* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download P3 Revision - the Redhill Academy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
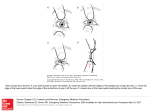
P3 Revision Medical Why are X-rays dangerous? They are ionising Medical Aside form X-ray pictures how else are X-rays used medically? Used to destroy cancerous tumours Medical What happens to the X-rays when a ‘picture’ of a broken bone is taken? Bones and teeth absorb the X-rays whilst soft tissue allows it to pass through Medical What is the range of human hearing? 20 – 20 000 Hz Medical What happens to the ultrasound wave at the boundary of each tissue boundary? It is partially reflected Medical What is the name of the device that produces and receives the ultrasound waves? Transducer Medical What are the advantages of ultrasound over X-rays? Non-ionising and can be used to scan organs and soft tissues Medical How do you calculate the distance travelled by an ultrasound wave? Distance = speed x time Medical How do you calculate the distance between the transducer and the tissue boundary? Distance = speed x time 2 Medical Aside from scanning how can ultrasound be used medically Ultrasound waves can be used to break up a kidney stone Medical Where does refraction occur? At the boundary of air and a transparent substance (glass or water) Medical What is Snell’s Law Refractive Index = sini /sin r Medical What is the refractive index? A measure of how much a substance can refract a light ray. Increasing Refractive Index Medical Speed away… slow toward what? The normal Medical When does total internal reflection occur? When angle of incidence of a light ray in a transparent substance is greater than the critical angle. Medical How does an endoscope work? Two bundles of optical fibres, one to carry the light the other to carry light back to the camera/eye. Light is totally internally reflected. Medical What is the relationship between the critical and gle and the refractive index? Refractive index = 1/critical angle Medical What is the critical Angle ? Angle of incidence of a light ray in a transparent substance that produces refraction along the boundary. Medical Draw how light rays behave when they strike a converging ( convex) lens One ray through centre of lens the other to the lens and through the focal point. Medical Draw how light rays behave when they strike a diverging ( concave) lens One ray through centre of lens the other to the lens and traced back through the focal point. Medical What is the difference between a real image and a virtual image? Real images produced where real light rays meet Medical Which three ways do we describe an image Real/virtual, magnified/ diminished, upright/inverted Medical How do you calculate the magnification? Image height / object height Medical What are the units for magnification? There are none. Medical How is a camera like the eye Both converging lenses, eye lens is variable, camera lens fixed but changes position, image formed on retina, camera uses film, iris in eye and aperture for control of light Medical Draw the eye and label as many structures as you can Cornea, lens, pupil, cliliary muscles, retina, blind spot, optic nerve, eye muscles Medical Draw how a short sighted eye sees Medical Draw how a long sighted eye sees Medical How do you calculate the power of a lens? Power of a lens = 1/focal length in metres Medical If a lens has a power with a positive value this means it is which type of lens? Converging ( convex) Medical If a lens has a power with a negative value this means it is which type of lens? Diverging ( concave) Medical What is the unit of power of a lens? Dioptre Medical What is the range of human vision? 25cm (near point) and infinity (far point)