* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II - Europe
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Britain (film) wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Operation Green (Ireland) wikipedia , lookup
Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
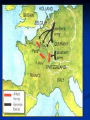
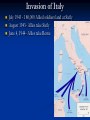
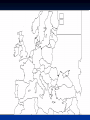
Warm Up What were Germany’s goals in WWII? What were Italy’s goals in WWII? What began WWII for Germany? What began WWII for Italy? What were Japan’s goals in WWII? What began WWII for Japan? World War II Day 1 – Lightening War A. Invasion of Poland September 1, 1939 Blitzkrieg – lightening war Airplanes and tanks Massive bombing of Warsaw Massive infantry invasion (1.5 million German soldiers) A. Invasion of Poland A. Invasion of Poland A. Invasion of Poland German bombers flew 1,150 sorties (missions) and destroyed 84% of Warsaw Incendiary (fire) bombs used Winston Churchill B. Tripartite / Axis Pact September 27, 1940 - signed in Berlin Germany – Adolph Hitler Italy – Foreign Minister Galeazzo Ciano Japan – Ambassador Saburo Kurusu C. Soviet Aggression September 17, 1939 – Soviet troops occupy eastern Poland Annexation (take over) of Latvia, Lithuania, and Estonia November 1939 – Soviets invade Finland C. Soviet Aggression C. Soviet Aggression Finland surrenders by March 1940 D. “Phony War” Ends April 9, 1940 – Hitler invades Denmark and Norway Demark surrenders in 4 hours Norway surrenders in 2 months D. “Phony War” Ends May 1940 Hitler attacks Netherlands, Belgium, and Luxembourg Goal : France 1. Describe the cartoon. 2. What countries are involved in the cartoon? 3. What is the cartoonist trying to say? E. Evacuation from Dunkirk May 26 – June 4, 1940 850 ships rescue 338,000 French soldiers Air coverage from the RAF Heavy German bombing World War II Day 2 – France and Britain A. France Surrenders June 1940 – France surrenders Nazi control “Vichy France” under Henri Petain A. France Surrenders A. France Surrenders June 1940 – France surrenders A. France Surrenders Charles de Gaulle in London – government in exile A. France Surrenders French Resistance French Underground B. Battle of Britain Operation Sea Lion Hitler wanted to successfully invade Britain (hadn’t happened since 1066) Goal: knock out the RAF and then invade with 250,000 soldiers 4,500 planes in the Luftwaffe, 2,900 in the RAF B. Battle of Britain Resistance Cracking Enigma RADAR B. Battle of Britain British propaganda British propaganda C. US Gets involved Destroyer Deal (September 2, 1940)- FDR transferred 50 old-model, four-funnel destroyers left over from WWI, in return for U.S. military rights to eight valuable defensive base sites Lend-Lease Act (March 1941) British needed equipment, didn’t have money to pay for it- arms and ships, would be lent to nations that needed them and returned when no longer needed $50 billion allocated, $31 billion to Britain alone Lend-Lease Act (March 1941) August 1941 FDR and Churchill meet off the coast of Newfoundland on the HMS Prince of Wales Agree to sign the Atlantic Charter What do the two nations agree to? How does this put the US one step closer to war? What are the ideologies behind this document? World War II Day 3 – Fight Drags On What was Napoleon’s biggest mistake? If you want to be a world dictator….don’t invade Russia! “We have only to kick in the door and the whole rotten structure will come crashing down” -Adolf Hitler A. Operation Barbarossa June 22, 1941 – Hitler invades Russia (in summer uniforms) Red Army – 5 million men, lacked supplies and equipment 500 miles – Russians conduct scorched earth A. Operation Barbarossa Siege at Leningrad September 8, 1941 – January 7, 1944 (900 days) German Army destroys food warehouses First winter – no heat, no water, almost no electricity, very little food Some attempt escape to mainland Food supply desperate – eating animal feed, cats, dogs, crows, rats 600,000+ die in Leningrad Attack on Moscow October 2, 1941 Counterattack by Russian General Georgi Zhukov (w/ 100 fresh divisions from Siberia) Germans repulsed – Hitler orders “no retreat” Dig in 125 miles west of Moscow – horrible winter (frozen fuel and oil) 500,000 Germans die in the attempt Casablanca Conference Casablanca Conference (January 1943) Roosevelt and Churchill met in Morocco and agreed on the term of “unconditional surrender.” Stalin is begging for a second front for help, decide to invade the “soft underbelly” of Italy Casablanca Conference North Africa Churchill’s strategy – N. Africa to Italy (angered Stalin) German General Erwin Rommel vs. British General Bernard “Monty” Montgomery Battle of El Alamein Gen. Montgomery attacked German forces and drove them West (October 1942) 107,000 US troops under Gen. Dwight D. Eisenhower land in Algeria and Morocco German Army in N. Africa destroyed by May 1943 Operation Torch Battle of Stalingrad August 23, 1942 Luftwaffe bombs the city November – Germans control 90% of the city November 19 – Soviet troops attack the city, cut off supplies Hitler orders to hold the city “at all costs” February 2, 1943 – 90,000 Germans surrender City is completely destroyed German Surrender at Stalingrad Invasion of Italy July 1943 - 180,000 Allied soldiers land at Sicily August 1943- Allies take Sicily June 4, 1944- Allies take Rome Italian Campaign Northern Italy Invasion of Italy July 25, 1943 – Mussolini arrested September 23 – Italy surrendered Germans take N. Italy and put Mussolini back in power Fighting drags on Mussolini captured, shot, and hanged in Milan– April 1945 World War II Day 4 – The Final Push Tehran Conference Tehran Conference- Roosevelt, Churchill, and Stalin agree to launch simultaneous attacks. Operation Overlord- General Eisenhower put in charge of a massive English channel invasion Operation Overlord Operation Overlord- General Eisenhower put in charge of a massive English channel invasion June 6, 1944—Operation Overlord Overlord Liberation of Paris, August 1944 The Last Days of Hitler December 16, 1944- Battle of the Bulge- tenday stopped by the 101st Airborne Division March 1945- US and Soviet troops marched toward Berlin Battle of the Bulge Race for Berlin Concentration Camps The End April 12, 1945- FDR died from a massive stroke April 30, 1945- Hitler committed suicide May 7, 1945 Germany surrendered Review: World War II Geography Label and color the Allied powers Label and color the Axis powers (visible in this map) Color four countries impacted by the German blitzkrieg Label the correct locations for: D-Day Invasion / Operation Overlord Battle of Britain / Operation Sea Lion Operation Torch Battle of El Alamein Liberation of Paris Operation Barbarossa Russian invasion of Finland STUDY FOR YOUR QUIZ TOMORROW! 35 Multiple choice Free response Yes, you should study your map Yes, we will work on our project when we finish