* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Wireless Media
Waveguide (electromagnetism) wikipedia , lookup
Superheterodyne receiver wikipedia , lookup
VHF omnidirectional range wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunication wikipedia , lookup
History of telecommunication wikipedia , lookup
Air traffic control radar beacon system wikipedia , lookup
German Luftwaffe and Kriegsmarine Radar Equipment of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Standing wave ratio wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Beams wikipedia , lookup
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Continuous-wave radar wikipedia , lookup
Antenna (radio) wikipedia , lookup
Active electronically scanned array wikipedia , lookup
Yagi–Uda antenna wikipedia , lookup
Microwave transmission wikipedia , lookup
Radio direction finder wikipedia , lookup
Cellular repeater wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
High-frequency direction finding wikipedia , lookup
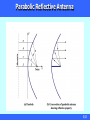
Chapter 4 – Transmission Media Wireless Media 1/23 Wireless Transmission Frequencies 1GHz to 40GHz Microwave frequency range highly directional beams are possible Point-to-point transmission Used also in satellite communications 30MHz to 1GHz Radio frequency range Omnidirectional (all directions) broadcast radio and TV 3 x 1011 to 2 x 1014 Hz Infrared portion of the spectrum Local point-to-point and multipoint applications (e.g., infrared remote control, wireless LAN) 2/23 Antennas Electrical conductor used to radiate or collect electromagnetic energy Transmission antenna radio frequency energy from transmitter converted to electromagnetic energy by antenna radiated into surrounding environment Reception antenna electromagnetic energy impinging on antenna converted to radio frequency electrical energy fed to receiver Same antenna is often used for both purposes 3/23 Antenna Radiation Pattern Power radiated in all directions Not same performance in all directions as seen in a radiation pattern diagram An isotropic antenna is a (theoretical) point in space reference antenna radiates in all directions equally with a spherical radiation pattern 4/23 Parabolic Reflective Antenna 5/23 Antenna Gain Measure of directionality of antenna Defined as the output power in particular direction compared to that produced by an isotropic antenna The antenna gain is related to the effective area of an antenna: G 4Ae 2 4f 2 Ae c2 G antenna gain Ae effective area c carrier wavelength f The isotropic antenna has a gain of 1=0dB with Ae 2 4 Example: what is the gain of a parabolic antenna with effective area Ae 0.56 A 0.56(r 2 ) , radius r=1m and f=12GHz? c f 3 108 12 109 0.025m 4Ae 4 0.56 G 2 35186 45.46dB 2 (0.025) 6/23 Terrestrial Microwave Used as an alternative to coaxial and fiber cables Requires fewer repeaters but line-of-sight Used also for short point-to-point links between buildings Use a parabolic dish to focus a narrow beam onto a receiver antenna 1-40GHz frequencies Higher frequencies give higher data rates Main source of loss is attenuation; the loss : 4d 4df 10 log 10 10 log 10 dB c 2 LdB 2 d distance wavelength f frequency 7/23 Satellite Microwave A satellite is a microwave relay station Receives on one frequency band (uplink), amplifies or repeats signal and transmits on another frequency band (downlink) eg. uplink 5.925-6.425 GHz & downlink 3.7-4.2 GHz A satellite operate on a number of frequency bands called transponders The satellite requires geo-stationary orbit height of 35,784km spaced at least 3-4° apart (to minimize interference from other satellites) typical uses Television distribution long distance telephone transmission private business networks Global Positioning System (GPS) 8/23 Satellite Point-to-Point Link 9/23 Satellite Broadcast Link 10/23 Broadcast Radio Use broadcast radio, 30MHz - 1GHz, for: FM radio UHF and VHF television Is omnidirectional Still need line-of-sight Suffers from multipath interference reflections from land, water, other objects 11/23 Infrared modulate infrared light are blocked by walls no licenses required typical uses TV remote control Infrared WLAN 12/23 Wireless Propagation: Ground Wave Ground wave is found in frequencies up to 2MHz The best-known example of ground wave communication is AM radio 13/23 Wireless Propagation: Sky Wave Sky wave propagation is found in frequencies from 2MHz to 30MHz A sky wave signal bounces back and forth between the ionosphere and the earth surface 14/23 Wireless Propagation: Line-Of-Sight (LOS) LOS propagation is found in frequencies above 30MHz the transmitting and receiving antennas must be within a line of sight of each other 15/23 Refraction velocity of electromagnetic wave is function of material density ~3 x 108 m/s in vacuum, less in anything else speed changes as move between media Index of refraction (refractive index) is: 1 n sin( 1 ) / sin( 2 ) 2 have gradual bending if medium density varies density of atmosphere decreases with height results in bending of radio waves towards earth hence optical LOS horizon and radio LOS horizon are not the same 16/23 Optical and Radio LOS The optical LOS to the horizon can be expressed as: d 3.57 h , where d : the distance between th e antenna and the horizon in Kilometers h: the antenna hight in meters The radio LOS to the horizon can be expressed as: d 3.57 Kh wher e K : adjustment factor to account for the refreactio n, usually K 4 / 3 The max. distance between two antennas for LOS propagation: d 3.57 Kh1 Kh2 wher e h2 and h2 are the hight of the two antennas 17/23 EXAMPLE The max. distance between two antennas for LOS transmission if one antenna is 100m high and the other at ground level is: d 3.57 Kh 3.57 (4 / 3)100 41Km Now suppose that the receiving antenna is 10m high. To achieve the same distance, how high must the transmitting antenna be? The result is 41Km 3.57 Kh1 Kh2 3.57 (4 / 3)h1 (4 / 3)10 h1 46.2m 18/23 Free Space Loss The free space loss for ideal isotropic antenna is: 2 P 4d LdB 10 log 10 t 10 log 10 20 log 10 20 log 10 d 21.98dB Pr 4df 10 log 10 20 log 10 f 20 log 10 d 147.56dB c 2 where Pt , Pr : signal power at the transmitt ing and receiving antennas c : speed of light (3 108 m/s) f , : carrier frequency and wavelengt h For other antennas, we must take into account antenna gain: Pt (4 ) 2 d 2 LdB 10 log 10 10 log 10 Pr Gt Gr 2 where Gt and Gr are the gains of the transmitt ing and receiving antennas 19/23 Free Space Path Loss The free space path loss is a function of both the distance and the carrier frequency: LdB 20 log 10 f 20 log 10 d 147.56dB 20/23 Example Determine the free space loss at 4GHz for the shortest path to a satellite from earth (35.863Km). c 3 108 0.075m 9 f 4 10 LdB 20 log 10 20 log 10 d 21.98dB 20 log 10 (0.075) 20 log 10 (35.853 106 ) 21.98dB 195.6dB Now consider the antenna gain of both the satellite and earth station antennas. Typical values are 44dB and 48dB, respectively. The free space path loss: LdB 195.6dB 44 48 103.6dB What is the received power at the satellite antenna if the transmitted power from the earth station antenna is 250W? 250W 24dB received power 24 103.6 79.6dB 21/23 Impairments in wireless LOS transmission Free space loss loss of signal with distance Atmospheric Absorption from water vapour and oxygen absorption Multipath multiple interfering signals from reflections Refraction bending signal away from receiver 22/23 Examples of Multipath Interference 23/23