* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download for starters
World War II casualties wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
United States home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
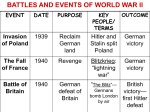
FOR STARTERS • Timeline Questions pgs. 772-773: • Write out and answer the following questions. 1.) When did France surrender to Germany? 2.) Why did the United States enter WWII? 3.) Where did Allied troops land on D-Day? FOR STARTERS • Read the Political Cartoon on pg.781 then answer questions 1-3 in the Political Cartoon Skills Box FOR STARTERS • You are a young person during World War II…create a list of 5 things you could do at home and in the community to help win the war. (if you are having trouble creating the list refer to page 789) FOR STARTERS • On page 786 read “Relocation of Japanese Americans” under Viewing History then answer the question in bold. FOR STARTERS • Write out and answer the following questions: 1.) What country did Germany invade in 1939? 2.) What was the name of the fictional factory worker we have discussed? 3.) What was the “Double V” campaign? FOR STARTERS • On page 798 read “Americans Remember the Holocaust” under Viewing History then answer the question in bold. FOR STARTERS YES OR NO?? • Should the United States have dropped atomic bombs on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki to end the war in the Pacific?...WHY? *BE READY TO DEFEND YOUR ANSWERS* FOR STARTERS Now that we have discussed the issue of the atomic bomb, has your opinion changed as to whether we should or shouldn’t have dropped the bombs? Explain your answer. FOR STARTERS Which World War II event or person do you think is the most interesting? Why? FOR STARTERS Write one paragraph describing the person you have been given for the “I Am” poem. FOR STARTERS Do you think another World War is possible? What do you think would be the result if it happened? FOR STARTERS • 3.2.1 Summary! List: 3 vocabulary words you have learned 2 Important People we have talked about AND… 1 Important event that took place CONTENT OBJECTIVES • 2.8.3 Read and use informational tools • 8.8.6 Identify causes, effects, and outcome of World War II, including: legacy of WWI, Pearl Harbor, Allies, Axis powers and leaders, atomic bomb, & United Nations • 8.8.7 Identify key elements of the Holocaust, including: “Aryan supremacy” , Kristallnacht, “Final Solution”, concentration and death camps • 8.8.8 Identify the effects of WWII on the home front in the United States and Nevada, including: end of the Great Depression, internment camps, rationing, propaganda, & “Rosie the Riveter” LANGUAUGE OBJECTIVES • SWBAT: • Fulfill the content objectives by analyzing primary sources, taking notes, and viewing pictures and photos. WORLD WAR II • • • • • • • • • • KEY TERMS: Totalitarian State Fascism Aggression Scapegoat Concentration Camp Appeasement Rationing Victory Garden Compensation Holocaust TOTALITARIAN STATE TOTALITARIAN STATE FASCISM AGGRESSION SCAPEGOAT CONCENTRATION CAMP APPEASEMENT RATIONING VICTORY GARDEN • During World War I and World War II, the United States government asked its citizens to plant gardens in order to support the war effort. Millions of people planted gardens. In 1943, Americans planted over 20 million Victory Gardens, and the harvest accounted for nearly a third of all the vegetables consumed in the country that year. Emphasis was placed on making gardening a family or community effort -- not a drudgery, but a pastime, and a national duty. COMPENSATION HOLOCAUST WORLD WAR II 1.) France 2.) Great Britain 3.) United States 4.) Soviet Union **50 Nations in ALL** Churchill Stalin de Gaulle Roosevelt Joseph Stalin gained power of the Soviet Union (U.S.S.R.) in 1924. He was a totalitarian dictator. He punished or killed his “enemies” Stalin modernized industry and agriculture Government took away all private property 3 Main Powers 1.) Germany 2.) Japan 3.) Italy (there was 9 countries in all) HITLER TOJO MUSSOLINI Hitler brought the National Socialist German Workers’ Party, or Nazis, to power in Germany in 1933. He ended democratic rule and created a militaristic totalitarian state. The government controlled the press, schools, and religion. He began to rebuild Germany’s military. Hitler blamed Jews and other traitors for Germany’s problems. Hitler preached that Germans belonged to a superior race. The Jews were deprived of citizenship, forbidden to use public facilities, and driven out of their jobs. Hitler would unleash his plan to kill all European Jews. Benito Mussolini and his Fascist party seized power in 1922. Mussolini outlawed all political parties except his own. He controlled the press and banned criticism. Critics were jailed or murdered. Mussolini promised to restore the greatness of ancient Rome. He began a program of military aggression. Japan suffered during the Great Depression. People grew impatient with their democratic government, and military leaders took power. Like Hitler, these leaders preached racial superiority. In 1938, Germany annexed Austria and later claimed the Sudetenland (Western Czechoslovakia) This action violated the Treaty of Versailles. • Britain and France should have declared war, but didn’t In September, leaders of Britain, France, Italy, and Germany met at the Munich Conference • Hitler promised that Germany would take no further territory once it had the Sudetenland. Britain and France agreed. (Aug. 1939) Hitler and Stalin signed Nazi-Soviet Pact. Agreed not to attack each other and they