* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anti-inflammatory Agents
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
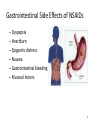
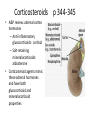
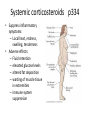
Chapter 12 Anti-inflammatory Agents Inflammation p 325 • Tissue response to injury • Characterized by – Vasodilation – Increased capillary permeability to plasma proteins – Release of histamine – Accumulation of leukocytes to the inflamed tissue – Increased vascular permeability and leakage • Erythema, warmth, swelling, tenderness Agents used to treat inflammation p326 • Nonsteroidal agents • Steroidal agents Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs p326 Table 12-1 p 327-330 • Salicylates – Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) (aspirin) • Anti-inflammatory effect in large dosages • Inhibits platelet aggregation • Most common adverse effect: GI intolerance and GI bleeding. • NSAIDS: – Celecoxib – Diclofenac – Etodolac – Ibuprofen – Naproxen Uses of NSAIDs p330 • Relief of mild to moderate pain caused by inflammation – Bone, joint, and muscle pain – Osteoarthritis – Rheumatoid arthritis – Dysmenorrhea • Pt need to give NSAIDs a 2 week trial to reach full therapeutic effect Gastrointestinal Side Effects of NSAIDs – Dyspepsia – Heartburn – Epigastric distress – Nausea – Gastrointestinal bleeding – Mucosal lesions - NSAIDs Contraindications • • • • Stomach ulcers G I bleeding Allergy to aspirin or sulfa Pregnancy Cardiovascular Side Effects of NSAIDs p326,330 • Second-generation NSAIDs (Celebrex) – Serious side effects: • Cardiac arrhythmias • Heart attack • Stroke Nursing Assessment NSAIDS • Before beginning therapy, perform thorough assessment for: – Gastrointestinal lesions or peptic ulcer disease – Bleeding disorders – Heart disorders Therapeutic Effects NSAIDs • Monitor for and document: – Decrease in swelling – Decrease in pain – Decrease in joint tenderness Client Education NSAIDS • Monitor for: – Unusual bleeding, abdominal pain, and cardiac problems • Enteric-coated tablets should not be crushed or chewed • Administration with food, milk, or antacids will reduce likelihood of GI upset Corticosteroids p 344-345 • A&P review: adrenal cortex hormones – Anti-inflammatory glucocorticoids: cortisol – Salt-retaining mineralocorticoids: aldosterone • Corticosteroid agents mimic these adrenal hormones and have both glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid properties Corticosteroids p 335-339 • Systemic use – – – – Dexamethasone Methylprednisone Prednisone Triamcinolone • Local injection – Dexamethasone – Hydrocortisone – Prednisolone • Topical use – – – – – Betamethasone Dexamethasone Fluticasone Hydrocortisone Mometasone Topical Corticosteroids p333 • Treat local inflammatory disorders – disorders of the skin • dermatitis • psoriasis – Example: hydrocortisone cream • Treat respiratory disease – Asthma – COPD – Example: mometasone Systemic Corticosteroids p333 Table 12-4 335-336 • Treat systemic inflammatory disorders – Bronchial asthma not well treated with inhaled corticosteroids – Neoplastic diseases – Autoimmune diseases – Example of drug: prednisone Systemic corticosteroids p334 • Suppress inflammatory symptoms: – Local heat, redness, swelling, tenderness • Adverse effects: – Fluid retention – elevated glucose levels – altered fat deposition – wasting of muscle tissue in extremities – immune system suppression Systemic corticosteroids p335 • Underlying cause of inflammation may remain and continue to progress • Masking potential • Systemic corticosteroids may cause: • gastric ulceration • suppression of the hypothalmic/pituitary/adrenal system • hypertension • changes in body fat deposits • Immune system suppression is a result of decreased lymphocytes Systemic corticosteroids p335 • Observe pt for therapeutic and adverse effects • Routinely assess vital signs • Pt that have been on corticosteroid meds must not abruptly discontinue their medication. – Physicians will taper off corticosteroid therapy. – Abrupt discontinuation will result in adrenal insufficiency with a hypotensive crisis. • It may take up to 2 years for a pt body to be able to secrete adequate adrenal hormones during times of stress. p348 Nursing considerations for pt on corticosteroids p344 • Monitor for: • GI bleeding • Elevated blood glucose levels • Weight gain • Labile emotions • Patients must carry identification and information about their meds • Dietary modifications: • Sodium restriction, • Increased calcium intake, • Take corticosteroids early in the day to avoid insomnia . Nursing considerations cont. • Teaching: – Do not abruptly discontinue steroids – S/S impending adrenal crisis • Hypotension • Restlessness • weakness • lethargy • headache • dehydration • nausea • vomiting • diarrhea .