* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Isolationism to World War II
German occupation of Czechoslovakia wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Anglo-German Naval Agreement wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
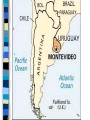
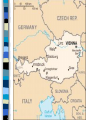
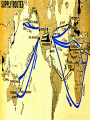
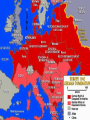
Moving from Isolationism to War Franklin Delano Roosevelt President at the start of World War II Elected to four terms as President *Other important events during presidency: • Great Depression Dictatorship a country, government, or the form of government in which absolute power is exercised by a dictator. EUROPE - DICTATORSHIPS ITALY – Benito Mussolini GERMANY – Adolf Hitler SPAIN – Francisco Franco Good Neighbor Policy The United States wanted to become better friends with their American neighbors. Why? • Rise of dictatorships in Europe and Asia worried U.S. about a possible rise in Latin America • U.S. had to establish friendlier relations with Latin America or else risk creating hostile neighbors. Montevideo Conference (Uruguay) U.S. pledges NOT to interfere in the affairs of its neighbors Constant intervention by U.S. was thought to breed anti-American sentiment among Latin Americans Montevideo Pact “No state has the right to intervene in the internal or external affairs of another state” – U.S. foreign policy change: no longer one of armed intervention in Latin America Trade Friendly Partners Canada, France, and Great Britain Laid groundwork for political cooperation in WWII REVIEW What was the Good Neighbor Policy? Who were our trading partners? Define “Dictatorship.” Name three, threatening dictators. Rise of Fascism System of government concentrating all political, economic, and cultural power in the state. Dictatorship What type of power does a dictator have? Who were the three dictators in Europe? DICTATORSHIPS Hitler Mussolini Franco What countries? Economic Situation What were the economic situations in these countries? How did that aid the rise of dictatorship? One last Dictator: (U.S. friend before the Cold War) Joseph Stalin (Soviet Union/Russia) – Friendly to U.S. • U.S. – suspicious of Stalin (Communism) PROPOGANDA Form of advertisement meant nobilize the home country and demonize the enemy. Propaganda and War Governments use propaganda during times of war • Why? Anti-west (Post WWII) Anti-western Propaganda (Cold War) Dictators Mussolini • Wanted Middle-East and Mediterranean Sea Japanese War Lords • Complete control of East Asia Hitler • World conquest Stalin • Spread communism Franco • Less aggressive than the other dictators • Came to power in Spain after a bloody civil war Dictators AGAINST – Free Speech – Free Press – Individual Freedom FOR – Glorifying FORCE – Strong military On the Move ITALY – 1935 invades Ethiopia • Use bombers • Poison Gas • What kind of defenses did Ethiopia have? Japan 1934-35 Rapidly build up military and navy • Break pledges made in Washington Conference – Washington Conference » Conference where naval powers of the world agreed to a set ratio limiting their naval power in a step toward peace and limiting future arms races. Germany 1936 Invade Rhineland Break Treaty of Versailles AXIS Powers Why called Axis? Which countries were in the Axis? Axis Term developed by Mussolini, the line from Rome to Berlin formed the “axis” on which the world would turn thereafter. Japan / Germany / Italy American People’s Feelings About the War Disillusioned that WWI did not bring peace Did not bring disarmament Did not bring democracy worldwide Failure to reduce armaments Quarreling among European powers Tariff wars Failure of the League of Nations Not an effective instrument of peace U.S. wise not to join because it was designed to fail How? Would U.S. joining have helped? League of Nations fail to check the aggressions of the Axis powers What did the League lack? WHY did it fail? U.S. Argument Against War #1 Atlantic and Pacific A natural protection Improved relations with Latin America gave even more protection/even if dictators won Europe and Asia U.S. Argument Against War #2 Depression Many Americans felt the U.S. priority was fixing the depression (What did the depression influence in the 1930’s?) U.S. Argument Against War #3 Pacifism Belief that ALL war was unjustified Backed isolationists Why? U.S. Argument Against War #4 Money Unpaid war debts from WWI Money from WWI benefited banks and business – It is typically viewed as a bad thing to make money off of something tragic (like war) Johnson Debt Default Act Forbade American Government and private American companies from lending money to any country that defaulted on their loans from WWI How is this a victory for the isolationists? American Annoyance Only Finland repaid war debt NOW countries