* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 7: Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom
Franck–Condon principle wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital diagram wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Mössbauer spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Energy applications of nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
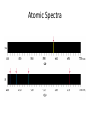
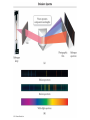
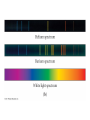
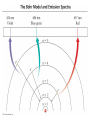
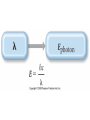
Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom Overview • Atomic Spectra • Nature of Matter & Energy Atomic Spectra • Absorption vs. Emission Phenomenon – Absorption – energy is supplied to promote electrons from ground state (lowest energy level) into higher energy levels (excited states). – Electrons prefer ground state (more stable). Atomic Spectra • Absorption vs. Emission Phenomenon – Emission – excited electrons loses energy (usually by emitting light) and returns to a lower energy state or the ground state. – Atoms give off light when heated or otherwise excited energetically; thereby providing a clue as to their chemical makeup. Atomic Spectra • Continuous Spectrum vs. Line Spectrum – Continuous spectrum contains all wavelengths of visible light. Observed as white light. – Line spectrum contains specific wavelengths that result in a unique “fingerprint” that is used to identify elements. No two elements have the exact same line spectrum. Atomic Spectra Atomic Spectra Atomic Spectra • Wavelength values found using Balmer-Rydberg Equation • 1/λ = R [1 / m2 – 1 / n2] • R = Rydberg Constant • (R = 1.097 x 10-2 nm-1) • The values (m & n) are integers such that n>m Nature of Matter & Energy • Relationship between energy, frequency, and wavelength. • Developed by two physicists (Max Planck & Albert Einstein) Nature of Matter & Energy • Max Planck proposed that matter & energy are not distinct in nature; they can be looked upon as one in the same. • Energy is only emitted in discrete packets called quanta. • E=nhν=nhc/λ h = 6.626 x 10-34 J sec Nature of Matter & Energy • Albert Einstein used the idea of quanta to explain the photoelectric effect. • He proposed that light behaves as a stream of particles called photons. • Also known for famous E = mc2 Nature of Matter & Energy • Louis deBroglie – used work of Planck & Einstein to propose the wave-particle duality concept. • He suggested waves can behave as particles and particles can behave as waves. • For a particle λ=h/mv • For light λ=h/mc