* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AMERICA IN WWII
Empire of Japan wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
India in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
United States home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
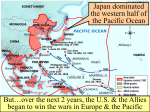
America in WWII 1941 - 1945 War Begins for the US Dec 8, 1941 – FDR asked & received from Congress a declaration of war against Japan Dec 11, 1941 – Germany & Italy declare war on US ABC-1 agreement with Britain- get Germany first – Stop Hitler first & then all the Allies would focus on Japan – Limited American strength would hold Japan The Shock of War National unity – including immigrants – WWII actually speeded the assimilation of immigrants Japanese – Americans – Mainly on the Pacific Coast – Forced into internment camps for fear of sabotage – Many lost literally everything – Korematsu v. US – upheld gov’t action of camps • 1988 – gov’t apologized & paid the survivors $20,000 The New Deal Ends Conservative Congress was elected in 1942 – Wiped out the CCC, WPA, & National Youth Administration Massive military orders ($100+ billion in 1942) helped relieve depression Production & WWII War Production Board – Halted production of nonessential items & focused on needed materials for war Gov’t imposed a national speed limit & gasoline rationing & developed synthetic-rubber plants Farmers – increased production Office of Price Administration – Brought inflation under control through regulation – Rationing held down consumption of critical goods Labor in WWII War Labor Board (WLB) – Imposed ceilings on wage increases Labor unions membership grew but resented the wage ceilings – United Mine Workers were called off the job by John L. Lewis Smith-Connally Anti-Strike Act – June 1943 – Authorized the gov’t to seize & operate tied-up industries – Made strikes against gov’t-operated industry a crime • Gov’t took coal mine & railroads Manpower & Womanpower Armed services – enlisted 15 million men & 216,000 women – Women /Noncombat units – WAACS, WAVES, SPARS Key industrial & agricultural workers were exempted from the draft Draft left many jobs open – 1942 – Mexico sent “braceros” to work in the US – Resulted in Zoot Suit Riots – 1943 in L.A. • Sailors on leave beat Mexicans Impact for Women More than 6 million women took jobs outside the home – Gov’t had to start some 3,000 day-care centers for “Rosie the Riveter’s” children – Began the revolution in the roles of women – Most women left the workforce after the war – “Baby Boom” Generation occurred after the war • Tens of millions of babies were born in the decade & a half after 1945 Wartime Migration Major population boom in War Industries areas – Los Angeles, Detroit, Seattle, & Baton Rouge FDR accelerated the South’s economic development 1.6 million African Americans moved out of the South to seek jobs in the North & West – Mechanical cotton picker eliminated the South’s need for cheap labor – Race relations developed over employment, housing, & segregated facilities Fair Treatment A. Philip Randolph – (Brotherhood of Sleeping Car Porters) – 1941 - Threatened a march on Washington: • demanded equal opportunities for blacks in war jobs & the armed forces FDR responds: – Forbid discrimination in defense industries – Fair Employment Practices Commission (FEPC) monitored compliance Blacks were drafted but were still assigned mainly to service branches instead of combat Minorities “Double V” - victory over the dictators abroad & over racism at home – Membership in NAACP increased – 1942 – CORE is founded • Congress for Racial Equality Native American Exodus – Many left the reservations & moved to cities or enlisted – 25,000 served – “code talkers” – Comanches in Europe & Navajos in Japan • codes were never broken Holding the Home Front Americans at home suffered little from the war compared to other countries – Economy was invigorated – Employment was high – Rationing – Office of Scientific Research & Development • Established a partnership between gov’t & universities National Debt skyrocketed - $259 billion in 1945 The Rising Sun in the Pacific Japanese – win quickly or lose slowly – Allied defeats: during the first 6 months, it looked like the Allied Powers would lose the war Japanese took: – Guam, Wake Island, Hong Kong, Singapore, Burma, Dutch East Indies, & the Philippines • Important Burma Road supply route into China from India was cut The Philippines US troops led by General Douglas MacArthur withdrew to Bataan, close to Manila, but eventually surrendered – Bataan Death March – 85 mile forced march of GIs who were tortured & eventually burned alive – MacArthur