* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WWII - Sign in | Movable Type
Reorganization of occupied dioceses during World War II wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Anglo-German Naval Agreement wikipedia , lookup
German occupation of Czechoslovakia wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Reichskommissariat Ostland wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
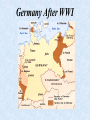
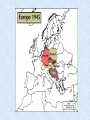
WWII - Introduction: • Most devastating war in human history • 55 million dead • 1 trillion dollars • Began in 1939 as strictly a European Conflict • Widened to include most of the world Remember: Celebration Time • Cheering the end of world war I, on Nov. 11, 1918. • The long, horrible war had taken the lives of nearly 10 million soldiers. Germany After WWI Third Reich • Nationalist • imperialism – Continental empire – Autarky – Elimination of nonGermans – Elimination of enemies The Empire of Japan – Autarky – Security – Expanding buffer zones • Anti-imperialist imperialism – Nationalist destiny – “Asia for the Asians” How It Began Lots of factors • WWI leftovers • Germany defeated in and had to pay cost of war. In huge economic depression • Italy victorious but wanted more territory • Japan victorious but wanted China • Outside factors… What Were These Outside Factors? • Germany reduced size • Organized League of Nations • French and Britain unsure • U.S. isolationist Fascism in Europe • Mussolini - “Il Duce”: 1922 – Invasion of Ethiopia - 1935 • Hitler - “Fuhrer”: Chancellor of Germany - 1933 – – – – Nazi Third Reich replaces Weimar Republic. Promise of German economic recovery. Beginnings of the Holocaust. German rearmament begins. • Spanish Civil War - 1930’s – Generalissimo Francisco Franco supported by fascists. • Agreement permits Germany to rebuild Navy - 1935. • Remilitarization of the Rhineland - 1936 – German rejection of the Treaty of Versailles. Rise of Hitler • Nazi Party organized, 1920s • Nazi party largest in Germany, 1932 • Hitler voted as chancellor, 1933 • New parliament created • 450, 000 members • Larger than German army Adolf Hitler “Fuhrer” Hitler Gets Busy • • • • • • Gestapo Created -- April, 1933 Jewish Boycott – April, 1933 Jewish Books Banned & Burned – May, 1933 27,000 People in Camps – July, 1933 60,000 People in Camps – 1938 Illegal to Leave Germany – October, 1941 German Territorial Gains • • • • • Austria – March, 1938 Border of Czechoslovakia – Sept., 1938 All of Czechoslovakia – March, 1939 Poland – Sept., 1939 By Summer of 1940, Germany Controlled Most of Europe • World shocked as France falls to Germans Beginnings of War in Europe • German annexation of Austria (Anschluss) - March 1938. • Munich Crisis - September 1938. – Czechoslovakia’s German-speaking Sudetenland. • • Appeasement of Hitler by Western leaders. British Prime Minister Chamberlain: “Peace in our time.” • German occupation of Czechoslovakia - March 1939. • Italian occupation of Albania - April 1939. • Guarantee of protection of Poland: Britain and France. – March 1939 (Also Holland and Belgium.) • Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact - August 1939 – Non-aggression treaty between Soviet Union and Germany. Start of World War II Germany's dictator, Adolf Hitler, had built Germany into a powerful war machine. World War II began on Sept. 1, 1939, when Germany invaded Poland. War in Europe • Invasion of Poland: Blitzkrieg - September 1939 – Tanks and Stuka dive bombers. – Soviet occupation of eastern Poland.. • May 1940 - Invasion of Netherlands, Belgium, and France. – Maginot Line proves ineffective to maneuver warfare. – Chamberlain yields office of Prime Minister to Churchill • Battle of Britain - Summer 1940. – Operation Sea Lion - planned German invasion of England. • Soviet annexation of Baltic States: June 1940. • Soviet invasion of Finland - November 1940. • German invasion of Soviet Union - June 1941. – Operation Barbarossa Germany Allies • Stalin and the Soviet Union, 1939 • Betrayed by 1941 • Mussolini and Italy, 1939 • Off and on betrayed until Italian defeat in 1943 Axis Powers Germany, Italy, and Japan formed an alliance known as the Axis. Six other nations eventually joined the Axis. Alliance That Changes War • Germany “allies” with Japan • Japan was “China Hungry” • Japanese angry over U.S. support of China • Agreed to peace negotiations with U. S. Japanese Imperialism in Asia • Expansion - Natural Resources – – – – Formosa (Taiwan) - Annexed: 1895 Korea - Protectorate: 1905 Annexed: 1910 Invasion of Manchuria - 1931 War with China - 1937 • USS Panay sunk on Yangtze River. • Chiang Kai-shek and Mao Tse-tung. – Occupation of French Indochina - 1940 • Embargo of oil and other natural resources - July 1941. – U.S., Great Britain, and the Netherlands. • General Tojo: Military government installed - October 1941. Hirohito Emperor of Japan World War II Pearl Harbor Dec. 7, 1941 Damages Allies United: U.S.S.R, England and The U.S. Normandy Invasion, D-Day General Eisenhower Speaks Talking to his men, general Dwight D. Eisenhower, commander of the Normandy invasion, wished paratroopers luck before they dropped behind German lines in France on d-day. D-Day - June 6, 1944 Landing on Normandy Beach It was the largest sea borne invasion in history. The Air War During world war II the B-24 bombers were used to strike factories, railroads, and other industrial targets. Some Casualties of World War II Prisoners Homeless Germany Surrenders May 7, 1945 Germany At The End Of WWII