who had defaulted on loans were pouring money into building up armaments ENTANGLING INVESTMENTS Neutrality Acts Prevented shipment of munitions to belligerents • belligerent Authorized President to list things other than munitions that could be sold to belligerents only on a “Cash and Carry” basis • Cash and Carry Against the law for Americans to travel on warring vessels • Lusitania Sinking 1915 • Restricted U.S. citizens on where and how they could travel The Other Side Not ALL Americans were isolationists Neutrality Acts made it difficult for U.S. to help victims of aggression – Moral duty to help victims Don’t act, may find ourselves surrounded by powerful enemies Quarantine Speech Compared Axis aggression as a disease Disease needs to be quarantined (like sick patients) U.S.S. Panay SUNK! Gunboat and 3 U.S. oil tankers Yangtze River Several Americans killed, many wounded Secretary of State Cordell Hull Demands full apology from Japan Compensation Promise not to have any future similar incidents. STILL Isolationist Attitude Prevailed – even after Panay Incident 54% of Americans believed U.S. should withdraw completely from China Aggression Continues How long will the U.S. hold out? Europe and the Axis Advance 1938 – Hitler moves his forces into Austria – Announces a German-Austrian union under Germany Hitler invades Sudeten Land Sudetenland – western part of Czechoslovakia (1938) Why? • Large area of Germany speaking people Hitler – Uniting the Germans Hitler saw his conquest of Austria and Czechoslovakia as uniting German Speaking peoples (Germans). Czechoslovakia Did not want to “unite” with Germany Had a well trained army Fellow democratic nations backed them • Who? Hitler Demands Sudetenland Czechoslovakia refuses • WHY? Munich Conference Hitler and Mussolini attended Great Britain and France attended • Great Britain forges a policy of appeasement • Will allow Hitler to invade as long as he will not move any farther • Hitler agrees • Appeasement? Prime Minister Chamberlain Believed a step toward peace Munich Conference Appeasement "The settlement of the Czechoslovakian problem which has now been achieved is in my view only the prelude to a larger settlement in which all Europe may find peace." Appeasement Why dangerous? What did it encourage? What did it show Hitler? Appeasement Hitler has the power to make demands Nation’s see the writing on the wall: begin to build up armaments at a faster speed. American Concern July 1938 Roosevelt asks Congress for appropriations to build up defenses • Appropriation Congress approves $1 Billion for a two ocean navy. Roosevelt Contacted Mussolini and Hitler Asked them to settle differences with negotiations and international cooperation Why did Mussolini and Hitler ignore the U.S.? • Isolationism Roosevelt Extends Monroe Doctrine to Canada Buenos Aires Conference of 1936 (threat to one is a threat to all) • Reaffirmed • 1938 Lima, Peru • 21 nations – Protect Western Hemisphere Pan-American Union To protect Western Hemisphere – Western Hemisphere Roosevelt’s Annual Message to Congress January 1939 Need appropriations for National Defense Reconsider Neutrality Legislation Axis Aggression Germany takes rest of Czechoslovakia – March 1939 Italy takes Albania – April 1939 Verge of World War Great Britain France • If Germany invades Poland, it means war. • What happens? • What does G.B. and France do? Soviet Union Great Britain and France Sign non-aggression pact with Germany – What does this mean for Germany? • No two front war • Cleared way for invasion of Poland Soviet Union Invades Poland from the east Germany invades Poland from the west Germany and Soviet Union split Poland Review What drew Britain and France into WWII Appeasement Why did Hitler invade Poland when he did? Great Britain and France Need military equipment U.S.A. can supply it Germany has plenty of armaments Neutrality Acts – How are they hurting Great Britain and France? Roosevelt “I regret that Congress passed the act” The Neutrality Acts favored Germany Britain and France really needed the military equipment Neutrality Laws Amended Anyone can buy munitions/arms from U.S. Must be transported on foreign ships. Declaration of Panama Pan American Union warns belligerents to keep war vessels out of a safety zone surrounding the continent (300-1000 miles wide) Disagreement Germany, France, Great Britain argue that no nation of group of nations had the right to close the high seas to their ships. Agreement showed cooperation of American countries Fall of France • April 9, 1940 Blitzkrieg – Lightning war Denmark, Norway, Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, N. France Italy declares war on France June 10, 1940 Sensed France was doomed Declares war on France France Signs Armistice Armistice June 22, 1940 a temporary suspension of hostilities by agreement of the warring