* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LIGHT
Gravitational lens wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Architectural lighting design wikipedia , lookup
Light pollution wikipedia , lookup
Bicycle lighting wikipedia , lookup
Holiday lighting technology wikipedia , lookup
Daylighting wikipedia , lookup
Photopolymer wikipedia , lookup
Doctor Light (Kimiyo Hoshi) wikipedia , lookup
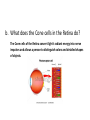
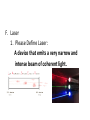
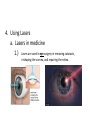
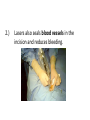
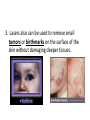
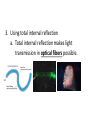
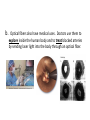
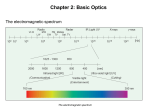
LIGHT Chapter 12 I. THE BEHAVIOR OF LIGHT – 12.1 A. Light and Matter 1. Opaque, translucent, and transparent a. Please Define Opaque: Material that absorbs or reflects all light and does not transmit any light. b. Please Define Translucent: Material that transmits and scatters light so that objects viewed through it appear blurry. c. Please Define Transparent: Material that transmits light without scattering so that objects are clearly visible through it. B. Reflection of Light 1. The law of reflection a. Please Define the Law of Reflection: The angle at which a light wave strikes a surface is the same as the angle at which it is reflected. 2. Regular and diffuse reflection a. Please Define Regular Reflection: A smooth, even surface like a pane of glass produces a sharp image by reflecting parallel light waves in only one direction. Reflection of light waves from a smooth surface is regular reflection. b. Please Define Diffuse Reflection: A brick wall has an uneven surface that causes incoming parallel light waves to be reflected in many different directions. The reflection of light from a rough surface is diffuse reflection. Diffuse reflection does not produce an image. 3. Microscopic roughness a. Please Define Microscopic Roughness: Even a surface that appears to be smooth can be rough enough to cause a diffuse reflection, as seen in the magnification of metal pot’s surface. C. Refraction of Light 1. Please Define Refraction: The bending of a wave caused by a change in its speed as it travels from one medium to another. 2. The index of refraction a. Please Define The index of Refraction: Property of a material indicating how much the speed of light is reduced in the material compared to the speed of light in a vacuum. 3. Prisms a. Please Define Prism: A triangular piece of glass that refracts or bends white light. This bending of light separates out white light to its various colors based on the colors wavelength. Red is bent the least and violet the most. 4. Rainbows a. A Rainbow acts as a large Prism and Refracts light into 7 colors. These colors in order of decreasing wavelength are: 1.) red 2.) orange 3.) yellow 4.) green 5.) blue 6.) indigo 7.) violet 5. Mirages a. Please Define Mirage: Image of a distant object produced by the refraction of light through air layers of different densities. II. LIGHT AND COLOR – 12.2 A. Colors 1. What is White color? White light is a blend of all colors of visible light. 2. What is Red color? A red object when struck by white light, it reflects more red light than green or blue light. 3. What is Green color? When a green object is struck by white light it reflects green light and absorbs the other colors. 4. What is Black “color”? Black is not a color that is present in visible light. Objects that are black absorb all colors of light and reflect little or no light back to your eye. B. Seeing Color 1. Light and the eye a. What does the Lens do? When light enters the eye it focuses the light on the retina. b. What does the Cone cells in the Retina do? The Cone cells of the Retina convert light’s radiant energy into nerve impulses and allows a person to distinguish colors and detailed shapes of objects. c. What does the Rod cells in the Retina do? The Rod cells are sensitive to dim light and is useful for night vision. 2. Interpreting color a. Your eyes have three types of cones, each of which responds to a different range of wavelength. 1.) Red cones respond mostly to red and green light. 2.) Green cones respond mostly to yellow and green light. 3.) Blue cones respond mostly to blue and violet light. 3. Color blindness a. About 8% of men and 0.5% of women are color-blind. b. Color-blind people have difficulty distinguishing between the two colors red and green. C. Filtering Colors 1. Please Define Filter: A transparent material that selectively transmits light. D. Mixing Colors 1. Mixing colored lights a. What are the three primary colors? 