* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
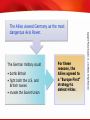
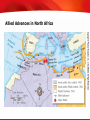
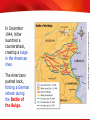
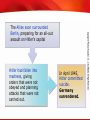
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Lead up to World War II TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Objectives • Explain how dictators and militarist regimes arose in several countries in the 1930s. • Summarize the actions taken by aggressive regimes in Europe and Asia. • Analyze the responses of Britain, France, and the United States to the aggressive regimes. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Terms and People • totalitarianism − theory of government in which a single party or leader controls the economic, social, and cultural lives of its people • Joseph Stalin − dictator and head of the Communist Party in Russia • Benito Mussolini − founder of the Fascist Party and Italian dictator • Adolf Hitler − leader of the Nazi Party in Germany who seized power and attempted world domination • anti-Semitic − prejudice and discrimination against Jewish people TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Terms and People (continued) • Spanish Civil War − Nationalist forces led by General Francisco Franco rebelled against the democratic Republican government of Spain • appeasement − policy of granting concessions to a potential enemy in the hope that it will maintain peace • Anschluss − union in which Hitler forced Austria to become part of Germany’s territory • Munich Pact − agreement in which Britain and France attempted to preserve peace by allowing Hitler to take more territory TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Why did totalitarian states rise after World War I, and what did they do? World War I and the Great Depression had devastating effects throughout the world. In some countries, people turned to new leaders, who would be responsible for creating an even deadlier global conflict. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. World War I ended when Germany surrendered to the Allies. An uneasy peace followed. • Germans resented the terms of the Treaty of Versailles, feeling humiliated in defeat. • Italy and Japan were angered by the treaty, expecting to receive more land as Allied victors. • Worldwide depression brought despair to many already suffering from war. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Overwhelming problems led some nations to turn to a new form of government called totalitarianism. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Totalitarian governments developed in several countries during the 1930s. Country Leader Soviet Union Joseph Stalin Italy Benito Mussolini Germany Adolf Hitler Each of these countries faced economic and political problems. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Totalitarian leaders promised to bring jobs, food, and prosperity. They promised to make their countries great again. In reality, however, the brutal tactics used by totalitarian leaders resulted in the deaths of millions of people. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Joseph Stalin took control of the Soviet Union following the death of Vladimir Lenin. • Attempted to turn the Soviet Union into an industrial power • Forced people to work in factories and on state-run farms • Killed or imprisoned suspected traitors during the Great Terror • Ruled through fear and massive propaganda TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Another totalitarian regime formed in Italy. • The government seemed unable to deal with the country’s many problems. • Benito Mussolini formed the Fascist Party. • Mussolini and his followers, the Black Shirts, fought to gain power. Mussolini, called Il Duce, took control of the government, using secret police to maintain control. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. In Germany, the Weimar Republic struggled with overwhelming economic and social problems. Adolf Hitler, the leader of the Nazi Party, was appointed chancellor. Hitler seized power and created a totalitarian state. Hitler making a speech TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Hitler rebuilt the nation’s army. His economic policies put people back to work. Many cheered his success. Yet Hitler ruled with unlimited power. • Controlled the press and education system • Used propaganda to boost his popularity • Used the secret police to silence opposition and restrict freedoms Violently anti-Semitic, Hitler openly attacked Jews, blaming them for all of the country’s problems. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Japan did not become a totalitarian dictatorship, but it did come under the influence of strong military leaders. These leaders attempted to solve their country’s economic problems through aggressive military conquests. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Japanese Expansion, 1931-1939 Japan invaded Manchuria, then China. The attack on Nanjing was especially brutal. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Acts of Aggression in Europe and Asia Germany • • • • • Italy • invaded Ethiopia Spain • Fascists rebelled against the government • Spanish Civil War Japan • conquered Manchuria and parts of China rebuilt military reclaimed Saar region from France invaded the Rhineland Anschluss invaded the Sudetenland TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. A weak League of Nations did little to stop the aggression of the totalitarian states or of Japan. • Many feared involvement in another war. • Some believed the Soviet Union posed a greater threat than the threat of Nazi Germany. • Others questioned the resolve of their own country and their allies, and embraced a policy of isolationism. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The appeasement of Hitler continued with the Munich Pact. Britain and France sacrificed the Sudetenland to Germany in return for peace. British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain and Hitler in Munich But peace was not to come. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Start of World War II and Early Years TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Objectives • Understand the course of the early years of World War II in Europe. • Describe Franklin Roosevelt’s foreign policy in the mid-1930s and the great debate between interventionists and isolationists. • Explain how the United States became more involved in the conflict. