* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WAN Technologies
TV Everywhere wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Serial digital interface wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Packet switching wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
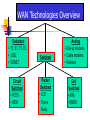
WAN Technologies Ch 7 Lecture 1 WAN Connectivity Provided through: Public Networks - PSTN and Internet Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) Also known as Plain Old Telephone System (POTS) Private Networks Leased lines PSTN International phone infrastructure Media Equipment Cheap (Economical) Readily available Highly accessible Disadvantages Software Advantages Satellites Antennas Routers Other devices Speed (slow) Security Good option for small organizations Private Networks Rent/lease Media Equipment Considerations Layout Level of complexity Security level Fiber, copper, or wireless Protocols Administration In-house Outsourced WAN Services WANs provide for the exchange of data packets/frames between routers/bridges and the LANs they support. A WAN interconnects LANs that are usually separated by large geographic areas. WANs connect devices. Such devices include routers, modems, etc. Routers Routers offer many services including: Internetworking WAN serial interfaces Routers can operate as... Internal Routers Backbone Routers Autonomous System Boundary Routers WAN Standards What layers of the OSI model do WAN standards describe? Physical and Data Link Layers Switching Methods Switching – moving data from one location to another via a communication path Packet-switching **Most popular Circuit-switching Message-switching Packet Switching Message is broken into packets Encapsulated with header Uses independent routing Source and destination addresses Router chooses the best path based on routing tables Packets may get to the destination out of order/sequence TCP re-sequences the packets Two types of Packet Switching Virtual Circuit Datagram Virtual Circuit Logical connection/link between source and destination is established The link has an id and the packets also contain that id. Remains active for as long as devices are available or short term (only for length of transmission) Established path (all packets use the same path) Used for connection-oriented services such as streaming video Datagram Packet Switching Sent best effort packets may be sent through different paths Received in non-sequential order TCP reconstructs Circuit-Switching Telephone conversation is good analogy Requires dedicated physical connection for duration of transmission session Guaranteed transfer rate Inefficient - once a session is established, transmission path is not available to others. WAN Technologies Overview Dedicated • T1, E1, T3, E3 • xDSL • SONET Circuit Switched • POTS • ISDN Switched Packet Switched • X.25 • Frame Relay Analog • Dial-up modems • Cable modems • Wireless Cell Switched • ATM • SMDS Dedicated Digital Services Dedicated Digital Services provide full-time connectivity through a point-to-point link T series in U.S. and E series in Europe Uses time division multiplexing to “slice up” data and assign time slots for transmissions T1 = 1.544 Mbps T3 = 44.736 Mbps E1 = 2.048 Mbps E3 = 34.368 Mbps •Uses twisted pair & fiber •Extremely popular •Moderate cost Digital Subscriber Lines (DSL) WAN technology for home use; decreasing bandwidth with increasing distance from the phone companies CO. Data rates 100Kbps - 51.84 Mbps Moderate expense and getting cheaper Dedicated Digital Services Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) 51.84 Mbps (OC-1) -- 9,952 Mbps (OC-192) Uses lasers to divide the wavelength of the light into sections that can carry large amounts of data (Wave Division Multiplexing) Very expensive; used by large ISPs and other Internet backbone entities. Circuit Switched Services Plain Old Telephone System (POTS) Not a computer data service but... POTS is an important component of our communication infrastructure and It is still the standard for designing reliable networks Dial-up Modems Limited to 56 kbps Works with existing phone network Low cost and widespread usage Cable Modems Data signals on the same cable as television signals Increasing in popularity Maximum bandwidth 10 Mbps, though this degrades as more users attach to a given network segment Cost is relatively low Wireless Terrestrial Bandwidths typically in the 11 Mbps range Cost is relatively low Line-of-sight is usually required Usage is moderate Satellite Can serve mobile users and remote users Usage is widespread Cost is very high Circuit Switched Services Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) Historically important--first dial-up digital service Cost is moderate max. bandwidth = 128 kbps for BRI (Basic Rate Interface) 2 B channels @ 64kps AND 1 D channel @ 16kps B (bearer) channels are voice/data channels; D (delta) channel for signaling