1.) red 2.) green 3.) blue 2. Paint pigments a. Please Define Pigment: Colored material that is used to change the color of other substances. b. Mixing pigments 1.) What are the three primary pigments? a.) magenta (bluish red) b.) cyan (greenish blue) c.) yellow 2.) Mixing the above three primary pigments produces what color? black 3.) Because the primary pigments produce black these primary pigments are called subtractive colors. III. PRODUCING LIGHT – 12.3 A. Incandescent Lights 1. Please Define Incandescent Light: Light produced by heating a piece of metal, usually tungsten, until it glows. B. Fluorescent Lights 1. Please Define Fluorescent Light: Light generated by using phosphors to convert ultraviolet radiation to visible light. 2. Efficient lighting a. Fluorescent lights use as little as ⅕ of the electrical energy to produce the same amount of light as incandescent bulbs. b. Fluorescent light also lasts much longer than incandescent bulbs. C. Neon Lights 1. The gas Neon is found in these glass tubes and gives off a bright red-orange color. D. Sodium-Vapor Lights 1. Sodium-Vapor lights gives off a yelloworange glow or color. E. Tungsten-Halogen Lights 1. Tungsten-Halogen Lights gives off an intense brighter light and is used in auto headlights and in underwater photography. F. Laser 1. Please Define Laser: A device that emits a very narrow and intense beam of coherent light. 2. Amplifying light 3. Coherent and incoherent light a. Please Define Coherent Light: Light of one wavelength that travels in one direction with a constant distance between the corresponding crests of the waves. b. Please Define Incoherent Light: Light that can contain more than one wavelength, travel in more than one direction, and has varying distances between the corresponding crests of the waves. 4. Using Lasers a. Lasers in medicine 1.) Lasers are used in eye surgery in removing cataracts, reshaping the cornea, and repairing the retina. 2.) Lasers also seals blood vessels in the incision and reduces bleeding. 3. Lasers also can be used to remove small tumors or birthmarks on the surface of the skin without damaging deeper tissues. b. CDs and videodiscs 1.) When a disc is produced, the information is burned into the surface of the disc with a laser. 2.) A videodisc or CD player also uses a laser to read the disc. The reflected light from the laser is converted to an electric signal that can be converted into sound or images. IV. USING LIGHT – 12.4 A. Polarized light 1. Please Define Linearly Polarized Light: Light whose magnetic field vibrates in only one direction. 2. Polarizing filters 3. Polarized lenses a. Lenses of polarized sunglasses are polarizing filters that block the reflected light with vertically vibrating magnetic fields, thus reducing glare. B. Holography 1. Please Define Holography: Technique that produces a complete three-dimensional photographic image of an object. 2. Making holograms a. Lasers are needed to produce holograms. One part illuminates the object and reflects onto the photographic film. The second part of the laser beam is also directed at the film with the two laser beams creating an interference pattern on the film and thus producing the Hologram. 3. Information in light a. A Hologram conveys more information than a photograph. It conveys the direction as well as the intensity of the light. Therefore, holograms is more difficult to copy and is used in credit cards and other identification cards. C. Optical Fibers 1. Partial Reflection 2. Total Internal Reflection a. Please Define Total Internal Reflection: The complete reflection of light at a boundary that occurs when light strikes at an angle greater than the critical angle, and light travels faster in the second medium than in the first medium. 3. Using total internal reflection a. Total internal reflection makes light transmission in optical fibers possible. 4. Using optical fibers a. Optical fibers are most often used in communications. Telephone conversations, television programs, and computer data can be coded in light beams. b. Optical fibers also have medical uses. Doctors use them to explore inside the human body and to treat blocked arteries by sending laser light into the body through an optical fiber. D. Optical Scanners 1. Please Define Optical Scanner: Device that reads intensities of reflected light and converts the information to digital signals. V. CHAPTER 12 REVIEW A. Please do Check Concepts 31-41 on page 394 in your Text. B. Please do Standardized Test Practice 1-11 on page 396 in your Text.