* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Europe at War
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Collaboration with the Axis Powers wikipedia , lookup
Resistance in the German-occupied Channel Islands wikipedia , lookup
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Budapest wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
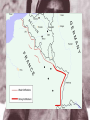
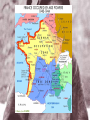
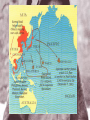
Europe at War • The 1939 invasion of Poland by Germany took just four weeks. • The speed and efficiency of the German army stunned the world. • Called blitzkrieg (“lightning war”), the Germans used panzer divisions (strike forces of about 300 tanks and soldiers) that were supported by airplanes. • On September 28, 1939, Germany and the Soviet Union divided Poland • In the spring of 1940, Hitler invaded Denmark and Norway • In May, Germany attacked the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. • The German armies broke through French lines and moved across northern France. • The French had fortified their border with Germany along the Maginot Line, but the Germans surprised them by going around it. • The Germans trapped the entire British army and French forces on the beaches of Dunkirk. • The British navy and private boats were able to evacuate 338,000 Allied troops, barely averting a complete disaster. • On June 22, the French signed an armistice with the Germans, who occupied three-fifths of France. • An authoritarian French regime under German control was set up to govern the rest of the country. • Led by Marshal Henri Pétain, it was named Vichy France. • Germany now controlled western and central Europe. • Only Britain remained undefeated. • On June 22, the French signed an armistice with the Germans, who occupied three-fifths of France. • An authoritarian French regime under German control was set up to govern the rest of the country. • Led by Marshal Henri Pétain, it was named Vichy France. • Germany now controlled western and central Europe. • Only Britain remained undefeated. • The British asked the United States for help. • The United States had a strict policy of isolationism. • A series of neutrality acts passed in the 1930s prevented the United States from involvement in European conflicts. • Though President Franklin D. Roosevelt denounced the Germans, the United States did nothing at first. • Roosevelt wanted to repeal the neutrality acts and help Great Britain. • Over time, the laws were slowly relaxed, and the United States sent food, ships, planes, and weapons to Britain. • Hitler understood that he could not attack Britain by sea unless he first controlled the air. • In August 1940, the Luftwaffe–German air force–began a major bombing offensive against military targets in Britain. • Aided by a good radar system, the British fought back but suffered critical losses. • In September, Hitler retaliated to a British attack on Berlin by shifting attacks from military targets to British cities. • He hoped to break British morale. However, the shift in strategy allowed the British to rebuild their air power and inflict crippling losses on the Germans. Britain would be lead through this trying time by the man that replaced Nevell Chamberlain-Winston Churchill. • Having lost the Battle of Britain, Hitler postponed the invasion of Britain indefinitely at the end of September. • We shall not flag or fail. We shall go on to the end. We shall fight in France, we shall fight on the seas and the oceans, we shall fight with growing confidence and growing strength in the air, we shall defend our island, whatever the cost may be. We shall fight on the beaches, we shall fight on the landing grounds, we shall fight in the fields and in the streets, we shall fight in the hills; we shall never surrender. • Winston Churchill “Never in the field of human conflict was so much owed by so many to so few.” Winston Churchill (speaking about the Royal Air Force) “Today we may say aloud before an awe-struck world: "We are still masters of our fate. We are still captain of our souls." Winston Churchill “Let us therefore brace ourselves to our duties, and so bear ourselves that if the British Empire and Commonwealth last for a thousand years, men will still say, This was their finest hour.” Winston Churchill • Hitler was convinced that the way to defeat Britain was to first smash the Soviet Union. • He thought that the British were resisting only because they were expecting Soviet support. • He also thought that the Soviets could be easily defeated. • He planned to invade in the spring of 1941 but was delayed by problems in the Balkans. • After the Italians had failed to capture Greece in 1940, the British still held air bases there. • Hitler seized Greece and Yugoslavia in April 1941. • Then Hitler invaded the Soviet Union in June 1941. • The attack on the Soviet Union stretched out for 1,800 miles. • German troops moved quickly and captured two million Russian soldiers by November. • The Germans were within 25 miles of