agreed to divide Poland. (Sept. 1939) Hitler launched a blitzkrieg, or lightning war, against Poland. The Poles surrendered and would be controlled by Germany in the west and the Soviet Union in the east. Hitler would eventually betray Stalin. Two days after Hitler’s invasion of Poland, Britain and France declared war on Germany. World War II had begun. By June of 1940 Germany had gained control of much of Europe including France Britain now stood alone against Germany. After the invasion of Poland, F.D.R. said U.S. would remain neutral even though many Americans favored the allies. The U.S. passed the Lend-Lease Act in March of 1941 (Britain was going broke) • This Act allowed the sales or loans of war materials to “any country whose defense the President deems vital to the defense of the U.S.” On Sunday morning, Dec. 7, 1941, Japanese planes attacked the American Pacific fleet anchored at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. Japan thought the attack would force the U.S. to beg for peace immediately. American aircraft carriers survived the attack because they were at sea at the time. The Japanese did not bomb the fuel oil tanks—a mistake because that fuel would help us in war. Americans were alarmed by Japanese aggression in Asia. In September 1940, Japan signed an alliance with Germany and Italy. The United States tried to stop Japanese aggression by refusing to sell oil and scrap metal to Japan. Japanese and American officials met in Nov. 1941. The two sides tried to reach an agreement. Neither side would compromise The first task was to train forces for combat. The government imposed rationing on the amounts of certain goods that people could buy. Americans planted victory gardens. The government raised taxes and borrowed money from citizens by selling war bonds. Almost five million women entered the work force. They replaced the men who joined the military War work gave women better pay and working conditions than before. Many women began to dress for work in trousers and overalls. Women gained a new sense of confidence. Rosie the Riveter was the face of working women “Rosie the Riveter” was a fictional factory worker, who became the symbol of American women’s contribution to the war effort Decided to pursue a “Double V” campaign—victory over the enemy abroad and victory over discrimination at home. Nearly a million enlisted or were drafted into WWII. Served in all-black units with white officers. Tuskegee Airmen, who were trained in Tuskegee, Alabama, were African American fighter pilots who destroyed or damaged roughly 400 enemy aircraft. After Pearl Harbor, Japanese Americans were forced from their homes to “relocation camps.” Even people who were American citizens by birth were relocated. Forced to sell property and businesses at a loss. Lived in crowded barracks behind barbed wire. 7 Future American Presidents Views of the World Were Formed by Their Service in World War II SUMMARIZE By 1942, Germany controlled most of Europe and their submarines were sinking ships faster then we could replace them. Japan was sweeping across Asia The situation did not look good for the Allied Forces. On June 6, 1944, a fleet of 4,000 Allied ships carried the invasion force to France. The troops scrambled ashore at Normandy. Despite intense German resistance, the Allies pushed on. The Allies reached Paris on August 25, 1944. Within a month, France was free. In 1944, President Roosevelt ran for a fourth term. His running mate was Harry S Truman of Missouri. Roosevelt and Truman won the election. While on vacation in Georgia in April 1945, Roosevelt died. By April 1945, Germany was collapsing. Allied forces were closing in. Sensing defeat Hitler would commit suicide. On May 7, 1945, Germany surrendered. On May 8, the Allies celebrated V-E Day— Victory in Europe. The United States had two goals: to regain the Philippines and to invade Japan. To gain control of the Pacific Ocean, American forces used the strategy of island-hopping. Japanese kamikaze pilots would fly their planes into American ships (like a bomb) Japanese leaders stressed an ancient code—the Way of the Warrior. To surrender was to be dishonored. In suicide missions, kamikaze pilots loaded old planes with bombs and crashed them into Allied ships. Navajo soldiers radioed messages from island to island in a code based on the Navajo language. The Japanese intercepted the messages but could not understand these Navajo code-talkers. Allied leaders sent a message warning Japan to surrender or face “prompt and utter destruction.” (Potsdam Declaration)--the Japanese ignored the message. On August 6, 1945, the American bomber Enola Gay dropped an atomic bomb on Hiroshima, Japan. The blast killed 70,000 people and injured an equal number. Many people died later from the effects of atomic radiation. On August 9, a second bomb was dropped on Nagasaki. Hiroshima Nagasaki On August 14, 1945, Emperor Hirohito announced that Japan would surrender. The formal surrender took place on September 2 aboard the USS Missouri in Tokyo Bay. V-J Day(Victory in Japan) sparked wild celebrations across the United States. World War II was the deadliest war in history. The exact number of casualties will probably never be known. Historians estimate that between 30 million and 60 million people were killed US Debt 1940 - $9 billion US Debt 1945 - $98 billion The war cost $330 billion -- 10 times the cost of WWI & as much as all previous federal spending since 1776 6 million Jews 1.5 5 million children under 12 million “Other Undesirables” 11 MILLION KILLED