* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Telescopes and Spacecraft
Arecibo Observatory wikipedia , lookup
Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Allen Telescope Array wikipedia , lookup
Lovell Telescope wikipedia , lookup
James Webb Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Optical telescope wikipedia , lookup
Very Large Telescope wikipedia , lookup
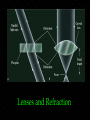
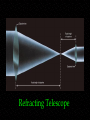
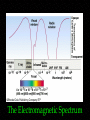
Telescopes Astronomy 315 Professor Lee Carkner Lecture 5 Blue star is hotter than red star From Wien’s law: short wavelength means higher temperature T (1/l) Image looks larger in photograph How can the red star be brighter even though it is cooler? Stefan-Boltzmann law P AT4 What colors are easy/hard to see? Eye is least sensitive to violet and red Alberio Star Colors What temperature are red, yellow and blue stars? Wein’s Law: 3,000,000/T = l Multiply each side by T Divide each side by l Red: l = 650 nm 3,000,000/650 = Yellow: l = 575 nm 3,000,000/575 = Blue: l = 475 nm 3,000,000/475 = History of Observing The earliest observing was done with the naked eye Around 1600 telescopes were invented Around 1670 Isaac Newton invented a telescope that used mirrors instead of lenses In 1990 the Hubble Space Telescope was placed in orbit, capping a decade of spaced-base observing Galileo’s Observations How Do Telescopes Work? Telescopes: Light gathering ability (not magnification) is the most important attribute of a telescope telescopes make faint things brighter Lenses Need a lens Lenses bend light (refraction) and focus all of the light incident on the front to a point (focus) a certain distance behind the lens (focal length) Lenses and Refraction Refracting Telescope If you put a second lens (eyepiece) behind the first lens(objective), you can magnify the image Magnification is equal to the ratio of the focal lengths in practice the magnification you can achieve is limited by the blurring effects of the Earth’s atmosphere Refracting Telescope Refractors and Reflectors It is hard to make large refracting telescopes A curved mirror can be used to gather and focus the light instead (reflecting telescope) Reflecting Telescopes Problem: The focal point is between the mirror and the sky Cassegrain Telescope -- secondary reflects light through a hole in the primary, most common type of large telescope Cassegrain Reflecting Telescope Path of Light Light beams enter from infinity and are initially parallel The eyepieces then magnifies the point image by taking the divergent rays from the focal and making them parallel again Telescope Misconceptions Magnification is the most important property of a telescope Astronomers peer through an eyepiece Telescopes stick out of the dome Telescopes fold up like a giant pirate’s spyglass Observing at Different Wavelengths To fully understand the universe you need telescopes that can observe all forms of radiation Space based astronomy began in the 1970’s and became very important in the 1980’s-1990’s The Electromagnetic Spectrum Telescope Taxonomy Radio and Millimeter -- penetrates atmosphere and everything else Example: Infrared (IR) -- we feel as heat Example: Optical -- what our eyes can see Example -- More Telescope Taxonomy Ultraviolet (UV) -- high energy radiation, causes sunburn Example -- X-ray -- very high energy Example -- Gamma Ray -- the highest energy Example -- The VLA Hubble Space Telescope What Can a Telescope Do? Imaging -Photometry -Spectroscopy -A spectrum is the amount of light at each wavelength. The shape of the spectrum tells you about the temperature, composition and motions of the object Types of Detectors Eye -- Photographic plate -- allows you to measure brightness and spectra Charge Coupled Device (CCD) -- Today, light is moved around with fiber optic cables and data is moved electronically Next Time Read Ch. 3.5, 4.1-4.3