* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WWII - West Linn High School
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
United States home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
The War That Came Early wikipedia , lookup
United States Navy in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
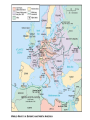
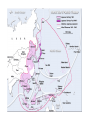
WWII Lecture Notes The American Mood: No More War • Most Americans did not want to intervene in European affairs • Congress passed a series of Neutrality Acts in 1935-37 – Isolationism Germany Steps Towards War • Hitler wanted to expand the German Empire • Hitler meets with Austrian chancellor Kurt von Schuschnigg – Put Nazi’s in the Austrian government – Germany “unites” with Austria, March 12, 2938 Going Against the Treaty of Versailles • Germany retakes the Sudetenland – Czechoslovakia – Czech’s were “abusing Sudeten Germans”. • Neville Chamberlain – British Prime Minister – “Peace in our time” • Winston Churchill – Appeasement – “They chose dishonor. They will have war.” Soviet Neutrality • Nonaggression Pact – August 23, 1939 – Agreement not to fight each other – Secret agreement to split Poland • Germany invades Poland September 1, 1939 – Blitzkrieg – Official start to WWII Jewish Refugees and America’s Response • Nuremberg Laws of 1935 – outlawed marriage, stripped Jews of citizenship, increased restrictions on social and economic life • Kristallnacht (Nov. 9-10, 1939) • Thousands of Jews left for the U.S. – Rejected From Isolation to Intervention • Roosevelt administration began to plan for war – Defeat of France led to peacetime draft • FDR won 3rd term in 1940 • Roosevelt proposed the “Lend-Lease” program in Jan. 1941 The War Economy • War Production Board – managed war-supply contracts – factories retooled to aid war effort • National War Labor Board – mediated labor disputes • Office of Price Administration – enforced price controls and rationing • American production won the war for the Allies The Home Front • Vast internal migration occurred during the war – movement to the West, urban areas • Women found opportunities in war industries – “Rosie the Riveter” – gender discrimination persisted • Children assisted with the war effort – collected scrap metal, rubber • American culture (movies, music, literature, art) were influenced by the war Propaganda and Politics • Office of War Information was created to shape public opinion • Media cooperated with the government to present a positive image of the war effort – created posters and films – Hollywood scripts were submitted for approval Noose Theory • The Allied approach to taking back Europe is sometimes referred to as the Noose Theory. – 3 fronts were involved (Eastern, Southern, Western) • The idea was to push Axis forces back to their homelands from all sides, effectively creating a noose. War in the Pacific • Japan continued to gain in the Pacific following Pearl Harbor – victories in Philippines, Singapore, Burma • Turning points came in spring of 1942 – Battle of the Coral Sea (May) – Battle of Midway (June) destroyed four Japanese aircraft carriers, ended efforts to expand in the Pacific The Pacific War • Allies led an “island hopping” campaign in the Pacific – air domination, capturing strategic islands • Japan, low on resources, began resorting to “kamikaze” tactics • U.S. prepared for an invasion of Japan The Atomic Bombs • Americans believed that Japan would fight to the death • Truman made the decision to drop the atomic bomb, which had been first tested just weeks before – Hiroshima – August 6, 1945 – Nagasaki – August 9, 1945 • Japan ceased hostilities on August 14th