* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
German occupation of Czechoslovakia wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Anglo-German Naval Agreement wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
The War That Came Early wikipedia , lookup
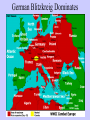
World War II World War II • Objective: – To Understand the causes of World War II. – To understand the major events that occurred during the war. – To understand the major turning points during the war. – To understand the events that led to the end of the war. ACTS OF AGGRESSION 1931 - Japan Invades Manchuria The Japanese army ignored the Japanese government and launched a fullscale invasion of Manchuria. Soon, it had occupied the whole of the province. The League of Nations opposes the attack and said it would deal with the government of the aggressor nation. But how could this succeed when the government had no control over the army which was the cause of the problem ? What does this incident tell us about the League of Nations? •The League could not enforce its authority. •A major power could get away with using force •An issue so far from Europe was not likely to attract the wholehearted support of the major European powers in the League. •Other powers would almost certainly see this episode as a sign that they too could get away with the use of force •The League also lost its most powerful member in the Far East and ultimately Japan was to unite with the two other nations that broke League rules - Germany and Italy. ACTS OF AGGRESSION 1935 – Italy Invades Ethiopia On October 3, 1935, Italy attacked Ethiopia from Eritrea and Italian Somaliland without a declaration of war. On October 7, the League of Nations unanimously declared Italy an aggressor but took no effective action. Benito Mussolini “I refuse to believe that the real people of Great Britain and France, who have never had discords with Italy, are prepared to run the risk of hurling Europe along the road to catastrophe for the sake of defending an African country universally branded as a country without the slightest shadow of civilization.” How Does Mussolini justify the attack of Ethiopia? Haile Selassie On June 30, Haile Selassie made a powerful speech before the League of Nations in Geneva in which he set forth two choices--support for collective security or international lawlessness. “It is my duty to inform the Governments assembled in Geneva, responsible as they are for the lives of millions of men, women and children, of the deadly peril which threatens them, by describing to them the fate which has been suffered by Ethiopia… Representatives of the World I have come to Geneva to discharge in your midst the most painful of the duties of the head of a State. What reply shall I have to take back to my people?” Acts of Aggression Lead to WWII Country Japan Italy Area Attacked Allies Reaction 1931 - Manchuria China 1. Need for natural resources. League of Nations condemned the action but did nothing. Ethiopia - Africa 1. Distract Italians from depression. 2. Promised to build the new Roman Empire League of Nations did nothing. Other nations concerned with their own problems. 1. Austria (1938) Germany Reason 2.Czechoslovakia/Sudeten -land (1938) 3. Poland (1939) 1. German people lived there. 1. None even though it was a direct violation of the treaty 2. German people lived there. 2. Hitler promised he was finished. Britain & France appeased and didn't fight. 3. Desire for land. 3. Britain and France declare war. AXIS POWER Adolf Hitler (right) is considered one of the most brutal dictators in history. After purging possible rivals for leadership, Hitler rearmed Germany into a modern war machine. He and Italian dictator Benito Mussolini (left), both Fascists, became allies in 1936. They are shown here in Munich, Germany, in 1937. GERMAN AGGRESSION Adolf Hitler preached to the Nazi party faithful that they were a superior race that deserved more than they had, including additional Lebensraum, or living space, and a higher standard of living. Hitler was an emotional speaker who had a mesmerizing effect on those who listened. By 1938 he had amassed the bestequipped, best-trained army in the world. GERMAN AGGRESSION Hitler invaded Austria in 1938. Many Austrians welcomed the Nazis and were content to see their country incorporated into Germany. The British Government, led by Neville Chamberlain, merely registered a diplomatic protest which was rejected by Germany. Hitler informs jubilant Nazi deputies in the Reichstag that Germany has annexed Austria, 1938. APPEASEMENT After Germany invaded the Sudetenland, the British and French met with Hitler at Munich on September 30, 1938. They agreed to allow the Nazi leader to seize the Sudeten districts of Czechoslovakia in return for an assurance from him that he had no further territorial claims in Europe. Their appeasement policy once again gave in to the demands of an aggressor. PEACE FOR OUR TIME! “My good friends… I have returned from Germany bringing peace with honor. I believe it is peace for our time… Go home and get a nice quiet sleep.” “An appeaser is one who feeds a crocodile, hoping it will eat him last.” - Winston Churchill On 15 March 1939, the German army occupied the remainder of Czechoslovakia. The Policy Of Appeasement Based on what you have learned, and these Dr. Seuss cartoons, what does ‘appeasement’ mean? Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact On August 23, 1939, the world was shocked when, suddenly, Russia and Germany signed a non-aggression pact. In addition, the two countries had a secret agreement to invade and divide Poland between them. What is the main idea of this political cartoon? GERMANY INVADES POLAND On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland. Hitler introduced a new kind of war called a blitzkrieg, which means “lightning war.” German bombers targeted railroads, shown here, which crippled Polish military mobilization. Hundreds of tanks smashed through Polish defenses and rolled deep into the country. The Poles fought hard, but on September 17, the Soviet Union invaded their country from the east. By the end of the month, Poland had fallen. Chamberlain Declares War Churchill is British Prime Minister for most of WWII . World War II Rages On Stage III: United States and Neutrality 1939 Isolationists The United States is sympathetic to the Allies but __________________ control the Congress. Roosevelt’s (FDR’s) Fireside Chats assure that the U.S. will remain __________________________. neutral _Lend Lease Act__: The U.S. will sell arms to Allies for cash and land in the Caribbean Islands French Refugees Taking only what they could carry, civilians flee Paris in 1940 in anticipation of the German invasion. The Invasion of France In May 1940, the Germans attacked France. The French army was caught off guard. The blitzkrieg sent French forces into a confused retreat, and as the Germans marched into Paris on June 14, the French government collapsed. German Blitzkreig Dominates The Battle of Britain In Summer of 1940, the German Luftwaffe hit London with the Blitz, with bombing raids on the capital and dog-fights in its sky during the Battle of Britain. Battle of Stalingrad (Invasion of the Soviet Union) Nazis Invade Russia Lend Lease Program March: _____________________________ The U.S. lends weapons to Britain who agrees to pay later. June: Hitler double crosses Stalin and invades the USSR, breaking the Nazi-Soviet Pact The Russian winter stalls the German advance. __________________. June: Japan joins the Axis Powers and seizes all colonies of Holland and France in Southeast Asia. August: Roosevelt and Churchill set goals for the postwar world in the ____________________. Atlantic Charter Some of the terms include: That no country seeks territorial gain, the support of the right of the people choose their own government and establish a system of world security. It also warned Germany neutral for much longer. that the U.S. would not remain _____________