* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Victory in Europe and the Pacific
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Collaboration with the Axis Powers wikipedia , lookup
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Operation Torch wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
German evacuation from Central and Eastern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
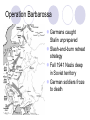
Section 3: Victory in Europe and the Pacific Allies Turn the Tide Nazis invaded Soviet Union but did not conquer it Pushed the Axis powers out of North Africa Allies invaded Italy, difficult battles Bombed Germany from bases in England Battle of Midway won by Allies (ended the Japanese advance) Germany Invades the Soviet Union An Unstoppable German Army Stalls June 1941, Hitler invades the Soviet Union Operation Barbarossa Frederick Barbarossa, medieval Germanic leader Why break the Nazi-Soviet Pact? Ural Mountains = raw materials Siberia = forests Ukraine = wheat fields Crush communism in Europe Operation Barbarossa Germans caught Stalin unprepared Slash-and-burn retreat strategy Fall 1941 Nazis deep in Soviet territory German soldiers froze to death Allies Turn the Tide 1942 Allies increase production May – Japanese are defeated at Coral Sea June – Japanese are defeated at Midway Nov. – Allies halt German advance in Africa Big Three agree to focus on war in Europe 1943 Jan. - Germans surrender at Stalingrad May – Rommel’s army surrenders in North Africa July – Allies land in Sicily Sept. – Italians surrender to Allies 1944 Allies bomb German facilities June – D-Day: Allies invade Normandy Aug. – Allies enter Paris Autumn – German defeat seems inevitable The Global Conflict: Allied Successes Nations mobilize for total war Democratic political power increases Economic resources directed to war effort Consumer good rationed Prices and wages regulated War puts an end to unemployment Democratic governments limit citizen rights Censored the press Use of propaganda Japanese containment camps – US West Coast Allied Victory in North Africa Turning points in the war in North Africa El Alamein 1942 Egypt British General Bernard Montgomery vs. German General Rommel “Desert Fox” Axis powers driven back across Libya into Tunisia American General Dwight Eisenhower Morocco and Algeria Traps Rommel’s army; surrendered in May 1943 Invasion of Normandy Operation Overlord: headed by Dwight Eisenhower Largest fleet ever assembled (4,400 ships) Deceived Germans: fake army set up near Calais D-Day: June 6, 1944 11,000 planes led the way Soldiers stormed the beaches Gained a foothold in France, 1st step to defeating Germany Liberation of Europe Allies Advance August 1944: Allies liberated Paris Hitler refused to surrender to Allied forces Battle of the Bulge (Hitler’s last offensive December 1944) Germany captured several key towns Reinforcements pushed Germans out of France Early 1945: Soviets and U.S. outside Berlin April 1945: Mussolini captured and executed April 30, 1945: Hitler commits suicide May 7, 1945: Germany surrenders Atomic Bomb Ends the War Manhattan Project July 16, 1945: 1st Atomic Bomb was tested Developed by scientists (many refugees) Truman’s Decision Invasion might cost: 1,000,000 U.S. lives Mattered more than Japanese civilian lives Hiroshima (8/6/1945) Nagasaki (8/9/1945) 95,000 civilians were killed Japan surrendered on August 15, 1945 (VJ Day)