Moscow. • However, winter came early in 1941 and, combined with fierce Russian resistance, forced the Germans to halt. • This marked the first time in the war that the Germans had been stopped. • The Germans were not equipped for the bitter Russian winter. • In December, the Soviet army counterattacked. • Why did Hitler decide to attack the Soviet Union after the two countries had signed a nonaggression pact? • On December 7, 1941, the Japanese attacked the U.S. naval base at Pearl Harbor in Hawaii. • They also attacked the Philippines and the British colony of Malaya. • Soon after, they invaded the Dutch East Indies and other islands in the Pacific Ocean. • In spite of some fierce resistance in places such as the Philippines, by the spring of 1942, the Japanese controlled almost all of Southeast Asia and much of the western Pacific. • http://www.nationalgeographic.com/pearlhar bor/ax/frameset.html • Videos • The Japanese created the Greater East-Asia Co-prosperity Sphere, which included the entire region under Japanese control. • Japan announced its intention to liberate colonial nations in Southeast Asia, but it first needed their natural resources. • The Japanese treated the occupied countries as conquered lands. • The Japanese thought that their attacks on the U.S. fleet would destroy the U.S. Navy and lead the Americans to accept Japanese domination in the Pacific. • However, the attack on Pearl Harbor had the opposite effect. • It united the American people and convinced the nation that it should enter the war against Japan. • Hitler thought that the Americans would be too involved in the Pacific to fight in Europe. • Four days after Pearl Harbor, he declared war on the United States. • World War II had become a global war. • How did the Japanese miscalculate the response of the United States to the bombing of Pearl Harbor? • A new coalition was formed called the Grand Alliance. • It included Great Britain, the Soviet Union, and the United States. • The three nations agreed to focus on military operations and ignore political differences. • They agreed in 1943 to fight until the Axis Powers–Germany, Italy, and Japan– surrendered unconditionally. • At the beginning of 1942, the Germans continued to fight the war against Britain and the Soviet Union. • The Germans were also fighting in North Africa. • The Afrika Korps under General Erwin Rommel broke through British lines in Egypt and advanced on Alexandria. • During the spring, the Germans captured the entire Crimea in the Soviet Union. • By the fall of 1942, the war had turned against the Germans. • In the summer of 1942, the British in North Africa had stopped the Germans at El Alamein. • The Germans retreated. • In November, British and American forces invaded French North Africa and forced the German and Italian troops to surrender by May. • videos • In his diary Joseph Goebbels recorded how he expected a quick victory in the Soviet Union (July 1941) • The Führer thinks that the action will take only 4 months; I think - even less. Bolshevism will collapse as a house of cards. We are facing an unprecedented victorious campaign. • Cooperation with Russia was in fact a stain on our reputation. Now it is going to be washed out. The very thing we were struggling against for our whole lives, will now be destroyed. I tell this to the Führer and he agrees with me completely. • On the Eastern Front, Hitler decided to attack Stalingrad, a major Soviet industrial center. • Between November 1942 and February 1943 the Soviets counterattacked. • They surrounded the Germans and cut off their supply lines. • In May, the Germans were forced to surrender. • They lost some of their best troops. • Hitler then realized that he would not defeat the Soviet Union. Statistics on Stalingrad • German Army Led by Paulus • 1,011,500 men • 10, 290 artillery guns • 675 tanks • 1,216 planes • Russian Army Led by Zhukov • 1,000,500 men • 13,541 artillery guns • 894 tanks • 1,115 planes • "My hands are done for, and have been ever since the beginning of December. The little finger of my left hand is missing and - what's even worse - the three middle fingers of my right one are frozen. I can only hold my mug with my thumb and little finger. I'm pretty helpless; only when a man has lost any fingers does he see how much he needs then for the smallest jobs. The best thing I can do with the little finger is to shoot with it. My hands are finished." Anonymous German soldier Why was this battle so important? • The failure of the German Army was nothing short of a disaster. A complete army group was lost at Stalingrad and 91,000 Germans were taken prisoner. With such a massive loss of manpower and equipment, the Germans simply did not have enough manpower to cope with the Russian advance to Germany when it came. • Despite resistance in parts – such as a Kursk – they were in retreat on the Eastern Front from February 1943 on. In his fury, Hitler ordered a day’s national mourning in Germany, not for the men lost at the battle, but for the shame von Paulus had brought on the Wehrmacht and Germany. Paulus was also stripped of his rank to emphaisze Hitler’s anger with him. Hitler commented: • "The God of War has gone over to the other side.