was ordered by Washington to leave secretly for Australia – “I shall return” Doolittle Raid : US executed a militarily insignificant raid on Japan in April, 1942 – Helped US moral Japan is Pushed Back Battle of the Coral Sea (May 1942) – Entire battle fought with aircraft – Japan prevented from successfully invading New Guinea & Australia Battle of Midway (June 4-7, 1942) – Turning point // Admiral Chester W. Nimitz – Allies broke the Japanese code – Japan suffered severe loses – Japan no longer had any hopes of attacking US mainland Island Hopping Campaign begins in 1943 – Eventually pushed Japanese forces all the way back to Japan – Sought to neutralize Japanese island strongholds with air and sea power & then move on – Battle of Guadalcanal (Solomon Islands – Aug 1942 – Feb 1943) • First Japanese land defeat after 6 months of bitter jungle fighting The Allied Halting of Hitler German U-boats sunk 8 million tons of allied supplies (25% of USSR’s) Germans were as far east as Stalingrad by fall 1942, & as deep as El Alamein, Egypt Battle of Stalingrad (Sept 1942) – Very important battle – First major NAZI defeat on land – German army in retreat from the east until Berlin is occupied by the Russians in the spring of 1945 – Stalin never forgave the Allies for not opening a 2nd front earlier, USSR had to bear the brunt of Nazi invasion North Africa Operation “Torch” – led by Gen. Eisenhower on Nov 8, 1943 – Germans were led by General Erwin Rommel (the Desert Fox) – Allied troops invaded N. Africa in Algeria & Morocco Battle of El Alamein – major victory for Allies – Signaled end of Nazi presence in N. Africa Italy Invasion of Italy commanded by George Patton – July 10, 1943 – British & US forces land on Sicily; victorious within 1 month – Mussolini was forced out of power (1943) – October 1943 – Italy declares war on Germany – June 4, 1944 – Allied march into Rome • First capital city freed from Nazi control – Other parts of Italy remain under NAZI control until Spring 1945 Tehran Conference Nov 28 – Dec 1, 1943 First meeting of the “Big Three” – FDR, Stalin, & Churchill Agree on an invasion of Western Europe Stalin confirmed Soviet commitment to war against Japan D-Day June 6, 1944 – “Operation Overlord” – Commanded by Eisenhower – 120,000 troops left England & landed at 5 beachheads at Normandy Coast • 800,000 more men within 3 weeks, 3 million total Significance: – Established a second front – Troops entered Paris on Aug 25 • By the end of summer, Belgium, France, & Luxembourg liberated Presidential Campaign 1944 Democrat – FDR & Harry S Truman Republican – Thomas Dewey – Platform: 12yrs was too long FDR is elected to a 4th term – Experience played a major role Last Days of Hitler Pre-invasion bombing – Berlin & other major cities were hit repeatedly • Especially factories & oil refineries Allied invasion (Sept 1944) repelled by Germany – Allies arrived on the edge of Germany by mid Sept Battle of the Bulge – Dec 16, 1944 – Germans launched a major offensive on US positions in Belgium & Luxembourg – General George Patton & his airborne division stopped Hitler’s last gasp counter-offensive – By Jan, the Allies were again advancing toward Germany War in Europe Comes to an End April 1945 – US approach Berlin from west while Soviets come from east – Hitler committed suicide in an underground bunker on April 30, 1945 – FDR dies of natural causes – April 12, 1945 • Truman steps in Depth of the Holocaust is uncovered V-E Day “Victory in Europe Day” – May 7, 1945 – Germany surrendered unconditionally Japan Dies Hard Feb 1945 – Iwo Jima – Fighter planes were now close enough to bomb Japan April – June, 1945 – Okinawa – Fierce fighting which virtually destroyed Japan’s remaining defenses Japan still showed no willingness to surrender Potsdam Conference Held in near Berlin in July 1945 US & Soviet Union warn Japan to surrender or be destroyed – Tens of thousands leaflets were dropped in Japan Japan refuses removal of emperor – show some signs that they may surrender if they can keep their emperor The 1st Atomic Bomb Manhattan Project – secret plans to build an atomic bomb – Albert Einstein worked on project Bomb was tested in New Mexico July 16, 1945 Aug 6, 1945 –Atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima – 180,000+ died – Bomb was dropped by the Enola Gay – Japanese still refuse to surrender nd 2 The Atomic Bomb Aug 9, 1945 – bomb dropped on Nagasaki – 80,000+ died Japan agreed to surrender under one condition: keep Emperor Hirohito – Allies accepted condition on Aug 14, 1945 Sept 2, 1945 – Official surrender on board the USS Missouri in Tokyo Bay (MacArthur was there) – V-J Day - “Victory in Japan Day”