* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Victory in Europe
Collaboration with the Axis Powers wikipedia , lookup
Spain during World War II wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
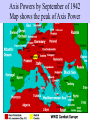
Joining the War Ike speaks to soldiers in Britain prior to D-Day Section 12.3 June 6, 1944 Capture: Americans in landing craft, June 6, 1944 What events led these Americans to end up in Normandy, France? Capture: Americans pull up to beach at Normandy Describe December 7, 1941. • “A date which will live in infamy.” • Japanese planes attacked Pearl Harbor, Hawaii (naval base) • Destroyed 19 battleships, 188 planes • Killed 2, 400 Americans • United Americans in call for war – “Remember Pearl Harbor” Above: Pearl Harbor burning; Below: FDR asks Congress for declaration of war on Japan Mobilizing America Capture: Times Square Times Square: Summer of 1941 Who were the Allies/the Axis Powers? Allies • United States • Great Britain • Soviet Union • And many others Axis Powers • Germany • Italy • Japan Left to Right: Stalin, Roosevelt, Churchill “The Big Three What was the Allied strategy for fighting WWII? • Defeating Germany is most important • Unconditional surrender of Axis powers • “Closing the Ring” – Plan to encircle Nazi Germany on all sides • Defensive war in Pacific World map showing areas of German and Japanese control Barbarossa Barbarossa: Hitler’s invasion of Soviet Union Describe the invasion of the Soviet Union. • Began June 22, 1941 (Summer) • Blitzkrieg tactics and surprise • Surrounded Leningrad for 900 days • 300 thousand Germans attacked Stalingrad • Access to oil • Russians stopped advance • Marks to turning point of the war • Stalin bitter about lack of Allied support Above: German tanks Below: Hitler heads in three directions Siege of Stalingrad Capture: Siege of Stalingrad Axis Powers by September of 1942 Map shows the peak of Axis Power Hitler’s Plan: Operation Barbarossa Capture the wheat fields of Ukraine, then advance east across North Africa and South from Russia to capture the oil fields of the Middle East. Oil Fields Stopping Hitler’s Advance • The Allies Finally Stopped Hitler’s Advance at Three Key Areas: • Battle of Britain • El Alamein in Egypt • Stalingrad in Russia See Map on Next Slide In spite of these losses, Hitler was firmly entrenched in Western Europe. (Map shows Allied counter-offensive) Russian Advance After Stalingrad Allied Invasion of N. Africa 11/42 To complete the encirclement of Hitler -‘Closing the Ring’the Allies needed to land somewhere in France. (Map shows location of Normandy Invasion) Normandy Beach, France June 6, 1944 Old Glory finally planted on Omaha Beach Place the following events in order from 1st to last. Now put the year they occurred. • • • • • • • • Event Operation Barbarossa Treaty of Versailles Hitler named Chancellor Munich Pact D-Day Invasion of Poland Pearl Harbor • Year What was Operation Overlord? • Allied invasion of Europe • Began with D-Day – Deliverance Day/ Disembarkment Day) June 6, 1944 • Bad weather delayed invasion by one day • Was it successful? – 10 thousand casualties in two weeks – Allies built man-made harbor – Allowed hundreds of thousands of soldiers and equipment to gain foothold in western Europe View from Higgins boat D-Day Military funeral of D-Day dead What was the Battle of the Bulge? • Hitler’s last major offensive • Caught Allies off guard • Goal was to capture Antwerp • Germans surrounded town of Bastogne asked for surrender – “Nuts” was the reply • Weather broke in January and supplies replenished Top: Map of the Ardennes; Bottom: corpses at Bastogne Bastogne Video capture: Americans at Bastogne The Progress of the War Axis Nations Allied Nations Neutral Nations Communist Nations World map showing the relative size and location of Axis and Allied nations The Camps Capture from ‘Band of Brothers’: Liberating the Camps What was the Holocaust? • Genocide or systematic murder of Jews, Gypsies, Slavs, and others the Nazis considered undesirable • Final Solution – Nazi decision to attempt to exterminate the Jewish race from Europe • 6 million Jews murdered (66% of the population in Europe) Entrance to the death camp at Auschwitz II Describe the process of the Final Solution. • Occurred gradually over time • Nuremberg Laws of 1935 – German laws used to identify and discriminate against Jews in Germany • Could not attend schools, hold public office, sit on park benches • Must wear yellow star • Ghettos (1939) – Jews were forced to reside in overcrowded, unsanitary areas of conquered cities Above and below: Nazis persecuting Jews The “Liquidation of the Ghetto” Video capture: German troops enter the Warsaw Ghetto “Wall of Death” for Polish political prisoners, before Auschwitz was turned into a death camp. Under the building on the right, Nazis first used poison gas to kill. Describe the process of the Final Solution • Wannsee conference – Meeting in Berlin in 1942 – decision to systematically kill the Jews of Europe • Einsatzgruppen (1940) – Killing squads – Rounded up Jews from conquered areas and executed them • Concentration Camps – 1st for “political reeducation” – slave labor, medical experiments, starvation, murder by gas chamber Above: Auschwitz from the air Mr. Morris by tracks at Birkenau station near Auschwitz Crematoria with tourists and memorial candle Clockwise from left, Gas Chamber, Zyklon B pellets, famous entrance with “Arbeit Macht Frei” arch, random line of doomed people Dear Fellow Party Member [Parteigenosse] Luther! Enclosed I am sending you the minutes of the proceedings that took place on January 20,1942. Since the basic position regarding the practical execution of the final solution of the Jewish question has fortunately been established by now, and since there is a full agreement on the part of all agencies involved. I would like to ask you at the request of the Reich Marshal to make one of your specialist officials available for the necessary discussion of details in connection with the completion of the draft that shows the organizational, technical and material prerequisites bearing on the actual starting point of the projected solutions. I want to schedule the first discussion along these lines for 10:30 a.m. on March 6, 1942 at 116 Kurfürstenstrasse, Berlin. I therefore ask you that for this purpose your specialist official contact my functionary in charge there, SS-Obersturmbannführer Eichmann. Reinhard Heydrich What was V-E Day? • “Victory in Europe” • May 8, 1945 • Germany surrendered unconditionally to the Allies • FDR had died April 12 • Hitler had committed suicide April 30 • US still at war with Japan Above and below: newspapers proclaim Victory in Europe VE Day Capture: V-E Day