“ Adolf Hitler • In 1942, the Allies had their first successes in the Pacific. • In the Battle of the Coral Sea in May, American naval forces stopped the Japanese and saved Australia from invasion. • In June, the Battle of Midway Island was the turning point in the Pacific war. • U.S. planes destroyed four Japanese aircraft carriers and established naval superiority. • VIDEOS • Why was the Battle of Midway Island so important? • U.S. planes destroyed four Japanese aircraft carriers and established naval superiority in the Pacific. • By the fall of 1942, Allied forces were about to begin two major operation plans against Japan. • One, led by General Douglas MacArthur, would move into the Philippines through New Guinea and the South Pacific Islands. • The other would move across the Pacific, capturing some of the Japanese-held islands and ending up in Japan. • By November 1942, after fierce battles in the Solomon Islands, the Japanese power was diminishing. Island Hopping in the Pacific • To defeat the Japanese the United States would have to take back Japanese controlled islands one by one. This strategy was referred to as island hopping. • Fighting in the Pacific Theater was terrible and extremely costly. One reason was the terrible weather conditions-at times weeks of monsoon like rain, volcanic ash on islands, and thick rainforests. • On each island we faced an enemy that had been preparing defenses for years and that refused to surrender. Often fighting did not end until almost every Japanese soldier was killed or committed suicide. • Islands like Peleliu and Guadalcanal were death traps. Allied forces would fight for weeks and months to control the island only to develop a false sense of security before fighting would erupt after short periods of stoppage. Civilian casualties were high in many of these locations and soldiers were faced to make gut-wrenching decisions during combat. • videos Last Years of the War • By early 1943, the tide had turned against the Axis forces. • In May, the Axis forces surrendered in Tunisia. • The Allies then moved north and invaded Italy in September. • Winston Churchill called Italy the “soft underbelly” of Europe. • As the bombing campaign increased against Germany, the invasion of Sicily moved ahead as well. • General Dwight D. Eisenhower was placed in overall command of the invasion. General Patton and General Montgomery of England controlled the troops on the ground. • In July of 1943, despite bad weather the Allied troops made it ashore with few causualties. A new vehicle the DUKW an amphibious truckproved to very effective at bringing in supplies and artillery to troops on beaches • Eight days later Patton’s troops smashed through enemy lines and captured the western half of the country-while his troops advanced Montgomery’s took the southern half-by August the Germans had evacuated • After the Allies captured Sicily, Mussolini was removed from office. • The king arrested him. • A new Italian government offered to surrender to the Allies. • However, the Germans rescued Mussolini and set him up as dictator of a puppet German state in northern Italy. • The allies would have to take this territory back. Allied troops landed behind enemy lines in Anzio. The German troops were not surprised and surrounded the allies. It took five months to break through the German lines at Cassino and Anzio. Fighting would continue until May of 1945. This campaign was one of the bloodiest of the war costing the allies 300,000 lives. • The Germans established a strong defense south of Rome. • The Allies had very heavy casualties as they slowly advanced north. • They did not take Rome until June 4, 1944. Roosevelt Meets Stalin at Tehran • Roosevelt met with Stalin before the invasion of France. In late 1943 Churchill, Roosevelt and Stalin met in Tehran, Iran • They agreed to several things-Soviets would attack German’s after invasion of France; Break up Germany after the war; Defeat Japan; create organization to keep peace. • Churchill and Roosevelt met in Egypt to plan the invasion-the first decision was to chose the leader of the campaign. Most expected George Marshall to lead the invasion, however Roosevelt depended on him for military advice. Dwight D. Eisenhower was chosen to lead the greatest military invasion in history. This invasion would be named Operation Overlord • The Germans realized that eventually the Allies would invade-they heavily fortified the coast of France • However the allies advantage was surprise-the Germans did not know when or where the invasion would be-they considered the most reasonable place was Pas-de-Calais-the area closest to France-to convince the Germans they were right the allies placed inflated tanks, tents and landing craft along the coast of Calais-to German spy planes the decoys looked real-the Germans were fooled and would not realize the actual target was Normandy • By the spring of 1944 everything