* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HMIS7
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
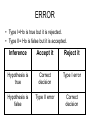
CONFIDENCE INTERVAL • It is the interval or range of values which most likely encompasses the true population value. • It is the extent that a particular sample value deviates from the population • A range or an interval around the sample value • Range or interval is called confidence interval. • Upper & lower limits are called confidence limits. TESTING THE STATISTICAL HYPOTHESIS • Null hypothesis or hypothesis of no difference (Ho) • Alternative hypothesis of significant difference (H)׀ • Test of significance to accept or reject hypothesis • A zone of acceptance • A zone of rejection Testing of hypothesis • Z- test when sample is more than 30 • T-test when sample is less than 30 • Chi square test when the data is in proportions TYPE 1 ERROR • Null hypothesis of no difference is rejected when estimate falls in the zone of acceptance at 5 % level. • We are changing the level of significance from 5% to 6,7,8 or 10%. • It is called type 1 error.(ά) TYPE II ERROR • Ho is accepted when it should been rejected because the estimate falls in the zone of rejection. • We are changing the level of acceptance from 5% to 4,3,2 or 1% level of significance. • This is committing of type II error or β error. ERROR • Type I=Ho is true but it is rejected. • Type II= Ho is false but it is accepted. Inference Accept it Reject it Hypothesis is true Correct decision Type I error Hypothesis is false Type II error Correct decision Minimize Errors • Take as large a random sample as possible and interpret the results at 5% i.e. critical level of significance. TESTS OF SIGNIFICANCE • Mathematical methods by which probability (p) or relative frequency of an observed difference, occurring by chance is found. • It may be a difference between means or proportions of sample and universe or between estimates of experiment and control group. Stages for tests • State the null hypothesis of no or chance difference • State the alternative hypothesis • Determine P value i.e. probability of occurrence of estimate by chance i.e. accept or reject hypothesis. (the distance from the mean at which Ho is rejected is called level of significance). • Draw conclusion on the basis of p value. • The difference observed is due to chance or play of some external factors on the sample under study. STANDARD ERROR • Standard error is the standard deviation of the means of different samples of population. • Standard error is the measure of chance variation. • S.E. is a measure which enables to judge whether a mean of a given sample is within the set of confidence limits or not, in a population. • S.E= SD/√n (it is the SD of the sample divided by the square root of number of observations in the sample). Uses of SE • To work out the limits of desired confidence within which population mean will lie. • To determine whether the sample is drawn from a known population or not. • To find SE of difference b/w two means to know the difference is real, statistically significant or insignificant due to chance. • To know the size of sample. Confidence limits • SBP of a random sample of 566 students were taken, mean BP was 128 mm and standard deviation is 13.05mm. Find 95% confidence limits of BP within which the population mean would lie? Confidence limits • SBP of a random sample of 566 students were taken, mean BP was 128 mm and standard deviation is 13.05mm. Find 95% confidence limits of BP within which the population mean would lie? • SE=0.55 Confidence limits • SD of blood sugar level in a population is 6 mg %. If population mean is not known, within what limits is it likely to lie if a random sample of 100 has a mean of 80 mg %? Confidence limits • In a population sample of children with mean height of 66 cm and SD=2.7 cm, can a sample of 100 with a mean of 67cm occur easily? If you find that the probability is low (P<0.01), what does it indicate? Sample size • L= 2 σ √n √n= 2 σ L n= 4 σ² L² Example: 1.mean pulse rate=70 Pop. Standard deviation(σ)=8 beats Calculate sample size? 2. Mean SBP=120,SD=10, calculate n? Sample size • Qualitative data • N=4pq L² e.g.