* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Refraction - cashmerephysics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
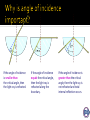
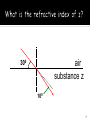
2 Angle of Incidence (°) Angle of Refraction (°) Angle of emerging ray(°) Refraction of light is the bending of light as it goes from one medium into another. This is because the speed of light changes. Angle of Incidence Angle of Refraction 5 When light waves travel from a less dense (air) to a more dense medium (glass), the ray is bent towards the normal. The speed of light depends on the material through which the light is travelling. When light enters a different material (e.g. from air into glass), the speed of light changes. This causes the light to bend or refract. air glass The speed of light is affected by the density of the material through which it is travelling. When light enters a more dense medium (from air into glass), its speed decreases and this is why refraction occurs Because the frequency of the wave is determined by the source, if the wave speed slows down, its wavelength must decrease. (And vice versa) Fast Medium low refractive index like air Slow Medium higher refractive index like glass Frequency stays the same 10 Refraction causes visual effects such as this ruler appearing to be bent. This happens because light from the part of the ruler in the water is refracted as it travels from the water into the air. How does refraction make this stone look closer to the surface of the water than it really is? image actual location Light rays from the stone are refracted as they leave the water. The brain assumes that these rays have travelled in straight lines and is fooled into forming an image where it thinks the light rays came from. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is refraction of light? Does the light bend towards or away from the normal when the light enters at an angle into a more dense medium? What happens to the speed of the light when it enters a more dense medium? What happens to the wavelength of the light when it enters a more dense medium? What is the speed of light? 12 is a measure of how much the speed is slowed when entering a medium from a vacuum (or air) n = speed of light in a vacuum speed of light in a medium Values include: n alcohol = 1.36 n diamond = 2.41 n glass = 1.52 n water = 1.33 Which substance does light travel the fastest? Why will you never get a number less than 1? 13 The speed of light in chloroform is = 2 x 108 ms-1 Calculate the refractive index (n) for cholorform Answer: n = 3 x 108 ms-1 2 x 108 ms-1 = 3/2 = 1.5 Calculate the speed of light in glass if n= 1.52 Answer: 1.52 = 3 x 108 ms-1 speed in glass Speed in glass = 3 x 108 = 1.9 x 108 ms-1 1.52 Calculate the speed of light in water and diamond Ans: in water = 2.26 x 108ms-1 :in diamond = 1.24 x 108ms-1 We can use the following equation: n1v1 = n2v2 Where n1 is the refractive index in medium 1 Where n2 is the refractive index in medium 2 Where v1 is the speed of light in medium 1 Where v2 is the speed of light in medium 2 A light ray travels from a vacuum (n1=1.0) into a container of water (n2=1.33). Calculate the speed of light in the water. Answer: n1v1 = n2v2 1 x 3 x 108 = 1.33 x v2 v2 = 2.26 x 108 ms-1 Dutch astronomer and mathematician Most famous for the law of refraction (Snell’s Law) Found a new method for calculating the radius of the earth as well as π 18 i Sin (i) r 15 10 30 18 45 29 60 32 75 39 90 41 Sin (r) 19 Plot a graph of sin (i) against sin (r) with sin (i) on the vertical axis. The gradient of the graph can be used to obtain the refractive index of the glass? Calculate the refractive index using this feature. n = sin (i) sin (r) A beam of light shines into a liquid. The angle of incidence is 31o and the angle of refraction is 22o. Calculate the refractive index of the liquid? Answer: n = sin 31 sin 22 = 0.51 = 1.4 0.37 n1v1 = n2v2 n1 n2 = v2 v1 = λ2 λ1 n1sin θ1 = n2 sin θ2 A ray of light enters plastic goggles from water at 25o to the normal. The ray deviates through an angle of 4.0o as it enters the plastic. The R.I. of the plastic is 1.5. Calculate the R.I. of the water. Answer: θ1 = 25o θ2 = 21o (it moves towards the normal because plastic if more optically dense) n1sin θ1 = n2 sin θ2 n1sin 25o = 1.5 x sin 21o n1 = 1.5 sin 21o sin 25o = 1.3 When a light ray hits the boundary between a material which is more dense (large n, slower speed) to a less dense medium d (e.g. glass and air), there is a critical angle θc at which the angle of refraction is 90o. If the angle of incidence of the light ray is greater than a specific value, called the critical angle, then the light ray is actually reflected. This is called total internal reflection. It makes the inner surface of glass act like a perfect mirror. If the angle of incidence is smaller than the critical angle, then the light ray is refracted. If the angle of incidence equals the critical angle, then the light ray is refracted along the boundary. If the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle, then the light ray is not refracted and total internal reflection occurs. 