was ready-over 1.5 million soldiers, 12,000 airplanes and more than 5 million tons of equipment had been sent to England. • The only thing left was to pick the date and give the command to go. The invasion would begin at night and arrive at low tide so that beach obstacles could be seen. The low tide had to come at dawn so the gunners bombarding the coast could see their target. Before the landing paratroopers would be dropped behind enemy lines. A date would have to be chosen when all of the conditions could be met. Bad weather would be disastrous to the mission. • Given all of these conditions there were only a few days each month that the mission could be launched. The first opportunity was between June 5-7, 1944. Eisenhower’s staff referred to any day that a mission began by the letter D. The date for invasion became known a D-Day. Bad weather made June 5th impossible, the next day the weather improved slightly. Eisenhower had to make a difficult decision and finally decided to move forward with the invasion. The Longest Day • Nearly 7,000 ships carried more than 100,000 troops towards the beaches, while 23,000 paratroopers were dropped behind enemy lines on June 6, 1944. Allied bomber and fighter planes raced up and down the coast hitting bridges, bunkers, and radar sites. As dawn broke warships let loose with a massive barrage of shells down on five beaches code namedGold, Omaha, Juno, Sword, Utah • The landing went well at Utah with only 200 troops being lostwithin three hours the beach had been taken-however at Omaha things went horribly wrong-An evacuation was almost ordered at this beach as men were killed by the thousandsAmazingly the tide slowly turned and when reinforcements arrived the German defenses broke and the beach was taken. By the end of the day over 100,000 allied troops had landed and the invasion was a major success. • . . . these men came here - British and our allies, and Americans - to storm these beaches for one purpose only, not to gain anything for ourselves, not to fulfill any ambitions that America had for conquest, but just to preserve freedom. . . . Many thousands of men have died for such ideals as these. . . but these young boys. . . were cut off in their prime. . . I devoutly hope that we will never again have to see such scenes as these. I think and hope, and pray, that humanity will have learned. . . we must find some way . . . to gain an eternal peace for this world. Eisenhowersenhower: A Soldier's Life • After the breakout, the Allies moved south and east. • French resistance fighters rose up in Germanoccupied Paris. • Paris was liberated by the end of August. • On 17 September 1944 thousands of paratroopers descended from the sky by parachute or glider up to 150 km behind enemy lines. Their goal: to secure the bridges across the rivers in Holland so that the Allied army could advance rapidly northwards and turn right into the lowlands of Germany, hereby skirting around the Siegfried line, the German defense line. If all carried out as planned it should have ended the war by Christmas 1944. • Unfortunately this daring plan, named Operation Market Garden, didn't have the expected outcome. The bridge at Arnhem proved to be 'a bridge too far'. After 10 days of bitter fighting the operation ended with the evacuation of the remainder of the 1st British Airborne Division from the Arnhem area. Battle of the Bulge • As the Allies closed in on Germany, Hitler decided to stage one last desperate offensive. His goal was to cut off Allied supplies coming through the port of Antwerp, Belgium. • December 16,1944 the battle began with six inches of snow on the ground and bitter coldGerman soldiers caught Americans by surprise-as the Germans moved west their lines bulged outward-the attack became known as the Battle of the Bulge • Part of the German plan called for the capture of the town of Bastogne, where several important roads converged. If the Allies held Bastogne, it would greatly delay the German advance. • At this town Germans surrounded the American forces that refused to surrender-Eisenhower sent Patton to rescue themIn three days-through a snowstorm-Patton’s troops slammed into German lines-when the weather cleared Allied aircraft began hitting German depots • On Christmas Eve out of fuel and weakened by heavy lossesthe Germans were forced to stop their move towards Antwerp. Two days later Patton’s troops were in Bastogne. The United States won the Battle of the Bulge and with the German arm being weakened there was little to stop the Allies from entering Germany • In March of 1945, the Allies crossed the Rhine River. • In the north they linked up with the Soviet army that was moving from the east. • In the north, Soviet troops occupied Warsaw in January 1945 and entered Berlin in April. • Along a southern front, the Soviets swept through Hungary, Romania, and Bulgaria. • The Soviets had turned the tables on the Germans in 1943. • They soundly defeated German troops in July at the Battle of Kursk in a huge tank battle. • Then they moved steadily westward. • By