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Terms and People • blitzkrieg − lightning war • Axis Powers − Germany, Italy, Japan, and other nations that fought together during World War II • Allies − Britain, France, the Soviet Union, the United States, China, and other nations that fought against the Axis Powers during World War II • Winston Churchill − British prime minister during World War II TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Terms and People (continued) • Neutrality Act of 1939 − American law that allowed nations at war to buy U.S. arms if they paid cash and carried them away on their own ships • Tripartite Pact − three-party agreement establishing an alliance between Germany, Italy, and Japan • Lend-Lease Act − American law that allowed the United States to lend, lease, sell, or otherwise provide aid to other nations if doing so helped in the defense of the United States TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Terms and People (continued) • Atlantic Charter − document signed by Roosevelt and Churchill that endorsed national self-determination and an international system of general security TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. How did Americans react to events in Europe and Asia in the early years of World War II? Americans were shocked by Japanese and German aggression. Yet they remained deeply divided over American involvement in another war— especially as they fought the despair of the Great Depression. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Hopes for peace in Europe faded as it became clear that efforts to appease Hitler had failed. • Hitler violated the Munich Pact, taking over the remainder of Czechoslovakia in 1939. • When Hitler invaded Poland in September 1939, Britain and France declared war on Germany. This marked the start of World War II. • Germany launched a series of attacks on its neighbors marked by speed and massive firepower— a blitzkrieg, or “lightning war.” • Denmark, Norway, and the Netherlands fell in 1940. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. In May of 1940 the Germans entered France. It fell in just 35 days and was divided into two sections, Occupied France and the smaller, French-controlled Vichy France. Nazi soldiers in Paris TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Beginning in July 1940, Hitler turned his fury on Britain. The Battle of Britain was waged in the air as pilots fought for control of the skies. The British hid in shelters and darkened homes as bombs rained down. Despite terrible destruction, the British held on. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Europe was again at war. In time, major powers around the world joined in alliances. Axis Powers Allies • Germany • Britain • Italy • France • Japan • Soviet Union The Tripartite Pact bound these nations together. • United States • China TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. German Aggression, 1936–1941 Many feared that Hitler was unstoppable. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. In the early days of the war, Congress declared neutrality. But as the war raged on in Europe, the United States began to take steps to support Europe’s democracies. • The Neutrality Act of 1939 contained a cash-and-carry provision favoring the Allies. • The Selective Service Act provided for a military draft. • FDR agreed to give Britain battleships in exchange for defense bases. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Not everyone agreed with FDR’s pro-Allies position. A loud debate soon raged between isolationists and interventionists. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. As conditions worsened overseas, Roosevelt described what was at stake, in an address to Congress. He highlighted four freedoms precious to Americans. • freedom of speech • freedom of worship • freedom from want • freedom from fear All of these freedoms, he argued, were threatened by German and Japanese militarism. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Congress then took another step to aid the British. In March 1941, Congress approved the Lend-Lease Act. The act, symbolically numbered 1776, amounted to an economic declaration of war. Many people, however, remained divided over American involvement in the war. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. In August 1941, Roosevelt and British prime minister Winston Churchill signed the Atlantic Charter, deepening the alliance between the two nations. German submarines began to fire on American ships supporting the Allies. Roosevelt ordered the navy to attack the U-boats on sight. War seemed inevitable. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. American Entry into the World War II TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Objectives • Explain why Japan decided to attack Pearl Harbor, and describe the attack itself. • Outline how the United States mobilized for war after the attack on Pearl Harbor. • Summarize the course of the war in the Pacific through the summer of 1942. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Terms and People • Hideki Tojo − Japanese general and prime minister during World War II • Pearl Harbor − American military base attacked by the Japanese on December 7, 1941 • Women’s Army Corps (WAC) − U.S. Army group established during World War II so that women could serve in noncombat roles. • Douglas MacArthur − general who served as commander of United States Army forces in Asia TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Terms and People (continued) • Bataan Death March − grueling march in which Japanese troops forced sick and malnourished prisoners of war to walk more than 60 miles to prison camps during World War II • Battle of Coral Sea − World War II battle that took place between Japanese and American aircraft carriers TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. How did the United States react to the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor? In early December 1941, the United States had engaged in warlike activity, but had not yet committed itself to join in World War II. A surprise attack on the American naval base at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, ended the debate between isolationists and interventionists. The United States was going to war. