* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download US History 8
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Propaganda in Japan during the Second Sino-Japanese War and World War II wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
United States home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Tora! Tora! Tora! wikipedia , lookup
Magic (cryptography) wikipedia , lookup
United States Navy in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
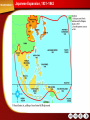
PresentationExpress The World War II Era (1935–1945) Aggression Leads to War The United States at War The War at Home Toward Victory Click a subsection to advance to that particular section. Advance through the slide show using your mouse or the space bar. 2 Aggression Leads to War The Rise of Dictators Main Idea: Postwar problems led to the rise of dictators in several nations. Military Aggression Main Idea: The rulers of Japan, Italy, and Germany sought to expand their territories and conquer other nations. American Neutrality Main Idea: The United States sought to stay out of growing world conflict while strengthening ties to Latin American. War Begins in Europe Main Idea: After invading Poland, German armies quickly conquered most of Europe. MapMaster: Aggression in Europe to 1939 Color Transparencies: Japanese Expansion, 1931–1942 Progress Monitoring Transparency TRANSPARENCY Japanese Expansion, 1931–1942 PM TRANSPARENCY Progress Monitoring Transparency The United States at War Moving Toward War Main Idea: Though the United States officially remained neutral, Roosevelt found ways to help Britain defend against the Nazis. The United States Enters the War Main Idea: The Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor brought the United States into World War II. Europe and North Africa Main Idea: The German advance was slowed by Soviet resistance and by Allied victories in North Africa. Japan Sweeps Through the Pacific Main Idea: Japan's rapid advance across the Pacific was finally halted in two major naval battles. History Interactive: Learn About Pearl Harbor Color Transparencies: Attack on Pearl Harbor MapMaster: World War II in North Africa Progress Monitoring Transparency TRANSPARENCY Attack on Pearl Harbor PM TRANSPARENCY Progress Monitoring Transparency The War at Home Organizing for War Main Idea: The United States increased the size of its military and directed the economy toward the war effort. Women in Industry Main Idea: During the war, American women took over many industrial jobs. Ordeal for Japanese Americans Main Idea: Because of wartime fears, many Japanese Americans were forced to live in detention camps. Tensions at Home Main Idea: Enemy aliens, African Americans, and Mexican Americans faced discrimination at home. Color Transparency: Rationing During World War II Progress Monitoring Transparency TRANSPARENCY Rationing During World War II PM TRANSPARENCY Progress Monitoring Transparency Toward Victory Victory in Europe Main Idea: The invasion of Italy and the D-Day landing in France set the stage for the defeat of Germany. Victory in the Pacific Main Idea: After a series of bloody battles on the Pacific Islands, the atomic bomb was finally used to defeat Japan. The Holocaust Main Idea: The world learned how the Nazis murdered 6 million Jews and millions of other people. Progress Monitoring Transparency PM TRANSPARENCY Progress Monitoring Transparency