* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Global Events Leading to World War II
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
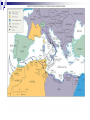
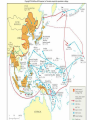
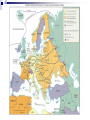
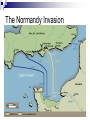
The Road to World War II HUSH Take Five for Pat Points… Why didn’t the League of Nations work? HUSH Take Five for Pat Points What were the reasons for the US not joining the League of Nations? Were we correct? Foreign Policy in the New Era (1919-1932) Fragile World Peace League of Nations Henry Cabot Lodge Washington Conference of 1921 Sec. of State Charles Hughes Five-Power Pact Kellogg-Briand Pact European Debt Dawes Plan Hoover’s Foreign Policy European nationalism Benito Mussolini National Socialist (NAZI) Party Adolf Hitler Benito Mussolini Adolf Hitler FDR’s Foreign Policy (1933---) World Economic Conference European debts U.S.-Soviet-Union relationship Latin America “Good-neighbor” policy Inter-American Conference Isolationism Father Coughlin & William Randolph Hearst Neutrality Acts (1935, 1936, 1937) Rise of Fascism The Formation of the Axis Coalition Japanese aggression Panay German aggression in Europe Appeasement Austrian invasion Lebensraum Sudetenland Munich Agreement British Prime Minister: Chamberlain: we have achieved “peace in our time” Violation of the Treaty of Versailles Jews fleeing Germany Nazi-Soviet Agreement Nonaggression Pact Joseph Stalin Joseph Stalin European Expansion (1939-1941) Germany invades Poland U.S.S.R. invades Latvia, Estonia, Lithuania and Finland Italy invades North Africa and the Balkans Polish “blitzkreig” A Divided Europe Allied powers Great Britain and its Empire, France Axis powers Germany, Italy and Japan The “Phony” War Anticipation…anxiety…nothing… Preparation along the Maginot Line “Blitzkreig” Scandinavia, Denmark, Norway Low Countries Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and Belgium Outflanking the Maginot Line German fighter plane Increased German Aggression “Blitzkrieg” The fall of France Vichy France Philippe Pe’tain Dunkirk Free French Resistance Charles de Gaulle Charles de Gaulle’s Free French Wounded in WWII Fleeing Paris War Destruction Appeal of Great Britain Battle of Britain Winston Churchill U.S. lifts the arms embargo U.S. Destroyers Winston Churchill Pat Points… Why did the US enter WWII? Who was the “Desert Fox”? What was so important to the allies in the middle east to protect? U.S. Public Opinion-Isolationists vs. Preparedness Burke-Wadsworth Act American First Committee Lend-lease Act The role of the British Empire Dominion states come to Great Britain’s aid Canada, New Zealand, Australia, S. Africa and India. Materials and troops for the war effort The British Empire stands alone North Africa Fighting against the Italians General Rommel Egypt-protecting the Suez Canal Fighting against the Germans General Rommel Continued German Aggression Invasion and control of Eastern Europe Hungary, Romania & Bulgaria Invasion of Yugoslavia Sending German troops to Greece Invasion of the U.S.S.R. Breaking the non-aggression pact Operation Barbarossa “scorched earth policy” Soviet winter The Road to War German expansion Invasion of the Soviet Union Submarine warfare Reuben James Atlantic Charter Tripartite Pact Germans in Stalingrad The U.S. Enters the War Japanese Aggression in the Pacific Attack on Pearl Harbor Admiral Yamamoto Attack of Guam, Wake Island, Malaya & Singapore U.S. Declaration of War Japanese internment camps U.S. Publicity campaign Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto Japanese “Zero” U.S. Declaration of War Off to War A War on Three Fronts Europe Stalingrad North African Offensive George S. Patton General Montgomery General Rommel The Pacific Battle of Bataan Death March “island-hopping” Battle of Midway Guadalcanal Dolittle Tokyo Raids U.S. Tank Division U.S. “Ace” in WWII—Maj. Richard Bong=40 “kills” Gen. Montgomery in N. Africa Guadalcanal Turning point of the war (1943-1945) Allied offensive in Europe Casablanca Conference Air raids Battle of Kursk Invasion of Italy D-Day The Normandy Invasion Reconquest of Belorussia Liberation of France Battle of the Bulge U.S. B-17 “Flying Fortress” The Normandy Invasion D-Day Troops General Eisenhower at Operation Overlord U.S. Destroying Romania Oil fields Plot against Hitler Gestapo SS Officers Hitler sends his sympathies Other world events The Death of FDR President Harry S. Truman Bringing an End to the War Allied forces invade Germany Berlin VE Day Hitler’s suicide Allied offensive in the Pacific Iwo Jima and Okinawa Kamikaze The development of the atomic bomb Manhattan Project General Leslie Groves Albert Einstein Truman’s ultimatum to Japan Hiroshima Enola Gay Nagasaki VJ Day Iwo Jima “Kamikaze raids” Atomic Bomb The Mushroom Cloud V-J Day-Japan Surrenders Take Five… Was it necessary for Truman to drop the second bomb on Japan in WWII? Why or why not? The American Homefront-A New Prosperity Wartime production Labor shortages “maintenance of membership” wildcat strikes Smith-Connally Act 1943 Fear of inflation Anti-Inflation Act 1942 Revenue Act of 1942 War Production Board Donald Nelson Take Five Describe the home front during WWII. What jobs were women and other minorities doing? What happened to the Hispanic population during WWII— they were deported during the Great Depression… Minorities in the War… Hispanics Zoot Suit Riots Braceros Japanese Americans Japanese Internment Camps Chinese Americans Native Americans “Code- Talkers” African Americans Women in the war “Rosie the Riveter” Women in the Military Decline of the family “Baby boomers” “Victory Bonds” Rosie the Riveter The Homefront (con’t) Entertainment and Leisure Rationing for the cause Swing clubs, movies and magazines Costs of the war Human causalities Financial costs Overall results of the war Take Five… Do you think that you could be convinced to “break the rules” or harm someone if someone in authority told you that it was acceptable? The Holocaust Balfour Declaration Kristallnacht “Night of the Broken Glass” The Wannsee Conference Concentration camps Auschwitz Resistance, Hiding and Jewish sympathizers Oskar Schindler Other Nazi atrocities Holocaust denial Auschwitz-”Hell’s Gate” Nazi “Doctors” Destroying Evidence Nuremberg Trials 16 Doctors were found guilty 7 convicted to death Japanese Atrocities Mass executions (China) Torture of P.O.W.’s Bataan Death March Soviet Atrocities Torture of Poles NKVD Labor Camps