parties Charles De Gaulle French National Committee pledges to continue resistance Rallied parts of French colonial empire against the Nazis Marshal Petain – new leader of German controlled French government. Battle of Britain Britain France has fallen Stood alone, and almost defenseless Winston Churchill Replaces Neville Chamberlain as Prime Minister of Britain. Churchill Rallied the British people Strengthened will to fight British will never surrender If Britain fell, it’s Empire beyond the seas would carry on the fight. Churchill “If we can stand up to him [Hitler], all Europe may be free and the life of the world may move forward into broad, sunlit uplands. But if we fail, then the whole world, including the United States, including all that we have known and cared for, will sink into the abuses of a new Dark age… Let us therefore brace ourselves to our duties, and so bear ourselves that, if the British Empire and its Commonwealth last for a thousand years, men will still say, ‘This was their finest hour.’ British August 1940 – Hitler unleashes blitzkrieg Royal Navy, Royal Air Force Hopelessly outnumbered Flew day and night Shot down 100 Nazi bombers in 1 day. Royal Air Force Hitler’s Reaction Adviser’s warn Hitler that an invasion of Britain would be suicidal American Response Building up defenses Alien Registration (Smith) Act Illegal for any person in the U.S. to advocate the overthrow of the government by force or violence, or to belong to an organization that advocated the violent overthrow of the government America Plans Act of Havana – Any American colony in danger, the American republics collectively would take control of the colony and maintain control through a group of trustees from the American republics. Permanent Joint Board of Defense Plan – Plan to defend the Western Hemisphere – Prime Minister Mackenzie of Canada Burke-Wadsworth Act September 1940 – All men 21-35 to register for the draft and made them liable for one year of military training. Lend Lease Program War materials flowing to Britain Britain does not have the cash for war materials Raise production of war materials so U.S. can LEND or LEASE materials to Allies Lend Lease Program FOR – Best hope for keeping us out of full participation in war AGAINST – Involve America in a shooting war Lend Lease Program $7 Billion for ships, planes, tanks, and anything else needed for Allies. Hitler invades Russia Non aggression pact? Two front war Lend Lease available to Russia The Atlantic Graveyard Ships being sunk by German submarines American ships convoy (accompany) merchant vessels carrying supplies Merchant ships would be armed, ordered to “shoot on sight” Atlantic Charter Churchill, Roosevelt Principals for a lasting peace. • Pledge for a world after war free of aggression • Every nation would have the right to adopt its own form of government Threat from Japan Occupied French Indonesia America’s Response Freezes Japanese assets Embargo on the shipment of • • • • Gasoline Machine Tools Scrap Iron Steel Trade between U.S. and Japan practically ends U.S. extends Lend-Lease to China. Japan America stiffening resistance Plans an attack Sends a ‘peace mission’ to U.S. Peace Mission November 1941 DEMANDS – U.S. must unfreeze assets – Supply Japan with as much gasoline as it wants – Cease aide to China United States Refuses Japanese demands Sunday December 7, 1941 Japan- further negotiations were useless U.S. showed no conciliation Before message got to U.S. planes were already attacking. Pearl Harbor December 7, 1941 Pacific Naval fleet damaged Pacific Air fleet nearly destroyed 2000 soldiers and civilians killed 2000 more wounded Pearl Harbor Roosevelt asks Congress for a declaration of war on Japan (Dec 8). Senate declares war unanimously, House only had one dissenting vote. American people, completely on board. December 11, 1941- Germany and Italy declare war on U.S. (U.S. then declares war on them) Pearl Harbor The United States enters WWII Essay Explain the 3 parts of the U.S. Neutrality Laws. What was the goal of the Neutrality Laws? In explaining the three parts, be sure to include what the Neutrality Laws prevented the shipment of, what they prevented U.S. citizens from doing, and explain the cash and carry policy. Name one country the laws favored? Name two countries the law hurt. How were the Nuetrality Laws amended (changed) and what country did the change favor? Essay Explain the Battle of Britain. Who was the Battle of Britain between? What role did Prime Minister Churchill play prior to, and during, the Battle of Britain? What challenge was the Royal Air force facing (think in terms of numbers)? For Hitler to invade Britain, what did he first have to gain control of? What two secret weapons/military intelligence did the British have against the Germans? If Britain fell, what did this mean for the United States?