1) 2) 3) 4) Trace the outline of the plastic cube onto a piece of paper. Shine a light into the block. Mark down where the path of the light as it is refracted. Use Snell’s Law to find out the refractive index of the plastic block. 27 When light travels from a high to low refractive index, it bends away from the normal. A particular angle of incidence will cause the light to refract at 90º, ie along the boundary between the media. 28 This angle of incidence is called the critical angle qc. This can be calculated by putting qr= 90º into Snell’s Law. n1sin θ1 = n2 sin θ2 n1sin θc = n2 sin θr 29 Find the critical angle for the light to be totally internally reflected in the semi-circular plastic block. 30 The refractive index of glass is 1.52 and air 1.00. Find the critical angle for the glass. n1sin θ1 = n2 sin θ2 1.52 sin θ1 = 1.00 sin 90o sin θ = = θ = 1/1.52 0.658 41.1° 31 Different materials have a specific value for the critical angle: The critical angle is the smallest angle of incidence at which total internal reflection occurs. Material Critical angle water 49° acrylic plastic 42° glass 41° diamond 24° Diamond has the lowest critical angle at 24°. This means that diamond reflects more light than the other materials and accounts for its characteristic sparkle. Optical fibres are thin strands of solid glass, about the size of a human hair. They are widely used in communication, medicine, lighting and as sensors. The first transatlantic telephone cable to use optical fibres went into operation in 1988. Optical fibres can transmit light signals at high speed over long distances and are used in phone and internet connections. Optical fibres do not have to be straight to carry light and can even carry light around corners. This curved Perspex rod shows how light travels in an optical fibre. Light travels through the Perspex rod, and optical fibres, by a process called total internal reflection. 1) Endoscopes (a medical device used to see inside the body): 2) Binoculars and periscopes (using “reflecting prisms”) 35 A ray of light enters the optical fibre. light enters optical fibre As the light enters the optical fibre, it is refracted. This means that the direction the light is travelling in changes. The ray of light hits the wall of the fibre and is totally internally reflected when the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle. The ray of light passes down the optical fibre by repeated total internal reflection. light leaves optical fibre A scuba diver working at a depth of 6.0m beneath a smooth surface stops long enough to watch the sun set. At what angle from the normal should she look if the refractive index of the seawater is 1.38 n1 sin q1 n2 sin q 2 n2 sin q c n1 1.00 q c sin 1.38 q c 460 1 460 38 air substance z 300 100 39 n2 sin q1 n1 sin q 2 0 nz sin 60 0 1 sin 50 nz 1.13 40 A prism splits a ray of white light into the colours of the rainbow. This process is known as dispersion. The colours that make up white light are called the spectrum. The order of the colours in the spectrum is always the same. Use this phrase to remember the order of colours: Richard Of York Gave Battle In Vain Which colour is diffracted the most through the prism? Violet is the most violently diffracted wavelength. Red is only slightly diffracted. Violet has the highest frequency, energy and smallest wavelength. The atmosphere is densest (thickest) at the bottom, near the Earth. It gradually thins out as you go higher and higher up. The blue colour of the sky is due to Rayleigh scattering. As light moves through the atmosphere, most of the longer wavelengths pass straight through. Little of the red, orange and yellow light is affected by the air. However, much of the shorter wavelength light is absorbed by the gas molecules. The absorbed blue light is then radiated in different directions. It gets scattered all around the sky. As the sun begins to set, the light must travel farther through the atmosphere before it gets to you. More of the light is reflected and scattered. As less reaches you directly, the sun appears less bright. The colour of the sun itself appears to change, first to orange and then to red. This is because even more of the short wavelength blues and greens are now scattered. Only the longer wavelengths are left in the direct beam that reaches your eyes.