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Tensions between the United States and Japan mounted as Japan continued its march into new lands, gaining territory and valuable natural resources. Roosevelt condemned Japanese aggression. He worked to slow Japan’s expansion with an embargo. Angered by American interference, Prime Minister Hideki Tojo decided it was time to eliminate the U.S. presence in the Pacific. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. On December 7, 1941, Japanese forces attacked the American naval base at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. The attackers struck with devastating power, taking the Americans by surprise. USS West Virginia and USS Tennessee TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Damage at Pearl Harbor The United States suffered terrible losses, but key parts of the fleet survived. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. After the attack, the United States declared war on Japan. Japan’s allies, Germany and Italy, then declared war on the United States. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. A wave of patriotism swept the United States following the attack. • Americans joined the military, the Red Cross, and other organizations. • Women responded by joining the Women’s Army Corps (WAC), Army Nurse Corps, and other military auxiliaries. • Americans took new jobs making weapons and supplies that supported the war effort. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The peacetime economy soon shifted to a wartime economy. Companies that once produced consumer goods mobilized to build ships, planes, and tanks. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The money that was poured into defense spending finally ended the Great Depression. American workers could once again find jobs. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. In 1944, American production levels were double those of all the Axis nations combined. This “production miracle” gave the Allies a crucial advantage. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. In the early years of the war, the outlook for the Allies was grim. Japan’s Advantages • Dominance of the Pacific • Technologically advanced weapons • Highly motivated and well-trained military TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Japanese armies quickly took Guam, Wake Island, and Hong Kong. Then they moved into the Philippines, forcing American General Douglas MacArthur to retreat. The remaining troops were surrounded, trapped. After a terrible siege, thousands died when they were forced to walk to prison camps during the Bataan Death March. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Japanese Aggression, December 1941–June 1942 TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. With hope for a quick victory fading, Americans finally got some good news. 1. Colonel James Doolittle’s surprise raid on Tokyo 2. The American victory at the Battle of Coral Sea Coral Sea was a battle of aircraft carriers. From that day on, the Pacific theater of battle would be won or lost on the strength of aircraft carriers and planes. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The momentum had shifted toward the Americans. A long fight lay ahead, but the darkest days of 1942 seemed to be over. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Turning Points in World War II TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Objectives • Analyze the reasons for and impact of the Allies’ “Europe First” strategy. • Explain why the battles of Stalingrad and Midway were major turning points in the war. • Discuss how the Allies put increasing pressure on the Axis in North Africa and Europe. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Terms and People • Dwight Eisenhower − American general and commander of Allied forces during World War II • George S. Patton, Jr. − American general and tank commander during World War II • unconditional surrender − giving up completely without any concessions • saturation bombing − dropping massive amounts of bombs to inflict maximum damage TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Terms and People (continued) • strategic bombing − dropping bombs on key targets to destroy the enemy’s capacity to make war • Tuskegee Airmen − African American squadron that escorted bombers in the air war over Europe during World War II • Chester Nimitz − Commander of the U.S. Navy in the Pacific • Battle of Midway − American victory and turning point of the war in the Pacific TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. How did the Allies turn the tide against the Axis? After the dark days of 1942, the Allies began to make important advances. Tough years of fighting lay ahead, but many began to see a glimmer of hope. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The Allies viewed Germany as the most dangerous Axis Power. The German military could • bomb Britain • fight both the U.S. and British navies • invade the Soviet Union For these reasons, the Allies agreed to a “Europe First” strategy to defeat Hitler. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The United States moved quickly to produce military supplies and send them to Europe. Hitler was determined to prevent the supplies from reaching Europe. German U-boats sank thousands of supply ships in the North Atlantic. New technology such as radar helped the Allies target the U-boats and restore the supply lines. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Germany had invaded the Soviet Union in June 1941. Millions of soldiers and civilians died in fierce fighting. After a long struggle, the Soviets defeated the Germans at Stalingrad in January 1943. Thousands of Germans surrendered. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The Battle of Stalingrad proved to be a major turning point of the war in Europe. • Nazi armies were forced to retreat westward, back toward Germany. • The Soviet Union was now on the offensive. • Hitler’s dream of dominating Europe was crushed. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Meanwhile, Allied forces pressured the Axis on another front—the deserts of North Africa. • General Dwight Eisenhower commanded the Allied invasion. • Heat, sandstorms, and scorpions made conditions difficult. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Tank battles dominated the fighting, pitting two brilliant tank strategists against each other. American General George S. Patton, Jr. German General Erwin Rommel, the “Desert Fox” Patton eventually defeated Rommel’s Afrika Korps, forcing a German surrender in May 1943. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Allied Advances in North Africa TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The Allied victory in North Africa paved the way for an invasion of Italy, with forces capturing Sicily. In 1943, Italy surrendered to the Allies, ending the rule of Benito Mussolini. However, German forces continued fighting the Allies in Italy into 1945. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The Allies next took the fight against Germany to the air. Bombers flying from Britain launched nonstop attacks in Germany. • massive saturation bombing to inflict maximum damage • pinpoint strategic bombing to destroy factories The goal was unconditional surrender. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. In 1943, Allied leaders agreed to open a second front in the war in Europe. American and British troops would cross the English Channel and invade France. • The secret operation was code-named Operation Overlord. • General Dwight D. Eisenhower was the mission’s commander. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Operation Overlord was a massive operation. It required careful planning and involved an elaborate hoax to fool the enemy about where troops would land. On D-Day, June 6, 1944, the Allies landed at Normandy. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Amid intense fighting, the Allies captured the beaches. Within a month, more than one million troops landed in France. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. American bomber planes were key to the war. • The B-24 Liberator was faster than previous bomber planes and had a greater long-range capacity. • Some planes escorted the bombers. The most celebrated of the escort crews were the Tuskegee Airmen, a special unit of African American pilots. In 1,500 missions, they never lost a bomber. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. While battles raged in Europe, the Allies continued to fight Japanese advances in the Pacific. Decoded messages told U.S. Admiral Chester Nimitz that Japan was going to attack the American base at Midway in June 1942. This was a vital location to the defense of Hawaii. Allied aircraft carriers and fighter planes were victorious after fierce fighting. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The Battle of Midway proved to be a major turning point of the war in the Pacific. • Japan’s momentum was finally halted. • Americans took the offensive, moving on to defeat the Japanese at Guadalcanal. • Now the Allies began advancing—toward Japan. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Home Front in World War II TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Objectives • Explain how World War II increased opportunities for women and minorities. • Analyze the effects of the war on civil liberties for Japanese Americans and others. • Examine how the need to support the war effort changed American lives. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Terms and People • A. Philip Randolph − African American labor leader • Executive Order 8802 − World War II measure that assured fair hiring practices in jobs funded with government money • bracero program − program in which laborers were brought from Mexico to work on American farms • internment − temporary imprisonment of members of a specific group TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Terms and People (continued) • Korematsu v. United States − Supreme Court case that upheld the government’s wartime internment policy • 442nd Regimental Combat Team − Japanese American combat team that became the most decorated military unit in American history • rationing − system that limits the amount of certain goods people can buy • Office of War Information (OWI) − encouraged support of the war effort TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. How did the World War II change America at home? World War II stirred patriotism even as it brought out long-simmering fears and tensions. Americans from different backgrounds living in different places across the country made huge sacrifices to support the war effort. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Wartime America saw industries gearing up to produce military goods. With men joining the army in huge numbers, women stepped into jobs in businesses and factories. Unlike the past, • Women worked in both light and heavy industries. • Married and older women worked. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Wartime changes to the workforce had long-lasting effects. • Women earned paychecks and gained knowledge and experience. • Future generations benefited from new opportunities. • Day-care options for children expanded. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. African Americans hoped for similar job opportunities, but were disappointed. Leaders called for a “Double V” campaign. Victory against fascism abroad Victory against discrimination at home Yet many jobs, including those in the government and the military, remained segregated. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Labor leader A. Phillip Randolph urged Roosevelt to end discrimination in government-funded training, employment, and military service. Under pressure, FDR issued Executive Order 8802. Assured fair hiring practices in government jobs Such victories set the stage for the civil rights struggles to come. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Migration patterns changed as people moved across the country—especially to cities—seeking jobs in wartime industries. Bracero program • To alleviate the loss of workers in rural areas, Mexican laborers were brought in to work on American farms. • Agricultural industries would continue to hire migratory labor in the West for years to come. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Population changes and racial tensions at times triggered violence. • Urban riots • Zoot suit attacks Despite this, African Americans and Mexican Americans continued to contribute to the war effort. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Wartime fears also led to discrimination against Americans from Germany, Italy, and Japan. In time, suspicion focused on Japanese Americans. They were targeted for a combination of reasons. • Racism • Lack of political clout • Their fewer numbers and relative isolation TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. By executive order, more than 100,000 Japanese Americans were forced to sell their homes and belongings. They were then sent to isolated internment camps. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. They remained in the camps for the rest of the war. Some Japanese Americans went to court to fight for their civil liberties. Their efforts failed. Still, when the military ban on Japanese Americans was lifted in 1943, many eagerly joined the 44nd Regimental Combat Team. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Korematsu v. United States (1944) The Facts The Issue The Decision • In 1942, FDR ordered that select people could be banned from war zones. • The army relocated Japanese Americans on the West Coast to internment camps. • Fred Korematsu was arrested for resisting the army’s orders. Korematsu argued that he was denied equal protection under the law because he was a Japanese American. The court held that the military order was justified for security reasons. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The war effort had a huge effect on the economy. • The national debt skyrocketed. • Taxes increased. • Wages and prices were controlled. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. As industries cranked out military goods, consumer goods became scarce. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Americans made many sacrifices, looking toward victory. The Office of War Information worked with the media to encourage support of the war effort Americans: • Shopped with ration books • Bought war bonds • Planted victory gardens • Collected scrap metal and other materials TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Allied Victory in World War II TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Objectives • Analyze the planning and impact of the D-Day invasion of France. • Understand how the Allies achieved final victory in Europe. • Explore the reasons that President Truman decided to use the atomic bomb against Japan. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Terms and People • D-Day − June 6, 1944, the day Allied forces invaded France • Battle of the Bulge − German counterattack that failed, resulting in an Allied victory • Harry S. Truman − President during the end of World War II • island hopping − American strategy of capturing selected islands in the Pacific in a steady path to Japan TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Terms and People (continued) • kamikaze − Japanese pilots who deliberately crashed their planes into American ships • Albert Einstein − world-famous scientist who alerted Roosevelt of the need to develop atomic weapons • Manhattan Project − code name for the program to develop an atomic bomb • J. Robert Oppenheimer − key leader of the Manhattan Project TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. How did the Allies defeat the Axis Powers? It took years of hard fighting to reverse Axis advances and move toward victory in World War II. A new weapon finally ended the war, changing both warfare and global politics forever. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. In 1943, Allied leaders agreed to open a second front in the war in Europe. American and British troops would cross the English Channel and invade France. • The secret operation was code-named Operation Overlord. • General Dwight D. Eisenhower was the mission’s commander. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Operation Overlord was a massive operation. It required careful planning and involved an elaborate hoax to fool the enemy about where troops would land. On D-Day, June 6, 1944, the Allies landed at Normandy. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Amid intense fighting, the Allies captured the beaches. Within a month, more than one million troops landed in France. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The Allies seized the momentum. The Americans and British advanced from the west, liberating Paris in August 1944. The Soviets advanced from the east, liberating Latvia, Romania, Slovakia, and Hungary. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. In December 1944, Hitler launched a counterattack, creating a bulge in the American lines. The Americans pushed back, forcing a German retreat during the Battle of the Bulge. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The Allies soon surrounded Berlin, preparing for an all-out assault on Hitler’s capital Hitler had fallen into madness, giving orders that were not obeyed and planning attacks that were not carried out. In April 1945, Hitler committed suicide. Germany surrendered. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. World War II in Europe, 1942–1945 TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. With the German surrender, the Allies celebrated V-E Day, hailing their hard-fought victory in Europe. FDR did not live to join the celebrations. He died a few weeks earlier. The new President was Harry S. Truman. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. War still raged in the Pacific, where the Allies were fighting their way toward Japan. • Battles during the island-hopping campaign were fierce, with high casualties on both sides. • Kamikazes crashed into American ships. Japanese troops fought to the death. • An intense bombing campaign leveled much of Tokyo. Still, Japan refused to surrender. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Something had to be done. Early in the war, Albert Einstein convinced FDR of the need to develop an atomic bomb. The program was codenamed the Manhattan Project. It was led by J. Robert Oppenheimer. The bomb was successfully tested in July 1945. Now it was up to Truman to decide if and when to use it. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The Japanese refused to surrender. An invasion of Japan could cost up to 1,000,000 American lives. Truman’s chief priority was to save American lives. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. On August 6, 1945, U.S. pilots dropped an atomic bomb on Hiroshima. Three days later, they dropped a second bomb on Nagasaki. On August 15, Emperor Hirohito surrendered. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The Allies celebrated V-J Day, marking victory in Japan. The most costly war in history was finally over. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. World War II in the Pacific, 1942−1945