* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Class 9
Lens (optics) wikipedia , lookup
Gamma spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Birefringence wikipedia , lookup
Harold Hopkins (physicist) wikipedia , lookup
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
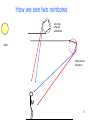
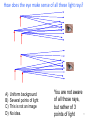
Physics 1230: Light and Color Ivan I. Smalyukh, Instructor Office: Gamow Tower, F-521 Email: [email protected] Phone: 303-492-7277 Lectures: Tuesdays & Thursdays, 3:30 PM - 4:45 PM Office hours: Mondays & Fridays, 3:30 PM – 4:30 PM TA: Jhih-An Yang [email protected] Class # 9 HW #1 (out of 10 points maximum) Exam #1: September 29 or October 4? Clicker question: which of the following statements is true • A. We can see two rainbows after the rain; • B. The observation of primary rainbow involves total internal reflection, refraction at 2 droplet-air interfaces, and dispersion; • C. The observation of the secondary rainbow involves two total internal reflections, refraction at 2 droplet-air interfaces, and dispersion; • D. All of the above; • E. None of the above. 4 How we see two rainbows two total internal reflections sun total internal reflection 5 6 Total internal reflection makes fiber optic communication possible The ray bends from the low n material toward the high n material. Demo: glass tube, laser pointer 7 Time for a demo! If we pull the cork, and water starts to pour out of the tank, the laser light will… A) Shine across the room to the wall. B) Stay entirely inside the tank C) Stay entirely inside the water stream D) Something else happens. 8 This illustration appears in "La Nature" magazine in 1884. Demo: tank 9 Lec. 6: Ch. 2 - Geometrical Optics 1. 2. 3. 4. We are here Shadows Reflection Refraction Dispersion Move to Chap. 3 1. Virtual images 10 10 How does the eye make sense of all these light rays? A) B) C) D) Uniform background Several points of light This is not an image No idea. You are not aware of all those rays, but rather of 3 11 points of light Chapter. 3 – Spherical Mirrors and Lenses We are here 1. 2. 3. 4. Virtual images (review) Spherical mirrors Spherical lenses Aberrations of lenses http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lens_%28optics%29 Skip 3.3c anamorphic art. 12 Review: plane mirrors, specular reflection • Equal angle rule • Similar triangles are useful qi qr Normal Mirror • Ray tracing a mirror Xobject = Ximage Image point is on the normal (mirror might need an extension) Xobject Extension Ximage 13 Review: What is an object? What is an image? Xobject Extension Ximage = We will often replace a real object (say a bottle) with an arrow, to simplify the drawing. 14 Review: What is an object? What is an image? Xobject Extension Ximage = In this context, an object is a point, or set of many points, that emits light rays in a range of directions: 15 What is an image? X object Extension Ximage = 16 Curved Mirrors First, a little geometry review: This line segment (from center of circle)... ...is perpendicular (or normal) to this tangent. 17 Rays reflecting from a convex (spherical) mirror • Ray aimed toward center of sphere comes straight back (specular reflection with normal incidence) • What about other rays? All rays aimed at the center C come straight back out. C 18 What happens to all rays that come in parallel to the OPTICAL AXIS (the line running through C)? • Specular reflection • Find where incoming ray hits mirror surface • Find surface normal at that point (along line from center--remember geometry review?) • Angle of incidence = angle of reflection • Reflection (of parallel ray) looks like it’s coming from F -- turns out this is true for all parallel rays! F C qi qr The focus is halfway to the center 19 What happens to all rays that come in parallel? Focal point = focus is behind the surface • Easy rule for parallel incoming rays (parallel to the line through F and C): they are reflected as if they came from F. F C The focus is halfway to the center 20 What about rays aimed at the focus? (This is the previous rule, backwards) • Easy rule for rays aimed at focus: • An incoming ray aimed at F gets reflected back parallel (to the C-F axis). Focal point = focus is behind the surface F C The focus is halfway to the center 21 Three easy rules for convex, spherical mirrors 1. All rays incident parallel to the CF axis are reflected so that they appear to be coming from the focal point F 2. All rays that (when extended) pass through the center C are reflected back on themselves. 3. All rays that (when extended) pass through the focal point F are reflected back parallel to the axis 3 F 1 C 2 22 Ray tracing: convex mirror F C What does the observer see in the mirror? 23 Ray tracing: convex mirror F C What does the observer see in the mirror? Draw in the rays and extrapolate back 24 Ray tracing: convex mirror F (A) Or (B) ?? • Is the image real or virtual? • Is the image larger or smaller than the object? • Is the image right-side-up or upside-down? • How could a mirror be useful when used like this? C 25 Rays reflecting from concave (cavity) mirrors Ray through the center reflects straight back at its source C 26 Incoming parallel rays reflect through focus • All (incoming parallel) rays reflect and go through the focus half way from center to mirror C F As usual, this rule works backwards: incoming rays that go through the focus reflect back parallel (to the C-F axis). 27 Rays through focus reflect back parallel to C-F axis. C F 28 Concave mirrors are very useful C light beam emitter (flashlight) F solar light collector or oven 29 Three easy rules for concave, spherical mirrors 1. All rays incident parallel to the C-F axis are reflected through the focal point F 2. All rays that pass through the center C are reflected back on themselves. 3. All rays that pass through the focal point F are reflected back parallel to the axis 1 C F 2 3 30 Ray tracing: concave mirror object outside center C F 31 Ray tracing: concave mirror object outside center C Questions: (A) OR (B) • Is the image real or virtual? • Is the image larger or smaller than the object? • Is the image right-side-up or upside-down? • How could a mirror be useful when used like this? F 32 Ray tracing: concave mirror object between center and focus C Questions: • Is the image real or virtual? • Is the image larger or smaller than the object? • Is the image right-side-up or upside-down? • How could a mirror be useful when used like this? F 33