* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Folds and Foliation
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
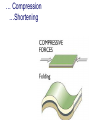
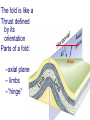
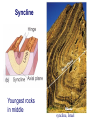
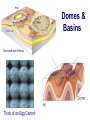
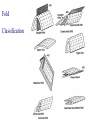
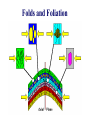
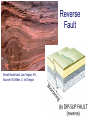
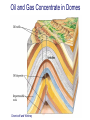
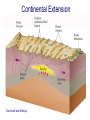
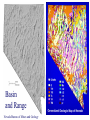
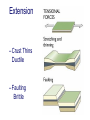
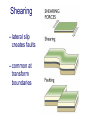
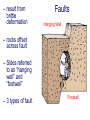
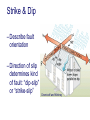
FOLDS and thrust Which deformation and stresses cause theses structures ? Folding of Shale-Sandstone sequence, Kings Canyon, California … Compression …Shortening The fold is like a Thrust defined by its orientation Parts of a fold: Hinge –axial plane – limbs –“hinge” Types of Folds • Anticline = arch • Syncline = trough • Monocline = stair step • Dome or Basin Chevron Fold, Laurel Mt., CA Syncline Youngest rocks in middle syncline, Israel Anticline Oldest rocks in middle Virgin anticline, southern Utah Domes & Basins Chernicoff and Whitney Think of an Egg Carton! Map from Topozone.com Grenville Dome: Sinclair, WY SynclineAnticline Pairs + Domes: Zagros Mts, Iran NASA “Earth as Art” web page Monocline Fold Classification Fold in Glacier, Antarctica Folds axis are perpendicular to the main direction of compression David Rogers Casey Moore, UCSC Little Shuteye, Sierra Nevada, CA Domes are not produced by horizontal but vertical compression Minor Folds and Foliation Are Clues to Much Larger Structures Foliation – pressure flattens and/or aligns minerals in a rock 1 mm – platy or sheet-like structure reflects the direction in which pressure was applied – Slate, schist, and gneiss foliated Microscope Image of Foliated Garnet Schist, VT Foliation In every case, the foliation is: In the direction of least resistance at right angles to the direction of greatest compression. Fold And Foliation Folds and Foliation How Geologists Use These Clues • Here's an outcrop that might be seen in the field. Minor Folds and foliations can be used to determine the axe of the fold Pay attention it migth look like folds • • • • K = Cretaceous J = Jurassic Tr = triassic At X, we have younger rocks surrounded by older rock But it is produced by differential errosion on a thrust • Dark green is older rock, thrust over the younger yellow rock • The Klippe (K) • W is a Fenster or Window Folds and and Thrust are often associated The overturned fold in the upper diagram may break, yielding an overthrust fold or thrust fault Folds and thrust have the same origin Reverse Fault Small thrust fault, Las Vegas, NV, Source: M. Miller, U. of Oregon Thrust Faults in Snow Folds and thrust are both responsible for the orogens R.W.H. Butler fold-thrust complex developed in Upper Jurassic limestones in the Haut Giffre area of the Subalpine thrust belt (Morcles nappe in France) Folded Appalachians Near Harrisburg, PA, Source: NASA Folding in Malaspina Glacier, AK, 1969 Oil and Gas Concentrate in Domes Chernicoff and Whitney Growth of Minerals Small Scale Structures Mimic Large Scale Structures!! Bohlen et al., 1987 Folded Amphibolite in Marble, Warrensburg (K. Hollocher, NYSGA field photo) Foliation Macroscopic and Microscopic Feldspar (strong) Quartz (weak) Foliated Slate, Shelburne, VT, UVM Foliated Gneiss, Nunavut,S. Tella Photo. Mulwaree fault zone, Australia Mulwaree fault zone, Australia, Tullis et al. Pressure Cararra Marble Deformation Experiments K. Hamblin A. Kronenberg Brittle Ductile Continental Extension Chernicoff and Whitney Basin and Range Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology Extension – Crust Thins Ductile – Faulting Brittle Shearing – lateral slip creates faults – common at transform boundaries – result from brittle deformation Faults Hanging Wall – rocks offset across fault – Sides referred to as “hanging wall” and “footwall” – 3 types of fault Footwall Strike & Dip – Describe fault orientation – Direction of slip determines kind of fault: “dip-slip” or “strike-slip” Chernicoff and Whitney Normal Fault Normal Fault, Lamb Canyon, CA Strike-Slip Fault Strike-slip fault near Las Vegas, NV, Source: M. Miller, U. of Oregon Strike-slip fault displacement in orchard Joints • • • • Brittle “cracks” in rocks Form near surface Regular spatial distribution No offset Preferential weathering of joints in Sandstone; Calcite veins in joints of marble, Laurel Mt., CA