the end of 1943, they had reoccupied Ukraine. • By early 1944, they had moved into the Baltic states. • Germany was now under attack from the East and West. Soon the Americans would cross the last line of defense-the Rhine River and enter the heart of the Nazi war machine. The Death of Hitler? • As German defenses crumbled-Americans closed in on Berlin. • Deep inside a Berlin bunker, Adolph Hitler knew the end was near. On April 30, 1945, he put a pistol in his mouth and pulled the trigger. His secretary carried his body outside and burned it. • The United States ordered an unconditional surrender. On May 7, 1945 Germany surrendered. The next day May 8, 1945 was declared V-E Day-the war in Europe was over • Sadly Franklin Roosevelt would not live to see the defeat of Germany-On April 12, 1945 while vacationing in Warm Springs, Georgiahe suffered a stroke and died • Vice President Harry S. Truman was now president . He at once began making decisions. Truman would have to make some of the most difficult decisions of the war. • On November 24, 1944 bombs began falling on Tokyo for the first time since the Doolittle raid. Unfortunately the bombing was ineffective because the bombs kept missing their targets. Japan was to far away and by the time the bombers got there coordinates were inaccurate due to changes in winds or navigational errors. • It was determined that the best solution was to invade a nearby island-they chose Iwo Jima Uncommon Valor on Iwo Jima • The island was perfectly located, but was covered with rocky terrain, caverns, and dozens of caves, as well as a dormant volcano Mount Surabachi • The Japanese had built a network of tunnels on the island and concrete bunkers • On February 19, 1945- 60,000 U.S. Marines landed on Iwo Jima. As the troops left there amphtracs they sank up to their ankles in soft ash as Japanese artillery began to pound the invaders ( quote pg. 768 ) • The Marines would crawl inch by inch, fighting their way with flamethrowers and explosives destroying Japanese bunkers-6,800 Marines would die on Iwo Jima-Admiral Chester Nimitz would say “ uncommon valor was a common virtue” • Curtis LeMay-the commander of the B-29’sdecided to use a new strategy to help the bombers hit their targets-they dropped bombs filled with napalm-a kind of jellied gasolineeven if they missed the fire would spread to the targets • The use of these firebombs was very controversial-the fires would kill civilians-but there was seemingly no other way to destroy Japanese production facilities-strong winds spread the fires and thousands asphyxiated80,000 would die and 250,000 buildings were sestroyed-67 cities were bombed The Invasion Of Okinawa • Despite the bombing by the spring of 1945 there were no signs that Japan was ready to surrender-It became clear Japan would have to be invaded • Okinawa was chosen as the site-Japanese soldiers took positions in the mountains of Okinawa-facing constant machine and artillery fire, American soldiers fought there way up steep slopes and by June 22, 1945 the island was captured at the expense of 12,000 The Terms of Surrender • Shortly after Okinawa was captured the emperor urged the government to find a way to end the war. The problem is that America was demanding an unconditional surrender. The Japanese were willing to surrender, but the emperor would have to stay in power. Most Americans blamed the emperor for the war and demanded he be removed. Truman did not wish to go against public opinion. He also knew that the United States was developing a new weapon that would force Japan to surrender-the weapon was the atomic bomb. The Manhattan Project • In 1939 Leo Szilard, one of the worlds top physicists, learned that German scientist had split the uranium atom. He believed that this could release an enormous amount of energy. • Worried that the Germans were gone to develop a weapon using this energy, he asked the worlds most famous physicists Albert Einstein to sign his letter to President Roosevelt warning that by using uranium-” extremely powerful bombs of a new type may be constructed.” • Roosevelt responded by setting up a scientific committee to study the issue. They were skeptic until they met with British scientists and 1941 that were already working on the bomb-they were so impressed they began to work on building a bomb. • The American project was called the Manhattan Project and was headed by General Leslie R. Groves. After the first nuclear reactor was built at Chicago University-Groves organized a team of engineers and scientists to build and test an atomic bomb at a secret lab in Los Alamos, New Mexico-the team was lead by Robert Oppenheimer-On July 16, 1945-they detonated the worlds first atomic bomb near Alamogordo, New Mexico. • “I have become death, the destroyer of worlds.”-from the Mayan Book of Death • J Robert Oppenheimer • Faced with such massive destruction and the shock of the Soviets entering the war-Japan surrendered-August 15, 1945-V-J Day On the other side of the world Americans celebrated. Quote pg. 771 The long war was finally over.