capture the Belgian port of Antwerp (vital for Allied supplies). • Very bad weather grounded most British/US aircraft. • 600 German tanks drove through the Ardennes forest (scene of Germany’s spectacular triumph in 1940) Battle of the Bulge • Despite initial success, the German tanks soon ran out of fuel and the improving weather made them vulnerable once more to overwhelming air attack. • The attack failed and proved the ‘last gamble’ of the German army in World War Two. • From January 1945 the Americans and British began their advance in to Germany, crossing the Rhine in March. • The Soviet Red Army captured Berlin in April/May 1945. • The American and Russian armies finally linked up in the middle of Germany at Torgau on the River Elbe. Not home by Christmas. German troops in the forest of the Ardennes, December 1944. New Year’s day 1945. An American GI attempts to fire his frozen machine gun. The misery of war. A wounded American GI being transported to hospital on the front of a jeep. Yalta conference • This was the last war-time conference of Roosevelt, Churchill and Stalin. • It was agreed that Germany would be split in to four zones of occupation (as would Berlin). • Germany was to be ‘de-nazified’ and a special trial held of its leaders. The Big Three. The Allied leaders meet for the last time at Yalta in February 1945 to discuss the future of Germany after the war. Iron Curtain – A term used by Winston Churchill to describe the separating of Those communist lands of East Europe from the West. Improve your knowledge • The Russians took very high casualties to capture Berlin in May 1945. They spent the early occupation trying to take over all zones of the city but were stopped by German democrats such as Willy Brandt and Konrad Adenauer. Reluctantly the Russians had to admit the Americans, French and British to their respective zones. April 1945 – meeting at Torgau The Soviet and American armies met at the town of Torgau. The press and film reporters were anxious to stress the American-Russian friendship Torgau All smiles and handshakes. American and Russian soldiers happily pose for reporters at Torgau. The fall of Berlin, May 1945. Soviet troops plant the red flag on the roof of the Reichstag.